Related Research Articles
A logic gate is an idealized model of computation or physical electronic device implementing a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has for instance zero rise time and unlimited fan-out, or it may refer to a non-ideal physical device.

A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.

A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, use only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between two other terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching.

Static random-access memory is a type of random-access memory (RAM) that uses latching circuitry (flip-flop) to store each bit. SRAM is volatile memory; data is lost when power is removed.
An EPROM, or erasable programmable read-only memory, is a type of programmable read-only memory (PROM) chip that retains its data when its power supply is switched off. Computer memory that can retrieve stored data after a power supply has been turned off and back on is called non-volatile. It is an array of floating-gate transistors individually programmed by an electronic device that supplies higher voltages than those normally used in digital circuits. Once programmed, an EPROM can be erased by exposing it to strong ultraviolet light source. EPROMs are easily recognizable by the transparent fused quartz window on the top of the package, through which the silicon chip is visible, and which permits exposure to ultraviolet light during erasing.

In digital logic, an inverter or NOT gate is a logic gate which implements logical negation. The truth table is shown on the right.
Transconductance, also infrequently called mutual conductance, is the electrical characteristic relating the current through the output of a device to the voltage across the input of a device. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance.
In semiconductor manufacturing, silicon on insulator (SOI) technology is fabrication of silicon semiconductor devices in a layered silicon–insulator–silicon substrate, to reduce parasitic capacitance within the device, thereby improving performance. SOI-based devices differ from conventional silicon-built devices in that the silicon junction is above an electrical insulator, typically silicon dioxide or sapphire. The choice of insulator depends largely on intended application, with sapphire being used for high-performance radio frequency (RF) and radiation-sensitive applications, and silicon dioxide for diminished short-channel effects in other microelectronics devices. The insulating layer and topmost silicon layer also vary widely with application.
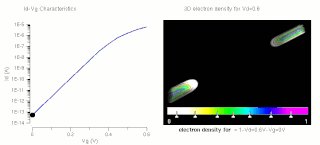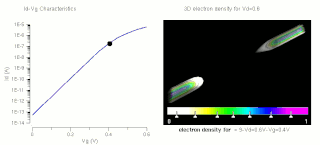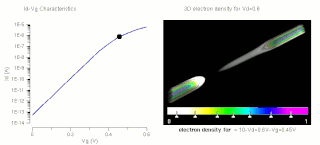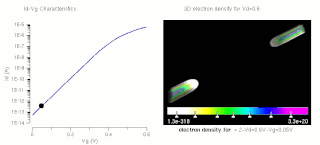
The threshold voltage, commonly abbreviated as Vth, of a field-effect transistor (FET) is the minimum gate-to-source voltage VGS (th) that is needed to create a conducting path between the source and drain terminals. It is an important scaling factor to maintain power efficiency.

An organic field-effect transistor (OFET) is a field-effect transistor using an organic semiconductor in its channel. OFETs can be prepared either by vacuum evaporation of small molecules, by solution-casting of polymers or small molecules, or by mechanical transfer of a peeled single-crystalline organic layer onto a substrate. These devices have been developed to realize low-cost, large-area electronic products and biodegradable electronics. OFETs have been fabricated with various device geometries. The most commonly used device geometry is bottom gate with top drain and source electrodes, because this geometry is similar to the thin-film silicon transistor (TFT) using thermally grown SiO2 as gate dielectric. Organic polymers, such as poly(methyl-methacrylate) (PMMA), can also be used as dielectric.. One of the benefits of OFETs, especially compared with inorganic TFTs, is their unprecedented physical flexibility, which leads to biocompatible applications, for instance in the future health care industry of personalized biomedicines and bioelectronics.
A linear integrated circuit or analog chip is a set of miniature electronic analog circuits formed on a single piece of semiconductor material.

Integrated injection logic (IIL, I2L, or I2L) is a class of digital circuits built with multiple collector bipolar junction transistors (BJT). When introduced it had speed comparable to TTL yet was almost as low power as CMOS, making it ideal for use in VLSI (and larger) integrated circuits. The gates can be made smaller with this logic family than with CMOS because complementary transistors are not needed. Although the logic voltage levels are very close (High: 0.7V, Low: 0.2V), I2L has high noise immunity because it operates by current instead of voltage. I2L was developed in 1971 by Siegfried K. Wiedmann and Horst H. Berger who originally called it merged-transistor logic (MTL). A disadvantage of this logic family is that the gates draw power when not switching unlike with CMOS.
The floating-gate MOSFET (FGMOS), also known as a floating-gate MOS transistor or floating-gate transistor, is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) where the gate is electrically isolated, creating a floating node in direct current, and a number of secondary gates or inputs are deposited above the floating gate (FG) and are electrically isolated from it. These inputs are only capacitively connected to the FG. Since the FG is completely surrounded by highly resistive material, the charge contained in it remains unchanged for long periods of time. Usually Fowler-Nordheim tunneling and hot-carrier injection mechanisms are used to modify the amount of charge stored in the FG.

A multigate device, multi-gate MOSFET or multi-gate field-effect transistor (MuGFET) refers to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) that incorporates more than one gate into a single device. The multiple gates may be controlled by a single gate electrode, wherein the multiple gate surfaces act electrically as a single gate, or by independent gate electrodes. A multigate device employing independent gate electrodes is sometimes called a multiple-independent-gate field-effect transistor (MIGFET). The most widely used multi-gate devices are the FinFET and the GAAFET, which are non-planar transistors, or 3D transistors.
LDMOS is a planar double-diffused MOSFET used in amplifiers, including microwave power amplifiers, RF power amplifiers and audio power amplifiers. These transistors are often fabricated on p/p+ silicon epitaxial layers. The fabrication of LDMOS devices mostly involves various ion-implantation and subsequent annealing cycles. As an example, The drift region of this power MOSFET is fabricated using up to three ion implantation sequences in order to achieve the appropriate doping profile needed to withstand high electric fields.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to electronics:

The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor which uses an electric field to control the flow of current. FETs are devices with three terminals: source, gate, and drain. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source.
A transmission gate (TG) is an analog gate similar to a relay that can conduct in both directions or block by a control signal with almost any voltage potential. It is a CMOS-based switch, in which PMOS passes a strong 1 but poor 0, and NMOS passes strong 0 but poor 1. Both PMOS and NMOS work simultaneously.

The memory cell is the fundamental building block of computer memory. The memory cell is an electronic circuit that stores one bit of binary information and it must be set to store a logic 1 and reset to store a logic 0. Its value is maintained/stored until it is changed by the set/reset process. The value in the memory cell can be accessed by reading it.

A field-effect transistor-based biosensor, also known as a biosensor field-effect transistor, field-effect biosensor (FEB), or biosensor MOSFET, is a field-effect transistor that is gated by changes in the surface potential induced by the binding of molecules. When charged molecules, such as biomolecules, bind to the FET gate, which is usually a dielectric material, they can change the charge distribution of the underlying semiconductor material resulting in a change in conductance of the FET channel. A Bio-FET consists of two main compartments: one is the biological recognition element and the other is the field-effect transistor. The BioFET structure is largely based on the ion-sensitive field-effect transistor (ISFET), a type of metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) where the metal gate is replaced by an ion-sensitive membrane, electrolyte solution and reference electrode.
References
- Freescale upends thinking on transistor channels (EE Times, December 5, 2005)
| This electronics-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |