Himalia may refer to:
- Himalia (moon), a moon of Jupiter
- Himalia (mythology), a nymph from Cyprus in Greek mythology
- Himalia Ridge, a ridge on the Ganymede Heights massif on Alexander Island, Antarctica
Himalia may refer to:
Dione may refer to:
Enceladus is a moon of Saturn.
Leda may refer to:
Phoebe or Phœbe may refer to:
Rhea may refer to:
Sinope may refer to:

Himalia, or Jupiter VI, is the largest irregular satellite of Jupiter, with a diameter of at least 140 km (90 mi). It is the sixth largest Jovian satellite, after the four Galilean moons and Amalthea. It was discovered by Charles Dillon Perrine at the Lick Observatory on 3 December 1904 and is named after the nymph Himalia, who bore three sons of Zeus. It is one of the largest planetary moons in the Solar System not imaged in detail, and the third largest not imaged in detail within the orbit of Neptune.

Elara is a prograde irregular satellite of Jupiter. It was discovered by Charles Dillon Perrine at Lick Observatory in 1905 in photographs taken with the 36" Crossley reflecting telescope which he had recently rebuilt. It is the eighth-largest moon of Jupiter and is named after Elara, one of Zeus's lovers and the mother of the giant Tityos.
Io, IO, iO, I/O, i/o, or i.o. may refer to:
Calyx or calyce, from the Latin calix which itself comes from the Ancient Greek κάλυξ (kálux) meaning "husk" or "pod", may refer to:
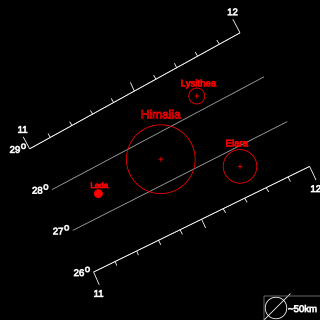
The Himalia group is a group of prograde irregular satellites of Jupiter that follow similar orbits to Himalia and are thought to have a common origin.
Ganymede most commonly refers to:
Ægir is a figure in Norse mythology.
Himalia Ridge is a ridge running east–west on the north side of the Ganymede Heights massif, north-east of Jupiter Glacier, in the east of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947 and mapped from these photographs by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1960. The ridge was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee following British Antarctic Survey geological work, 1983–84, after Himalia, a satellite of the planet Jupiter, in association with Jupiter Glacier. The site lies within Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.147.
Paha is a settlement in Novo Mesto, Slovenia.
Scilla is a genus of perennial herbs. Scilla may also refer to

Ersa, also designated Jupiter LXXI, is a small outer natural satellite of Jupiter discovered by Scott S. Sheppard on 11 May 2018, using the 4.0-meter Víctor M. Blanco Telescope at Cerro Tololo Observatory, Chile. It was announced alongside nine other Jovian moons on 17 July 2018 and it provisionally designated S/2018 J 1 by the Minor Planet Center, after observations were collected over a long enough time span to confirm the satellite's orbit. The satellite has been found in precovery observations as early as 6 August 2000.

Pandia, also designated Jupiter LXV, is a small outer natural satellite of Jupiter discovered by Scott S. Sheppard on 11 May 2018, using the 4.0-meter Víctor M. Blanco Telescope at Cerro Tololo Observatory, Chile. It was announced alongside nine other Jovian moons on 17 July 2018 and it provisionally designated S/2017 J 4 by the Minor Planet Center, after observations were collected over a long enough time span to confirm the satellite's orbit. The satellite has been found in precovery observations as early as 2003.
S/2018 J 2 is a small outer natural satellite of Jupiter discovered by Scott S. Sheppard on 12 May 2018, using the 4.0-meter Víctor M. Blanco Telescope at Cerro Tololo Observatory, Chile. It was announced by the Minor Planet Center four years later on 20 December 2022, after observations were collected over a long enough time span to confirm the satellite's orbit. The satellite has been found in precovery observations as early as 27 March 2003.
S/2011 J 3 is a small outer natural satellite of Jupiter discovered by Scott S. Sheppard on 27 September 2011, using the 6.5-meter Magellan-Baade Telescope at Las Campanas Observatory, Chile. It was announced by the Minor Planet Center 11 years later on 20 December 2022, after observations were collected over a long enough time span to confirm the satellite's orbit.