Related Research Articles

Khosrow II, commonly known as Khosrow Parviz, is considered to be the last great Sasanian king (shah) of Iran, ruling from 590 to 628, with an interruption of one year.

Peroz I was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II, he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III, eventually seizing the throne after a two-year struggle. His reign was marked by war and famine. Early in his reign, he successfully quelled a rebellion in Caucasian Albania in the west, and put an end to the Kidarites in the east, briefly expanding Sasanian rule into Tokharistan, where he issued gold coins with his likeness at Balkh. Simultaneously, Iran was suffering from a seven-year famine. He soon clashed with the former subjects of the Kidarites, the Hephthalites, who possibly had previously helped him to gain his throne. He was defeated and captured twice by the Hephthalites and lost his recently acquired possessions.

Yazdegerd III was the last Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 632 to 651. His father was Shahriyar and his grandfather was Khosrow II.

Balash was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 484 to 488. He was the brother and successor of Peroz I, who had been defeated and killed by a Hephthalite army.

Jamasp was Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 496 to 498/9. He was a son of Peroz I and younger brother of Kavad I. Jamasp was installed on the Sasanian throne upon the deposition of the latter by the nobility and clergy.

Bahrām Chōbīn or Wahrām Chōbēn, also known by his epithet Mehrbandak, was a nobleman, general, and political leader of the late Sasanian Empire and briefly its ruler as Bahram VI.

The First Perso-Turkic War was fought during 588–589 between the Sasanian Empire and Hephthalite principalities and its lord the Göktürks. The conflict started with the invasion of the Sasanian Empire by the Turks and ended with a decisive Sasanian victory and the reconquest of lost lands.
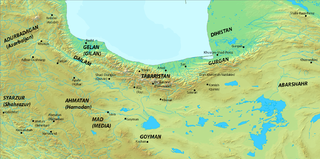
Abarshahr or Nishapur was a Sasanian satrapy (province) in Late Antiquity, that lay within the kust of Khorasan. The province bordered Media in the west, Hyrcania in the north west, Margiana in the north east, and Harev in the south east. The governor of Abarshahr is attested to have held the unique title of kanarang, distinguished from the title of marzban given to governors of frontier provinces. Abarshahr came to be known as one of the nicknames of the city of Nishapur which was considered to be the capital city of the province of Abarshahr during the Sassanian period and later on.
Varaztirots II Bagratuni was an Armenian nakharar from the Bagratuni family, the son of Smbat IV Bagratuni. He was marzpan of Armenia c. 628, fled to the Byzantine Empire soon thereafter and was exiled for several years to Africa for his participation in a plot against Heraclius. On his return c. 645/6, he was named curopalates and presiding prince of Armenia, but died before being formally invested.
In 615, during the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 602–628 with the Sasanian army under spahbod Shahin invaded Asia Minor and reached Chalcedon, across the Bosporus from Constantinople. It was at this point, according to Sebeos, that Heraclius had agreed to stand down and was about ready to become a client of the Sasanian emperor Khosrow II, allowing the Byzantine Empire to become a client state of the Sasanid Empire, as well as even allow Khosrow II to choose the emperor. The Sassanids had already captured Byzantine Syria and Palestine in the previous year. After negotiations with Byzantine Emperor Heraclius, an ambassador was sent to Sasanian Shahanshah Khosrow II, and Shahin withdrew again to Syria.

The kanārang was a unique title in the Sasanian military, given to the commander of the Sasanian Empire's northeasternmost frontier province, Abarshahr. In Byzantine sources, it is rendered as chanaranges and often used, for instance by Procopius, in lieu of the holder's actual name.

Vistahm or Bistam, was a Parthian dynast of the Ispahbudhan house, and maternal uncle of the Sasanian king of kings of Iran, Khosrow II. Vistahm helped Khosrow regain his throne after the rebellion of another Parthian noble Bahram Chobin, of House of Mihran, but later led a revolt himself, and ruled independently over a region which encompassed the entire Iranian East until he was defeated by Khosrow and his allies.
Smbat IV Bagratuni was an Armenian prince from the Bagratuni dynasty who served first in the Byzantine army before switching, ca. 595, to the Sasanian Empire, where he had a distinguished military career and earned high honours until his death in 616/7. He was succeeded by his son, Varaztirots.

Sukhra was an Iranian nobleman from the House of Karen, who was the de facto ruler of the Sasanian Empire from 484 to 493. He was active during the reign of shah Peroz I, Balash and Kavad I. He is often confused with his father Zarmihr Hazarwuxt and son Zarmihr Karen.
The Battle of Nishapur was fought in 652 between the Karen family and the Rashidun Caliphate along with their allies, the Kanārangīyān family.
The Battle of Badghis was fought in 654 between the Karen family and their Hephthalite allies against the Rashidun Caliphate.
Shapur Mihran, known in Armenian sources as Shapuh Mihran, was a Sasanian nobleman from the House of Mihran. He served as the marzban of Persian Armenia briefly in 482.

The Muslim conquest of Khorasan, or Arab conquest of Khorasan, was the last phase of the heavy war between the Arab Rashidun caliphate against the Sasanid Empire.

Harev, was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, that lay within the kust of Khorasan. The province bordered Kushanshahr in the west, Abarshahr in the east, Marv in the north, and Sakastan in the south.

Mard ō mard was an ancient Iranian tradition of single combat, the Sasanian Empire being most known for using it. During a battle, the Sasanian troops would use taunts and war cries to provoke the enemy into a single duel with a Sasanian champion. The tradition meant much to the Sasanians—in 421, during Bahram V's war against the Romans in 421–422, Ardazanes, a member of the "Immortals", was in a single duel killed by the Roman comes Areobindus, which contributed to Bahram V's acceptance of the defeat in the war and making peace with the Romans.