ANSI C, ISO C, and Standard C are successive standards for the C programming language published by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 22/WG 14 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Historically, the names referred specifically to the original and best-supported version of the standard. Software developers writing in C are encouraged to conform to the standards, as doing so helps portability between compilers.
MPEG-4 is a group of international standards for the compression of digital audio and visual data, multimedia systems, and file storage formats. It was originally introduced in late 1998 as a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) under the formal standard ISO/IEC 14496 – Coding of audio-visual objects. Uses of MPEG-4 include compression of audiovisual data for Internet video and CD distribution, voice and broadcast television applications. The MPEG-4 standard was developed by a group led by Touradj Ebrahimi and Fernando Pereira.

JPEG 2000 (JP2) is an image compression standard and coding system. It was developed from 1997 to 2000 by a Joint Photographic Experts Group committee chaired by Touradj Ebrahimi, with the intention of superseding their original JPEG standard, which is based on a discrete cosine transform (DCT), with a newly designed, wavelet-based method. The standardized filename extension is .jp2 for ISO/IEC 15444-1 conforming files and .jpx for the extended part-2 specifications, published as ISO/IEC 15444-2. The MIME types for JPEG 2000 are defined in RFC 3745. The MIME type for JPEG 2000 is image/jp2.

VRML is a standard file format for representing 3-dimensional (3D) interactive vector graphics, designed particularly with the World Wide Web in mind. It has been superseded by X3D.
X3D is a set of royalty-free ISO/IEC standards for declaratively representing 3D computer graphics. X3D includes multiple graphics file formats, programming-language API definitions, and run-time specifications for both delivery and integration of interactive network-capable 3D data. X3D version 4.0 has been approved by Web3D Consortium, and is under final review by ISO/IEC as a revised International Standard (IS).
COLLADA is an interchange file format for interactive 3D applications. It is managed by the nonprofit technology consortium, the Khronos Group, and has been adopted by ISO as a publicly available specification, ISO/PAS 17506.
The Extensible MPEG-4 Textual Format (XMT) is a high-level, XML-based file format for storing MPEG-4 data in a way suitable for further editing. In contrast, the more common MPEG-4 Part 14 (MP4) format is less flexible and used for distributing finished content.
Manufacturing Message Specification (MMS) is an international standard dealing with messaging systems for transferring real time process data and supervisory control information between networked devices or computer applications. The standard is developed and maintained by the ISO Technical Committee 184 (TC184). MMS defines the following
MPEG-4 Part 11Scene description and application engine was published as ISO/IEC 14496-11 in 2005. MPEG-4 Part 11 is also known as BIFS, XMT, MPEG-J. It defines:
Demicron WireFusion an authoring tool for creating interactive Web3D presentations. A typical work flow consists of loading a 3D model, configuring/optimizing the 3D model and lastly adding widgets and logic to the presentation. The 3D model is created in a 3D modeling program, like 3DS Max, Maya or any other 3D modeling program that can export as X3D or VRML. The resulting presentations can run in browsers supporting Java 1.1+.
Web3D Consortium is an international not-for-profit, member-funded industry consortium, originally founded in 1997. Web3D Consortium members from governmental, nonprofit and research organizations worldwide, including working alongside individual professional members to collaborate in a consensus process and encouraging development and implementation of open standards for 3D content and services.
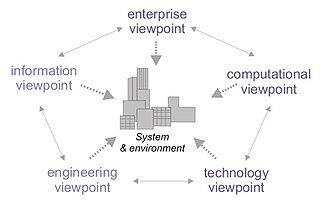
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems.
Flux was a software suite released by Media Machines which consisted of Flux Player and Flux Studio.
Seamless3d is an open-source 3D modeling software available under the MIT license.
Web3D, also called 3D Web, is a group of technologies to display and navigate websites using 3D computer graphics.

Tony Parisi, one of the early pioneers in virtual reality and the metaverse, is an entrepreneur, inventor and developer of 3D computer software. The co-creator of Virtual Reality Modeling Language (VRML), he has written books and papers on the future of technology. He works on WebGL and WebVR and has written two books on the former, and an introductory book on virtual reality programming. He is the chief strategy officer at Lamina1. Parisi is also a musician, composer and producer working on multiple projects.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 24 Computer graphics, image processing and environmental data representation is a standardization subcommittee of the joint subcommittee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), which develops and facilitates standards within the field of computer graphics, image processing, and environmental data representation. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 24 is the British Standards Institute (BSI) located in the United Kingdom.

glTF is a standard file format for three-dimensional scenes and models. A glTF file uses one of two possible file extensions: .gltf (JSON/ASCII) or .glb (binary). Both .gltf and .glb files may reference external binary and texture resources. Alternatively, both formats may be self-contained by directly embedding binary data buffers. An open standard developed and maintained by the Khronos Group, it supports 3D model geometry, appearance, scene graph hierarchy, and animation. It is intended to be a streamlined, interoperable format for the delivery of 3D assets, while minimizing file size and runtime processing by apps. As such, its creators have described it as the "JPEG of 3D."





