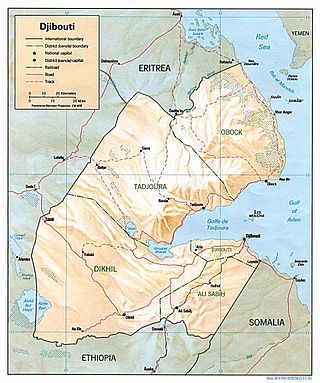
Djibouti is a country in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. To the east is its coastline on the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. Rainfall is sparse, and most of the territory has a semi-arid to arid environment. Lake Assal is a saline lake which lies 155 m (509 ft) below sea level, making it the lowest point on land in Africa and the third-lowest point on Earth after the Sea of Galilee and the Dead Sea. Djibouti has the fifth smallest population in Africa. Djibouti's major settlements include the capital Djibouti City, the port towns of Tadjoura and Obock, and the southern cities of Ali Sabieh and Dikhil. It is the forty-six country by area in Africa and 147st largest country in the world by land area, covering a total of 23,200 km2 (9,000 sq mi), of which 23,180 km2 (8,950 sq mi) is land and 20 km2 (7.7 sq mi) is water.

The Gulf of Aden is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, the Socotra Archipelago, Puntland in Somalia and Somaliland to the south. In the northwest, it connects with the Red Sea through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, and it connects with the Arabian Sea to the east. To the west, it narrows into the Gulf of Tadjoura in Djibouti. The Aden Ridge lies along the middle of the gulf, and tectonic activity at the ridge is causing the gulf to widen by about 15 mm (0.59 in) per year.

The Bab-el-Mandeb, the Gate of Grief or the Gate of Tears, is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden and by extension the Indian Ocean.

The Obock Region is a region in northern Djibouti. It has a land area of 4,700 square kilometres, and had a population of 37,856 in 2009. It lies along the Red Sea, Bab-el-Mandeb, Gulf of Aden, Gulf of Tadjoura and includes the Seven Brothers, Doumeira Islands and the coastal city of Obock. It lies along a portion of the national border with Eritrea. In total area, it is larger than Cape Verde and smaller than Trinidad and Tobago. The topography of the region has highland and coastal plains.

Djibouti is the capital of Djibouti. It is located in the coastal Djibouti Region on the Gulf of Tadjoura.
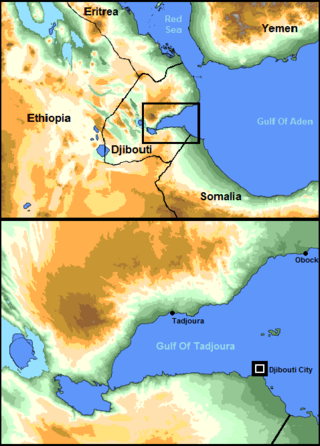
The Gulf of Tadjoura is a gulf or basin of the Indian Ocean in the Horn of Africa. It lies south of the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb, or the entrance to the Red Sea, at 11.7°N 43.0°E. The gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive coral reefs, and abundant pearl oysters. Most of its coastline is the territory of Djibouti, except for a short stretch on the southern shore, which is part of the territory of Somaliland.
Arta, ARTA, or Artà may refer to:
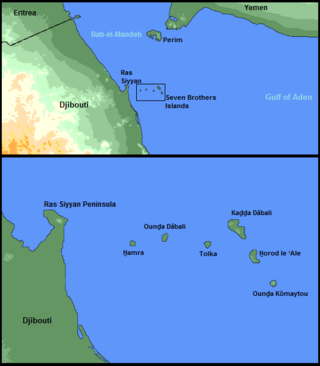
The Seven Brothers Islands, also known as the Sawabi Islands or Seba Islands, is an archipelago in the Dact-el-Mayun section of the Bab-el-Mandeb strait. They are within the Obock sub-prefecture of Djibouti, and are a notable diving site. Even in English publications, the group is often called by its French name, îles des Sept Frères.

The Bab Iskender (Arabic: باب اسكندر Iskander's Strait, also variously known as the Eastern strait, the small strait, the narrow pass or the small pass, is the eastern section of the Bab-el-Mandeb straits, which separates Ras Menheli, Yemen, on the Arabian Peninsula from Ras Siyyan, Djibouti, on the Horn of Africa. The strait is 2 miles wide and 16 fathoms deep. The Yemeni island of Perim divides the strait into two channels, Bab Iskender and Dact-el-Mayun respectively.
The wildlife of Djibouti, consisting of its flora and fauna, is in a harsh landscape with forest accounting for less than one percent of its area. Most species are found in the northern part of the country in the Day Forest National Park at an average elevation of 1,500 metres (4,900 ft), including the massif Goda, with a peak of 1,783 metres (5,850 ft). It covers an area of 3.5 square kilometres (1.4 sq mi) of Juniperus procera forest, with many of the trees rising to 20 metres (66 ft) height. This forest area is the main habitat of the critically endangered and endemic Djibouti spurfowl, and another recently noted vertebrate, Platyceps afarensis. The area also contains many species of woody and herbaceous plants, including boxwood and olive trees, which account for sixty percent of the identified species in the country.
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. The remainder of the border is formed by the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. The main police force is the Djibouti national police and Djiboutian National Gendarmerie

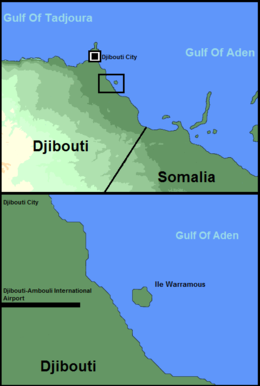
Moucha Island is a small coral island off the coast of Djibouti. It is located at the center of the Gulf of Tadjoura. The island is part of the Djibouti Region; the island has a total population of about 20 inhabitants, which increases considerably during the summer.

Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area of 23,200 km2 (8,958 sq mi).

Tourism in Djibouti is one of the growing economic sectors of the country and is an industry that generates 53,000 and 73,000 arrivals per year, with its favorable beaches and climate and also including islands and beaches in the Gulf of Tadjoura and the Bab al-Mandab. The main tourist activities are scuba diving, fishing, trekking and hiking, discovering the nomadic way, bird watching, and sun, sea and sand.

The Maskali Islands are located off the coast of Djibouti in the Gulf of Tadjoura. The islands are part of the Djibouti Region.

Kaḏḏa Dâbali Island, often called Big Island, is an uninhabited rocky island off the coast of Obock Region of Djibouti in the Bab-el-Mandeb strait. It is the largest one of the Seven Brothers Islands.

The Persian shearwater is a seabird in the family Procellariidae formerly lumped in with Audubon's shearwater.
Djibouti–Japan relations are bilateral relations between Djibouti and Japan. Djibouti has maintained an embassy in Tokyo since 1989, whilst Japan has maintained an embassy in Djibouti City since 2009.

Somalia's coastline consists of the Gulf of Aden to the north, the Guardafui Channel to the northeast and the Indian Ocean to the east. The total length of the coastline is approximately 3333 km, giving the country the longest coastline on mainland Africa. The country has second-longest coastline in all of Africa, behind the island nation of Madagascar.