Related Research Articles
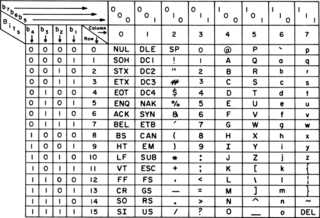
ASCII, abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of technical limitations of computer systems at the time it was invented, ASCII has just 128 code points, of which only 95 are printable characters, which severely limited its scope. Many computer systems instead use Unicode, which has millions of code points, but the first 128 of these are the same as the ASCII set.
In computing and telecommunication, a control character or non-printing character (NPC) is a code point in a character set that does not represent a written character or symbol. They are used as in-band signaling to cause effects other than the addition of a symbol to the text. All other characters are mainly graphic characters, also known as printing characters, except perhaps for "space" characters. In the ASCII standard there are 33 control characters, such as code 7, BEL, which rings a terminal bell.
The null character is a control character with the value zero. It is present in many character sets, including those defined by the Baudot and ITA2 codes, ISO/IEC 646, the C0 control code, the Universal Coded Character Set, and EBCDIC. It is available in nearly all mainstream programming languages. It is often abbreviated as NUL. In 8-bit codes, it is known as a null byte.
ISO/IEC 2022Information technology—Character code structure and extension techniques, is an ISO/IEC standard in the field of character encoding. Originating in 1971, it was most recently revised in 1994.

The Alt keyAlt on a computer keyboard is used to change (alternate) the function of other pressed keys. Thus, the Alt key is a modifier key, used in a similar fashion to the Shift key. For example, simply pressing A will type the letter 'a', but holding down the Alt key while pressing A will cause the computer to perform an Alt+A function, which varies from program to program. The international standard ISO/IEC 9995-2 calls it Alternate key. The key is located on either side of the space bar, but in non-US PC keyboard layouts, rather than a second Alt key, there is an 'Alt Gr' key to the right of the space bar. Both placements are in accordance with ISO/IEC 9995-2. With some keyboard mappings, the right Alt key can be reconfigured to function as an AltGr key although not engraved as such.
T.61 is an ITU-T Recommendation for a Teletex character set. T.61 predated Unicode, and was the primary character set in ASN.1 used in early versions of X.500 and X.509 for encoding strings containing characters used in Western European languages. It is also used by older versions of LDAP. While T.61 continues to be supported in modern versions of X.500 and X.509, it has been deprecated in favor of Unicode. It is also called Code page 1036, CP1036, or IBM 01036.

A compose key is a key on a computer keyboard that indicates that the following keystrokes trigger the insertion of an alternate character, typically a precomposed character or a symbol.

On computer keyboards, the Esc keyEsc is a key used to generate the escape character. The escape character, when sent from the keyboard to a computer, often is interpreted by software as "stop", and when sent from the computer to an external device marks the beginning of an escape sequence to specify operating modes or characteristics generally.
The C0 and C1 control code or control character sets define control codes for use in text by computer systems that use ASCII and derivatives of ASCII. The codes represent additional information about the text, such as the position of a cursor, an instruction to start a new line, or a message that the text has been received.
UTF-1 is a method of transforming ISO/IEC 10646/Unicode into a stream of bytes. Its design does not provide self-synchronization, which makes searching for substrings and error recovery difficult. It reuses the ASCII printing characters for multi-byte encodings, making it unsuited for some uses. UTF-1 is also slow to encode or decode due to its use of division and multiplication by a number which is not a power of 2. Due to these issues, it did not gain acceptance and was quickly replaced by UTF-8.

〒 is the service mark of Japan Post and its successor, Japan Post Holdings, the postal operator in Japan. It is also used as a Japanese postal code mark since the introduction of the latter in 1968. Historically, it was used by the Ministry of Communications, which operated the postal service. The mark is a stylized katakana syllable te (テ), from the word teishin. The mark was introduced on February 8, 1887.
Diacritical marks of two dots¨, placed side-by-side over or under a letter, are used in a number of languages for several different purposes. The most familiar to English-language speakers are the diaeresis and the umlaut, though there are numerous others. For example, in Albanian, ë represents a schwa. Such dots are also sometimes used for stylistic reasons.
On personal computers with numeric keypads that use Microsoft operating systems, such as Windows, many characters that do not have a dedicated key combination on the keyboard may nevertheless be entered using the Alt code. This is done by pressing and holding the Alt key, then typing a number on the keyboard's numeric keypad that identifies the character and then releasing Alt.

A Hebrew keyboard comes in two different keyboard layouts. Most Hebrew keyboards are bilingual, with Latin characters, usually in a US Qwerty layout. Trilingual keyboard options also exist, with the third script being Arabic or Russian, due to the sizable Arabic- and Russian-speaking populations in Israel.
ISO/IEC 9995Information technology — Keyboard layouts for text and office systems is an ISO/IEC standard series defining layout principles for computer keyboards. It does not define specific layouts but provides the base for national and industry standards which define such layouts.
Language input keys, which are usually found on Japanese and Korean keyboards, are keys designed to translate letters using an input method editor (IME). On non-Japanese or Korean keyboard layouts using an IME, these functions can usually be reproduced via hotkeys, though not always directly corresponding to the behavior of these keys.

Unicode input is the insertion of a specific Unicode character on a computer by a user; it is a common way to input characters not directly supported by a physical keyboard. Unicode characters can be produced either by selecting them from a display or by typing a certain sequence of keys on a physical keyboard. In addition, a character produced by one of these methods in one web page or document can be copied into another. In contrast to ASCII's 96 element character set, Unicode encodes hundreds of thousands of graphemes (characters) from almost all of the world's written languages and many other signs and symbols besides.
The Universal Coded Character Set is a standard set of characters defined by the international standard ISO/IEC 10646, Information technology — Universal Coded Character Set (UCS), which is the basis of many character encodings, improving as characters from previously unrepresented typing systems are added.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2 Coded character sets is a standardization subcommittee of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), that develops and facilitates standards within the field of coded character sets. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2 is the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (JISC), located in Japan. SC 2 is responsible for the development of the Universal Coded Character Set which is the international standard corresponding to the Unicode Standard.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 35 User interfaces is a standardization subcommittee (SC), which is part of the joint technical committee, ISO/IEC JTC 1, of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), that develops standards within the field of user-system interfaces in information and communication technology (ICT) environments. The subcommittee was founded at the 1998 Sendai ISO/IEC JTC 1 Plenary meeting, before which it was a working group directly under ISO/IEC JTC 1. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 35 is AFNOR, located in France.