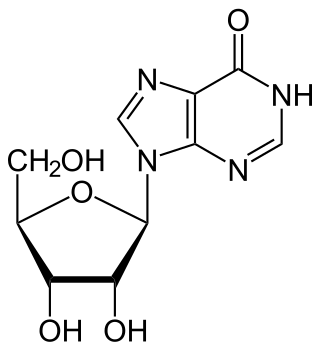
Inosine is a nucleoside that is formed when hypoxanthine is attached to a ribose ring (also known as a ribofuranose) via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. It was discovered in 1965 in analysis of RNA transferase. Inosine is commonly found in tRNAs and is essential for proper translation of the genetic code in wobble base pairs.
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase, PNP, PNPase or inosine phosphorylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NP gene. It catalyzes the chemical reaction

Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (OPRTase) or orotic acid phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis. It catalyzes the formation of orotidine 5'-monophosphate (OMP) from orotate and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate. In yeast and bacteria, orotate phosphoribosyltransferase is an independent enzyme with a unique gene coding for the protein, whereas in mammals and other multicellular organisms, the catalytic function is carried out by a domain of the bifunctional enzyme UMP synthase (UMPS).
Purine metabolism refers to the metabolic pathways to synthesize and break down purines that are present in many organisms.
GMP reductase EC 1.7.1.7 is an enzyme that catalyzes the irreversible and NADPH-dependent reductive deamination of GMP into IMP.

Bifunctional purine biosynthesis protein PURH is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATIC gene.
In molecular biology, the protein domain Saccharopine dehydrogenase (SDH), also named Saccharopine reductase, is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of the amino acid lysine, via an intermediate substance called saccharopine. The Saccharopine dehydrogenase enzyme can be classified under EC 1.5.1.7, EC 1.5.1.8, EC 1.5.1.9, and EC 1.5.1.10. It has an important function in lysine metabolism and catalyses a reaction in the alpha-Aminoadipic acid pathway. This pathway is unique to fungal organisms therefore, this molecule could be useful in the search for new antibiotics. This protein family also includes saccharopine dehydrogenase and homospermidine synthase. It is found in prokaryotes, eukaryotes and archaea.
In enzymology, carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (CODH) (EC 1.2.7.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an adenosine-phosphate deaminase (EC 3.5.4.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Alcohol dehydrogenase class-3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADH5 gene.
NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 2, also known as QR2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NQO2 gene. It is a phase II detoxification enzyme which can carry out two or four electron reductions of quinones. Its mechanism of reduction is through a ping-pong mechanism involving its FAD cofactor. Initially in a reductive phase NQO2 binds to reduced dihydronicotinamide riboside (NRH) electron donor, and mediates a hydride transfer from NRH to FAD. Then, in an oxidative phase, NQO2 binds to its quinone substrate and reduces the quinone to a dihydroquinone. Besides the two catalytic FAD, NQO2 also has two zinc ions. It is not clear whether the metal has a catalytic role. NQO2 is a paralog of NQO1
NQO2 is a homodimer. NQO2 can be inhibited by resveratrol. One of QR2's binding sites responds to 2-iodomelatonin, and has been referred to as MT3.

Bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTHFD2 gene.

D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BDH1 gene.

Inosine-5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) is a purine biosynthetic enzyme that catalyzes the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent oxidation of inosine monophosphate (IMP) to xanthosine monophosphate (XMP), the first committed and rate-limiting step towards the de novo biosynthesis of guanine nucleotides from IMP. IMPDH is a regulator of the intracellular guanine nucleotide pool, and is therefore important for DNA and RNA synthesis, signal transduction, energy transfer, glycoprotein synthesis, as well as other process that are involved in cellular proliferation.

Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase 1, also known as IMP dehydrogenase 1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IMPDH1 gene.

Morpheeins are proteins that can form two or more different homo-oligomers, but must come apart and change shape to convert between forms. The alternate shape may reassemble to a different oligomer. The shape of the subunit dictates which oligomer is formed. Each oligomer has a finite number of subunits (stoichiometry). Morpheeins can interconvert between forms under physiological conditions and can exist as an equilibrium of different oligomers. These oligomers are physiologically relevant and are not misfolded protein; this distinguishes morpheeins from prions and amyloid. The different oligomers have distinct functionality. Interconversion of morpheein forms can be a structural basis for allosteric regulation, an idea noted many years ago, and later revived. A mutation that shifts the normal equilibrium of morpheein forms can serve as the basis for a conformational disease. Features of morpheeins can be exploited for drug discovery. The dice image represents a morpheein equilibrium containing two different monomeric shapes that dictate assembly to a tetramer or a pentamer. The one protein that is established to function as a morpheein is porphobilinogen synthase, though there are suggestions throughout the literature that other proteins may function as morpheeins.
Phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase (EC 2.1.2.2, 2-amino-N-ribosylacetamide 5'-phosphate transformylase, GAR formyltransferase, GAR transformylase, glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylase, GAR TFase, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate:2-amino-N-ribosylacetamide ribonucleotide transformylase) is an enzyme with systematic name 10-formyltetrahydrofolate:5'-phosphoribosylglycinamide N-formyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase 2, also known as IMP dehydrogenase 2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the IMPDH2 gene.
Alcohol dehydrogenase (azurin) (EC 1.1.9.1, type II quinoprotein alcohol dehydrogenase, quinohaemoprotein ethanol dehydrogenase, QHEDH, ADHIIB) is an enzyme with systematic name alcohol:azurin oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction















