Related Research Articles

The Object Management Group (OMG) is a computer industry standards consortium. OMG Task Forces develop enterprise integration standards for a range of technologies.
Health Level Seven or HL7 refers to a set of international standards for transfer of clinical and administrative data between software applications used by various healthcare providers. These standards focus on the application layer, which is "layer 7" in the OSI model. The HL7 standards are produced by Health Level Seven International, an international standards organization, and are adopted by other standards issuing bodies such as American National Standards Institute and International Organization for Standardization.
Model-driven architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model-driven architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001.
Service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a style of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network. A SOA service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online. SOA is also intended to be independent of vendors, products and technologies.
ISO 10303 is an ISO standard for the computer-interpretable representation and exchange of product manufacturing information. Its official title is: Automation systems and integration — Product data representation and exchange. It is known informally as "STEP", which stands for "Standard for the Exchange of Product model data". ISO 10303 can represent 3D objects in Computer-aided design (CAD) and related information.

The Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF) is an architecture framework for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) that provides visualization infrastructure for specific stakeholders concerns through viewpoints organized by various views. These views are artifacts for visualizing, understanding, and assimilating the broad scope and complexities of an architecture description through tabular, structural, behavioral, ontological, pictorial, temporal, graphical, probabilistic, or alternative conceptual means. The current release is DoDAF 2.02.
The HL7 Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) is an XML-based markup standard intended to specify the encoding, structure and semantics of clinical documents for exchange. In November 2000, HL7 published Release 1.0. The organization published Release 2.0 with its "2005 Normative Edition."
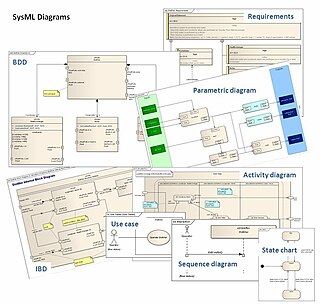
The Systems Modeling Language (SysML) is a general-purpose modeling language for systems engineering applications. It supports the specification, analysis, design, verification and validation of a broad range of systems and systems-of-systems.
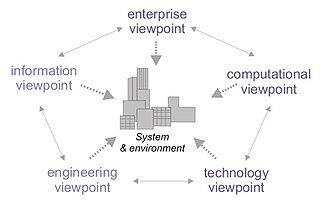
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems.
The Public Health Information Network (PHIN) is a national initiative, developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), for advancing fully capable and interoperable information systems in public health organizations. The initiative involves establishing and implementing a framework for public health information systems.
The European Committee for Standardization (CEN) Standard Architecture for Healthcare Information Systems, Health Informatics Service Architecture or HISA is a standard that provides guidance on the development of modular open information technology (IT) systems in the healthcare sector. Broadly, architecture standards outline frameworks which can be used in the development of consistent, coherent applications, databases and workstations. This is done through the definition of hardware and software construction requirements and outlining of protocols for communications. The HISA standard provides a formal standard for a service-oriented architecture (SOA), specific for the requirements of health services, based on the principles of Open Distributed Processing. The HISA standard evolved from previous work on healthcare information systems architecture commenced by Reseau d’Information et de Communication Hospitalier Europeen (RICHE) in 1989, and subsequently built upon by a number of organizations across Europe.
The OASIS Reference Model for Service Oriented Architecture (SOA-RM) is an abstract framework for understanding significant entities and relationships between them within a service-oriented environment, and for the development of consistent standards or specifications supporting that environment. It is based on unifying concepts of SOA and may be used by architects developing specific service oriented architectures or in training and explaining SOA.
Service Component Architecture (SCA) is a software technology designed to provide a model for applications that follow service-oriented architecture principles. The technology, created by major software vendors, including IBM, Oracle Corporation and TIBCO Software, encompasses a wide range of technologies and as such is specified in independent specifications to maintain programming language and application environment neutrality. Many times it uses an enterprise service bus (ESB).
Enterprise interoperability is the ability of an enterprise—a company or other large organization—to functionally link activities, such as product design, supply chains, manufacturing, in an efficient and competitive way.
SoaML is an open source specification project from the Object Management Group (OMG), describing a UML profile and metamodel for the modeling and design of services within a service-oriented architecture.
This article documents the effort of the Health Level Seven(HL7) community and specifically the HL7 Architecture Board (ArB) to develop an interoperability framework that would support services, messages, and Clinical Document Architecture(CDA) ISO 10871.
The system of concepts to support continuity of care, often referred to as ContSys, is an ISO and CEN standard . Continuity of care is an organisational principle that represents an important aspect of quality and safety in health care. Semantic interoperability is a basic requirement for continuity of care. Concepts that are needed for these purposes must represent both the content and context of the health care services.
International HL7 implementations is a collection of known implementations of the HL7 Interoperability standard. These do not necessarily refer to cross-border health information systems.
Health Level Seven International (HL7) is a non-profit organization ANSI-accredited standards development organization dedicated to providing standards and solutions that empower global health data interoperability.

Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect is a visual modeling and design tool based on the OMG UML. The platform supports: the design and construction of software systems; modeling business processes; and modeling industry based domains. It is used by businesses and organizations to not only model the architecture of their systems, but to process the implementation of these models across the full application development life-cycle.
References
The references in this article are unclear because of a lack of inline citations .(July 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |