Heptanone may refer to the following ketones with seven carbon atoms the formula C7H14O:

In organic chemistry, an oxime is a organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula RR’C=N−OH, where R is an organic side-chain and R’ may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted oximes form a closely related family of compounds. Amidoximes are oximes of amides with general structure R1C(=NOH)NR2R3.
Methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP) is an organic peroxide with the formula [(CH3)(C2H5)C(O2H)]2O2. MEKP is a colorless oily liquid. It is widely used in vulcanization (crosslinking) of polymers.
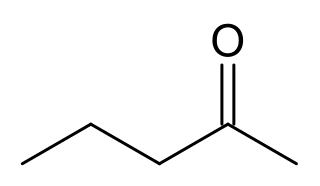
2-Pentanone or methyl propyl ketone (MPK) is a ketone and solvent of minor importance. It is comparable to methyl ethyl ketone, but has a lower solvency and is more expensive. It occurs naturally in Nicotiana tabacum (Tobacco) and blue cheese as a metabolic product of Penicillium mold growth.
Pentanone may refer to the following ketones containing five carbon atoms:
Perfluoro(2-methyl-3-pentanone) is a fluorinated ketone with the structural formula CF3CF2C(=O)CF(CF3)2, a fully-fluorinated analog of ethyl isopropyl ketone. It it used as an electronics coolant liquid and fire protection fluid sold commercially by 3M under brand names such as Novec 1230 and Novec 649. It is also known as “waterless water” or “dry water”.
Thailand's Psychotropic Substances Act is a law designed to regulate certain mind-altering drugs. According to the Office of the Narcotics Control Board, "The Act directly resulted from the Convention on Psychotropic Substances 1971 of which Thailand is a party." The Act divides psychotropic drugs into four Schedules. Offenses involving Schedule I and II drugs carry heavier penalties than those involving Schedule III and IV drugs. Note that this statute does not regulate most opioids, cocaine, or some amphetamines. The vast majority of narcotic painkillers, along with cocaine and most amphetamines are regulated under the Narcotics Act.

The Controlled Drugs and Substances Act is Canada's federal drug control statute. Passed in 1996 under Prime Minister Jean Chrétien's government, it repeals the Narcotic Control Act and Parts III and IV of the Food and Drugs Act, and establishes eight Schedules of controlled substances and two Classes of precursors. It provides that "The Governor in Council may, by order, amend any of Schedules I to VIII by adding to them or deleting from them any item or portion of an item, where the Governor in Council deems the amendment to be necessary in the public interest."

Ethyl isopropyl ketone (2-methyl-3-pentanone) is an aliphatic ketone with used as a reagent in organic chemistry and as a solvent.
The Corey–Kim oxidation is an oxidation reaction used to synthesise aldehydes and ketones from primary and secondary alcohols. It is named for American chemist and Nobel Laureate Elias James Corey and Korean-American chemist Choung Un Kim.
This is the list of extremely hazardous substances defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act. The list can be found as an appendix to 40 C.F.R. 355. Updates as of 2006 can be seen on the Federal Register, 71 FR 47121.

Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) is an organic compound with the formula OC(OCH3)2. It is a colourless, flammable liquid. It is classified as a carbonate ester. This compound has found use as a methylating agent and more recently as a solvent that is exempt from the restrictions placed on most volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the US. Dimethyl carbonate is often considered to be a green reagent.
The molecular formula C6H12O may refer to:

2-Heptanone, also known as methyl n-amyl ketone, or Heptan-2-one, is a ketone with the molecular formula C7H14O. It is a colorless, water-like liquid with a banana-like, fruity odor. 2-Heptanone has a neutral formal charge, and is only slightly soluble in water.
Hexanone may refer to the following ketones containing six carbon atoms:

2-Hexanone is a ketone used as a general solvent and in paints. It dissolves cellulose nitrate, vinyl polymers and copolymers, and natural and synthetic resins. It is recommended as a solvent because it is photochemically inactive; however it has a very low safe threshold limit value. 2-Hexanone is absorbed through the lungs, orally and dermally and its metabolite, 2,5-hexanedione, is neurotoxic. Animal tests have shown that the neurotoxic effect of 2-hexanone may be potentiated by simultaneous administration of 2-butanone.

3-Hexanone (ethyl propyl ketone) is an organic compound with the formula C6H12O. It is a ketone used as a solvent and as a chemical intermediate.
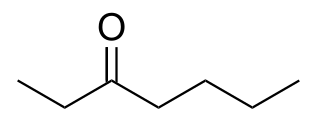
3-Heptanone, is a seven carbon ketone. It is a colorless liquid with a "green odor," also described to have a fruity scent. It is often used as a perfume/fragrance, as a solvent for cellulose, nitrocellulose, or vinyl resins, and as a synthetic building block in the preparation of other organic molecules.

3-Methyl-2-pentanone is an aliphatic ketone and isomer of 2-hexanone. It is used as a solvent and as an intermediate for syntheses. Its industrial importance is low. It is produced by base-catalyzed aldol condensation of 2-butanone with acetaldehyde, forming 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-pentanone, which is dehydrated to 3-methyl-3-penten-2-one over an acid catalyst, followed by hydrogenation over a palladium catalyst.
5-Nonanone, or dibutyl ketone, is the organic compound with the formula (CH3CH2CH2CH2)2CO. This colorless liquid is a symmetrical ketone.