Related Research Articles

Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), also known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD), describes an array of painful conditions that are characterized by a continuing regional pain that is seemingly disproportionate in time or degree to the usual course of any known trauma or other lesion. Usually starting in a limb, it manifests as extreme pain, swelling, limited range of motion, and changes to the skin and bones. It may initially affect one limb and then spread throughout the body; 35% of affected people report symptoms throughout their whole bodies. Two subtypes exist. Having both types is possible.

Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix. Symptoms commonly include right lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite. However, approximately 40% of people do not have these typical symptoms. Severe complications of a ruptured appendix include widespread, painful inflammation of the inner lining of the abdominal wall and sepsis.
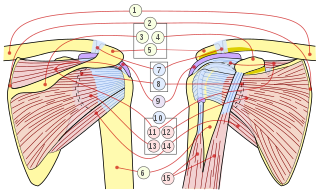
In anatomy, the rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are the supraspinatus muscle, the infraspinatus muscle, teres minor muscle, and the subscapularis muscle.
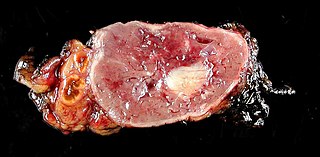
Pheochromocytoma is a rare, chromaffin cell tumor of the adrenal medulla. When a tumor composed of the same cells as a pheochromocytoma develops outside the adrenal gland, it is referred to as a paraganglioma. These neuroendocrine tumors are capable of producing and releasing massive amounts of catecholamines, metanephrines, or methoxytyramine, which result in the most common symptoms, including hypertension, tachycardia, and diaphoresis (sweating). However, not all of these tumors will secrete catecholamines. Those that do not are referred to as biochemically silent, and a predominately located in the head and neck. While patients with biochemically silent disease will not suffer from the typical disease manifestations described above, the tumors grow and compress the surrounding structures of the head and neck, and can result in pulsatile tinnitus, hearing loss, aural fullness, dyspnea, and hoarseness. While tumors of the head and neck are parasympathetic, their sympathetic counterparts are predominantly located in the abdomen and pelvis, particularly concentrated at the organ of Zuckerkandl.

A bone tumor is a neoplastic growth of tissue in bone. Abnormal growths found in the bone can be either benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous).

A thymoma is a tumor originating from the epithelial cells of the thymus that may be benign or malignant. Thymomas are frequently associated with the neuromuscular disorder myasthenia gravis; thymoma is found in 20% of patients with myasthenia gravis. Once diagnosed, thymomas may be removed surgically. In the rare case of a malignant tumor, chemotherapy may be used.

Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. Causes in order of frequency include: 1) a gallstone impacted in the common bile duct beyond the point where the pancreatic duct joins it; 2) heavy alcohol use; 3) systemic disease; 4) trauma; 5) and, in minors, mumps. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event; it may be recurrent; or it may progress to chronic pancreatitis.
Blumberg's sign is a clinical sign in which there is pain upon removal of pressure rather than application of pressure to the abdomen. It is indicative of peritonitis. It was named after German surgeon Jacob Moritz Blumberg.

A rotator cuff tear is an injury where one or more of the tendons or muscles of the rotator cuff of the shoulder get torn. Symptoms may include shoulder pain, which is often worse with movement, or weakness. This may limit people’s ability to brush their hair or put on clothing. Clicking may also occur with movement of the arm.

A paraganglioma is a rare neuroendocrine neoplasm that may develop at various body sites. When the same type of tumor is found in the adrenal gland, they are referred to as a pheochromocytoma. They are rare tumors, with an overall estimated incidence of 1/300,000. Unlike other types of cancer, there is no test that determines benign from malignant tumors; long-term followup is therefore recommended for all individuals with paraganglioma. The five-year survival in the setting of metastatic disease is 90% to 100%.

