Kittson County is a county in the U.S. state of Minnesota along the Canada–US border, south of the Canadian province of Manitoba. As of the 2010 census, the population was 4,552. Its county seat is Hallock.
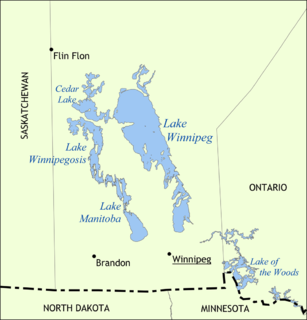
Lake Winnipeg is a very large, but relatively shallow 24,514-square-kilometre (9,465 sq mi) lake in North America, in the province of Manitoba, Canada. Its southern end is about 55 kilometres (34 mi) north of the city of Winnipeg. It is the largest lake within southern Canada's borders, and is part of the most undeveloped large watershed of southern Canada.

The Red River Valley is a region in central North America that is drained by the Red River of the North; it is part of both Canada and the United States. Forming the border between Minnesota and North Dakota when these territories were admitted as states in the United States, this fertile valley has been important to the economies of these states and to Manitoba, Canada.

The Driftless Area is a region in southeastern Minnesota, southwestern Wisconsin, northeastern Iowa, and the extreme northwestern corner of Illinois, of the American Midwest. The region escaped glaciation during the last ice age and, consequently, is characterized by steep, forested ridges, deeply-carved river valleys, and karst geology characterized by spring-fed waterfalls and cold-water trout streams. Ecologically, the flora and fauna of the Driftless Area are more closely related to those of the Great Lakes region and New England rather than those of the broader Midwest and central Plains regions. Colloquially, the term includes the incised Paleozoic Plateau of southeastern Minnesota and northeastern Iowa. The region includes elevations ranging from 603 to 1,719 feet at Blue Mound State Park and covers an area of 24,000 square miles (62,200 km2). The rugged terrain is due both to the lack of glacial deposits, or drift, and to the incision of the upper Mississippi River and its tributaries into bedrock.

Big Stone Lake is a long, narrow freshwater lake and reservoir forming the border between western Minnesota and northeastern South Dakota in the United States. The lake covers 12,610 acres (5,100 ha) of surface area, stretching 26 miles (42 km) from end to end and averaging around 1 mile (1.6 km) wide, and at an elevation of 965 feet (294 m) is the lowest point in South Dakota. Big Stone Lake is the source of the Minnesota River, which flows 332 miles (534 km) to the Mississippi River.

Lake Traverse is the southernmost body of water in the Hudson Bay watershed of North America. It lies along the border between the U.S. states of Minnesota and South Dakota. A low continental divide separates the land at the southern shore of Lake Traverse from Big Stone Lake, the headwaters of the south-flowing Little Minnesota River, which is part of the Mississippi River System. Both lakes lie within a mile of the town of Browns Valley, Minnesota with Wheaton, Minnesota ; and Ortonville, Minnesota.

The Little Minnesota River is a 71.4-mile-long (114.9 km) headwaters tributary of the Minnesota River in northeastern South Dakota and west-central Minnesota in the United States. Via the Minnesota River, it is part of the Mississippi River watershed.

Buffalo River State Park is a state park of Minnesota, United States, conserving a prairie bisected by the wooded banks of the Buffalo River. Together with the adjacent Bluestem Prairie Scientific and Natural Area owned by The Nature Conservancy, it protects one of the largest and highest-quality prairie remnants in Minnesota. With the closest swimming lake to the Fargo–Moorhead metropolitan area, however, it is most popular for swimming and picnicking. The 1,068-acre (432 ha) park is located just off U.S. Route 10 in Clay County, 4.5 miles (7.2 km) east of Glyndon and 14 miles (23 km) east of Moorhead.
Minnesota State Highway 11 is a highway in northwest and north-central Minnesota, which runs from North Dakota Highway 66 at the North Dakota state line and continues east to its eastern terminus at the community of Island View at Rainy Lake, near International Falls.

The geology of Minnesota comprises the rock, minerals, and soils of the U.S. state of Minnesota, including their formation, development, distribution, and condition.

