The diagnostic tests in cardiology are methods of identifying heart conditions associated with healthy vs. unhealthy, pathologic heart function.
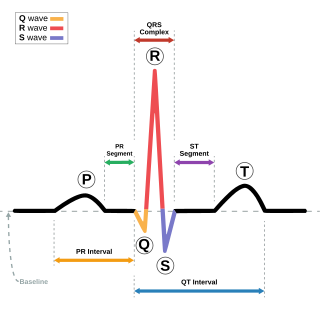
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram, a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including:

Willem Einthoven was a Dutch medical doctor and physiologist. He invented the first practical electrocardiograph in 1895 and received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1924 for it.
Quest for Fame is a music video game developed by Virtual Music Entertainment and distributed by IBM. They were eventually acquired by Namco to create karaoke machines.

Apollo Hospitals Enterprise Limited is an Indian multinational healthcare group headquartered in Chennai. It is the largest for-profit private hospital network in India, with a network of 71 owned and managed hospitals. Along with the eponymous hospital chain, the company also operates pharmacies, primary care and diagnostic centres, telehealth clinics, and digital healthcare services among others through its subsidiaries.
A biomedical scientist is a scientist trained in biology, particularly in the context of medical laboratory sciences or laboratory medicine. These scientists work to gain knowledge on the main principles of how the human body works and to find new ways to cure or treat disease by developing advanced diagnostic tools or new therapeutic strategies. The research of biomedical scientists is referred to as biomedical research.

Acute pericarditis is a type of pericarditis usually lasting less than 4 to 6 weeks. It is the most common condition affecting the pericardium.

Robert Arthur Bruce was an American cardiologist and a professor at the University of Washington. He was known as the "father of exercise cardiology" for his research and development of the Bruce Protocol.
A cardiovascular technician, also known as a vascular technician, is health professional that deal with the circulatory system.

Left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) is an abnormal condition of the left ventricle of the heart, related to, but distinguished from, left bundle branch block (LBBB).

Thomas Fearn Frist was an American physician and businessman who co-founded the Hospital Corporation of America.

Wellens' syndrome is an electrocardiographic manifestation of critical proximal left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery stenosis in people with unstable angina. Originally thought of as two separate types, A and B, it is now considered an evolving wave form, initially of biphasic T wave inversions and later becoming symmetrical, often deep, T wave inversions in the anterior precordial leads.

Abbott Northwestern Hospital is a 686-staffed bed teaching and specialty hospital based in Minneapolis, Minnesota. It is a part of the Allina Health network of hospitals and clinics.

Italy's healthcare system is consistently ranked among the best in the world. The Italian healthcare system employs a Beveridge model, and operates on the assumption that health care is a human right that should be provided to everyone regardless of their ability to pay. Life expectancy is the 4th highest among OECD countries and the world's 8th highest according to the WHO. Healthcare spending accounted for 9.7% of GDP in 2020.

ST elevation is a finding on an electrocardiogram wherein the trace in the ST segment is abnormally high above the baseline.

ST depression refers to a finding on an electrocardiogram, wherein the trace in the ST segment is abnormally low below the baseline.

Electrocardiography in suspected myocardial infarction has the main purpose of detecting ischemia or acute coronary injury in emergency department populations coming for symptoms of myocardial infarction (MI). Also, it can distinguish clinically different types of myocardial infarction.

Healthcare in Belgium is composed of three parts. Firstly there is a primarily publicly funded healthcare and social security service run by the federal government, which organises and regulates healthcare; independent private/public practitioners, university/semi-private hospitals and care institutions. There are a few private hospitals. Secondly is the insurance coverage provided for patients. Finally, industry coverage; which covers the production and distribution of healthcare products for research and development. The primary aspect of this research is done in universities and hospitals.

Malda Medical College and Hospital (MMC&H) is a medical college run by the government of West Bengal in Malda, West Bengal, India. It is recognised by the National Medical Commission and affiliated to West Bengal University of Health Sciences. The college was established in 2011.
Arnot Ogden Medical Center is a medical facility in Elmira, New York, previously known as Arnot-Ogden Memorial Hospital, founded in 1888.














