
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure over diastolic pressure in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in kilopascals (kPa).
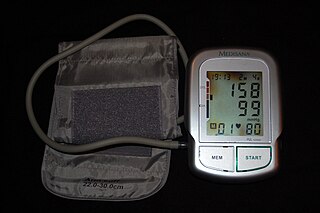
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. High blood pressure, however, is a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide.
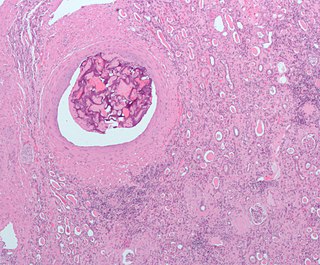
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule, a bubble of air or other gas, amniotic fluid, or foreign material. An embolism can cause partial or total blockage of blood flow in the affected vessel. Such a blockage may affect a part of the body distant from the origin of the embolus. An embolism in which the embolus is a piece of thrombus is called a thromboembolism.
Baroreceptors are sensors located in the carotid sinus and in the aortic arch. They sense the blood pressure and relay the information to the brain, so that a proper blood pressure can be maintained.

Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia and respiratory failure. It is due to either failure of the left ventricle of the heart to remove oxygenated blood adequately from the pulmonary circulation, or an injury to the lung tissue directly or blood vessels of the lung.

Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). It represents the force that the heart generates each time it contracts. Normal pulse pressure is approximately 40 mmHg, whereas a pulse pressure that is less than 25% of the systolic pressure is low or narrowed, and a pulse pressure of greater than 100 mmHg is high or widened, although some sources consider a pulse pressure of 60 mmHg to be unusually high or wide, and a pulse pressure of 50 mmHg or more increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this does not naturally close after birth it is referred to as a patent (open) foramen ovale (PFO). It is common in patients with a congenital atrial septal aneurysm (ASA).

Pulmonary hypertension is a condition of increased blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fainting, tiredness, chest pain, swelling of the legs, and a fast heartbeat. The condition may make it difficult to exercise. Onset is typically gradual.

Eisenmenger syndrome or Eisenmenger's syndrome is defined as the process in which a long-standing left-to-right cardiac shunt caused by a congenital heart defect causes pulmonary hypertension and eventual reversal of the shunt into a cyanotic right-to-left shunt. Because of the advent of fetal screening with echocardiography early in life, the incidence of heart defects progressing to Eisenmenger syndrome has decreased.
Compliance is the ability of a hollow organ (vessel) to distend and increase volume with increasing transmural pressure or the tendency of a hollow organ to resist recoil toward its original dimensions on application of a distending or compressing force. It is the reciprocal of "elastance", hence elastance is a measure of the tendency of a hollow organ to recoil toward its original dimensions upon removal of a distending or compressing force.

Endothelins are peptides with receptors and effects in many body organs. Endothelin constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. The endothelins are normally kept in balance by other mechanisms, but when overexpressed, they contribute to high blood pressure (hypertension), heart disease, and potentially other diseases.
Severely elevated blood pressure is referred to as a hypertensive crisis, as blood pressure at this level confers a high risk of complications. People with blood pressures in this range may have no symptoms, but are more likely to report headaches and dizziness than the general population. Other symptoms accompanying a hypertensive crisis may include visual deterioration due to retinopathy, breathlessness due to heart failure, or a general feeling of malaise due to kidney failure. Most people with a hypertensive crisis are known to have elevated blood pressure, but additional triggers may have led to a sudden rise.

Bosentan, sold under the brand name Tracleer and Safebo among others, is a dual endothelin receptor antagonist medication used in the treatment of pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH).

Iloprost is a medication used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), scleroderma, Raynaud's phenomenon and other diseases in which the blood vessels are constricted and blood cannot flow to the tissues. This damages the tissues and causes high blood pressure. There is ongoing research into using it as a frostbite treatment. Iloprost works by opening (dilating) the blood vessels to allow the blood to flow through again. It was developed by the pharmaceutical company Schering AG and is marketed by Bayer Schering Pharma AG in Europe and Actelion Pharmaceuticals in the USA. Iloprost is given via inhalation, and a therapeautic benefit of the drug is that a very low dose is required because of the deposition in the lung. Iloprost has few systemic side effects for that reason.

Beraprost is a pharmaceutical drug used in several Asian countries, including Japan and South Korea, as a vasodilator and antiplatelet agent. It is classified as a prostacyclin analog.

Ambrisentan is a drug indicated for use in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension.
Persistent fetal circulation is a condition caused by a failure in the systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation to convert from the antenatal circulation pattern to the "normal" pattern. Infants experience a high mean arterial pulmonary artery pressure and a high afterload at the right ventricle. This means that the heart is working against higher pressures, which makes it more difficult for the heart to pump blood.

Riociguat, sold under the brand name Adempas, is a medication by Bayer that is a stimulator of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC). It is used to treat two forms of pulmonary hypertension (PH): chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Riociguat constitutes the first drug of the class of sGC stimulators. The drug has a half-life of 12 hours and will decrease dyspnea associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension.

Arterial embolism is a sudden interruption of blood flow to an organ or body part due to an embolus adhering to the wall of an artery blocking the flow of blood, the major type of embolus being a blood clot (thromboembolism). Sometimes, pulmonary embolism is classified as arterial embolism as well, in the sense that the clot follows the pulmonary artery carrying deoxygenated blood away from the heart. However, pulmonary embolism is generally classified as a form of venous embolism, because the embolus forms in veins. Arterial embolism is the major cause of infarction.














