Histone demethylase may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Histone demethylase. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Histone demethylase may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Histone demethylase. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Histone methylation is a process by which methyl groups are transferred to amino acids of histone proteins that make up nucleosomes, which the DNA double helix wraps around to form chromosomes. Methylation of histones can either increase or decrease transcription of genes, depending on which amino acids in the histones are methylated, and how many methyl groups are attached. Methylation events that weaken chemical attractions between histone tails and DNA increase transcription, because they enable the DNA to uncoil from nucleosomes so that transcription factor proteins and RNA polymerase can access the DNA. This process is critical for the regulation of gene expression that allows different cells to express different genes.
Demethylases are enzymes that remove methyl (CH3-) groups from nucleic acids, proteins (in particular histones), and other molecules. Demethylase enzymes are important in epigenetic modification mechanisms. The demethylase proteins alter transcriptional regulation of the genome by controlling the methylation levels that occur on DNA and histones and, in turn, regulate the chromatin state at specific gene loci within organisms.
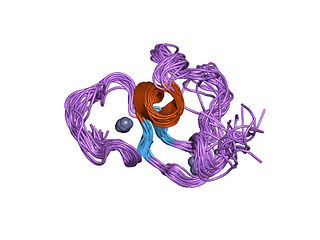
The PHD finger was discovered in 1993 as a Cys4-His-Cys3 motif in the plant homeodomain proteins HAT3.1 in Arabidopsis thaliana and maize ZmHox1a. The PHD finger motif resembles the metal binding RING domain (Cys3-His-Cys4) and FYVE domain. It occurs as a single finger, but often in clusters of two or three, and it also occurs together with other domains, such as the chromodomain and the bromodomain.

Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (LSD1) also known as lysine (K)-specific demethylase 1A (KDM1A) is a protein in humans that is encoded by the KDM1A gene. LSD1 is a flavin-dependent monoamine oxidase, which can demethylate mono- and di-methylated lysines, specifically histone 3, lysines 4 and 9. This enzyme can have roles critical in embryogenesis and tissue-specific differentiation, as well as oocyte growth. KDM1A was the first histone demethylase to be discovered though more than 30 have been described.
UTY may refer to:

Lysine-specific demethylase 5A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KDM5A gene.

Lysine-specific demethylase 4A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KDM4A gene.

Lysine-specific demethylase 2A (KDM2A) also known as F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 11 (FBXL11) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KDM2A gene. KDM2A is a member of the superfamily of alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases, which are non-haem iron-containing proteins.

Lysine-specific demethylase 5B also known as histone demethylase JARID1B is a demethylase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KDM5B gene. JARID1B belongs to the alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylase superfamily.

Lysine-specific demethylase 6A also known as Ubiquitously transcribed tetratricopeptide repeat, X chromosome (UTX), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the KDM6A gene. It belongs to the 2-oxoglutarate (2OG)-dependent dioxygenase superfamily.

PHD finger protein 21A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PHF21A gene.

Lysine-specific demethylase 4D is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KDM4D gene. KDM4D belongs to the alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylase superfamily.
(Histone-H3)-lysine-36 demethylase (EC 1.14.11.27, JHDM1A, JmjC domain-containing histone demethylase 1A, H3-K36-specific demethylase, histone-lysine (H3-K36) demethylase, histone demethylase, protein-6-N,6-N-dimethyl-L-lysine,2-oxoglutarate:oxygen oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name protein-N6,N6-dimethyl-L-lysine,2-oxoglutarate:oxygen oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

The human KDM2B gene encodes the protein lysine (K)-specific demethylase 2B.

Lysine (K)-specific demethylase 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KDM1B gene.

Lysine demethylase 3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KDM3A gene.

Jumonji domain containing 1C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JMJD1C gene.

Lysine demethylase 6B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KDM6B gene.

Lysine demethylase 7A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KDM7A gene.

Lysine demethylase 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KDM8 gene.