A glomus tumor is a rare neoplasm arising from the glomus body and mainly found under the nail, on the fingertip or in the foot. They account for less than 2% of all soft tissue tumors. The majority of glomus tumors are benign, but they can also show malignant features. Glomus tumors were first described by Hoyer in 1877 while the first complete clinical description was given by Masson in 1924.
In medicine, Murphy's sign is a maneuver during a physical examination as part of the abdominal examination. It is useful for differentiating pain in the right upper quadrant. Typically, it is positive in cholecystitis, but negative in choledocholithiasis, pyelonephritis, and ascending cholangitis.
The McMurray test, also known as the McMurray circumduction test is used to evaluate individuals for tears in the meniscus of the knee. A tear in the meniscus may cause a pedunculated tag of the meniscus which may become jammed between the joint surfaces.
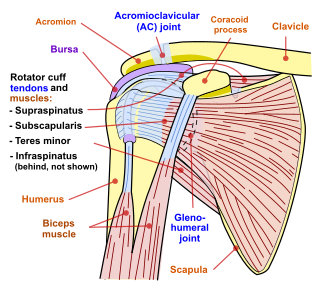
Subacromial bursitis is a condition caused by inflammation of the bursa that separates the superior surface of the supraspinatus tendon from the overlying coraco-acromial ligament, acromion, and coracoid and from the deep surface of the deltoid muscle. The subacromial bursa helps the motion of the supraspinatus tendon of the rotator cuff in activities such as overhead work.
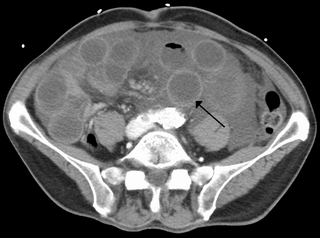
Mesenteric ischemia is a medical condition in which injury to the small intestine occurs due to not enough blood supply. It can come on suddenly, known as acute mesenteric ischemia, or gradually, known as chronic mesenteric ischemia. The acute form of the disease often presents with sudden severe abdominal pain and is associated with a high risk of death. The chronic form typically presents more gradually with abdominal pain after eating, unintentional weight loss, vomiting, and fear of eating.
Breast cancer management takes different approaches depending on physical and biological characteristics of the disease, as well as the age, over-all health and personal preferences of the patient. Treatment types can be classified into local therapy and systemic treatment. Local therapy is most efficacious in early stage breast cancer, while systemic therapy is generally justified in advanced and metastatic disease, or in diseases with specific phenotypes.
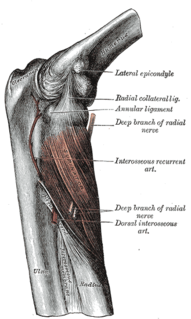
Radial tunnel syndrome (RTS) is caused by increased pressure on the radial nerve as it travels from the upper arm to the hand and wrist.

Ulnar neuropathy is a disorder involving the ulnar nerve. Ulnar neuropathy may be caused by entrapment of the ulnar nerve with resultant numbness and tingling. Motor function can be assessed by testing for a positive Froment's sign, or making an OK sign, little finger abduction can be tested as well.

Shoulder impingement syndrome is a syndrome involving tendonitis of the rotator cuff muscles as they pass through the subacromial space, the passage beneath the acromion. It is particularly associated with tendonitis of the supraspinatus muscle. This can result in pain, weakness, and loss of movement at the shoulder.
Durkan's test is a medical procedure to diagnose a patient with carpal tunnel syndrome. It is a new variation of Tinel's sign that was proposed by JA Durkan in 1991.
References
- ↑ Hildreth DH (1970). "The ischemia test for glomus tumor: a new diagnostic test". Rev Surg. 27 (2): 147–8. PMID 4315716.
- ↑ GIELE, H (1 April 2002). "Hildreth's Test is a Reliable Clinical Sign for the Diagnosis of Glomus Tumours". The Journal of Hand Surgery: Journal of the British Society for Surgery of the Hand. 27 (2): 157–158. doi:10.1054/jhsb.2001.0724. PMID 12027491. S2CID 29745831.