Minnesota is the northernmost state outside Alaska; its isolated Northwest Angle in Lake of the Woods is the only part of the 48 contiguous states lying north of the 49th parallel. Minnesota is in the U.S. region known as the Upper Midwest. The state shares a Lake Superior water border with Michigan and Wisconsin on the northeast; the remainder of the eastern border is with Wisconsin. Iowa is to the south, North Dakota and South Dakota are west, and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Manitoba are north. With 87,014 square miles (225,370 km2), or approximately 2.26 % of the United States, Minnesota is the 12th largest state.

The glacial history of Minnesota is most defined since the onset of the last glacial period, which ended some 10,000 years ago. Within the last million years, most of the Midwestern United States and much of Canada were covered at one time or another with an ice sheet. This continental glacier had a profound effect on the surface features of the area over which it moved. Vast quantities of rock and soil were scraped from the glacial centers to its margins by slowly moving ice and redeposited as drift or till. Much of this drift was dumped into old preglacial river valleys, while some of it was heaped into belts of hills at the margin of the glacier. The chief result of glaciation has been the modification of the preglacial topography by the deposition of drift over the countryside. However, continental glaciers possess great power of erosion and may actually modify the preglacial land surface by scouring and abrading rather than by the deposition of the drift.

The Traverse Gap is an ancient river channel occupied by Lake Traverse, Big Stone Lake and the valley connecting them at Browns Valley, Minnesota. It is located on the border of the U.S. states of Minnesota and South Dakota. Traverse Gap has an unusual distinction for a valley: it is crossed by a continental divide, and in some floods water has flowed across that divide from one drainage basin to the other. Before the Anglo-American Convention of 1818 it marked the border between British territory in the north and U.S. – or earlier, French – territory in the south.
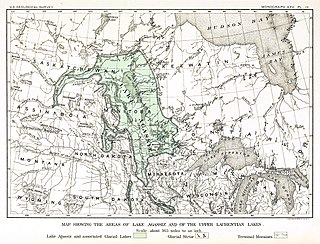
Glacial River Warren or River Warren was a prehistoric river that drained Lake Agassiz in central North America between 11,700 and 9,400 years ago. The enormous outflow from this lake carved a large valley now occupied by the much smaller Minnesota River and the Upper Mississippi River. A part of the uppermost portion of the river channel was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1966.
The River Warren Falls was a massive waterfall on the glacial River Warren initially located in present-day Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. The waterfall was 2700 feet (823 m) across and 175 feet (53 m) high.

The Yellow Bank River is a 12.0-mile-long (19.3 km) tributary of the Minnesota River in western Minnesota in the United States. It is formed by the confluence of two longer streams, the North Fork Yellow Bank River and the South Fork Yellow Bank River, which also flow in northeastern South Dakota. Via the Minnesota River, the Yellow Bank River is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of approximately 460 square miles (1,190 km²) in an agricultural region.

The proglacial lakes of Minnesota were lakes created in what is now the U.S. state of Minnesota in central North America in the waning years of the last glacial period. As the Laurentide ice sheet decayed at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation, lakes were created in depressions or behind moraines left by the glaciers. Evidence for these lakes is provided by low relief topography and glaciolacustrine sedimentary deposits. Not all contemporaneous, these glacial lakes drained after the retreat of the lobes of the ice sheets that blocked their outlets, or whose meltwaters fed them. There were a number of large lakes, one of which, Glacial Lake Agassiz, was the largest body of freshwater known to have existed on the North American continent; there were also dozens of smaller and more transitory lakes filled from glacial meltwater, which shrank or dried as the ice sheet retreated north.
The Glacial Lake Souris occupied the basin of the Souris River from the most southern portion of this river's loop in North Dakota to its elbow in Manitoba, where it turned sharply northward and passed through the Tiger Hills. The length of Lake Souris was about 170 miles, from latitude 48° to latitude 50°35', and its maximum width, north of Turtle Mountain, was nearly 70 miles. It was situated near the far southeast corner of the large glacial Lake Agassiz, separated from it by another small glacial body, Glacial Lake Hind.