USS Nonsuch was a moderately successful privateer built in 1812 and then an armed schooner in the United States Navy during the War of 1812. She was sold for breaking up in 1826.

Reaper was a Massachusetts privateer schooner that Captain Ephraim Sturdivant commanded during the War of 1812. Captain Sturdivant was officially charged by President James Madison to use the ship to attack British shipping. There is no evidence that she captured any British vessels.
HMS Pictou was a 14-gun schooner that the Royal Navy captured in 1813. She served briefly on the Royal Navy's North American station, capturing one or two merchantmen before the American frigate USS Constitution captured her during the War of 1812.
HMS Anaconda was an 18-gun brig-sloop of the Royal Navy during the War of 1812. She was cruising as an American privateer until sailors from HMS Sceptre captured her in 1813. She served briefly in the Royal Navy during the later stages of the War of 1812, especially at the Battle of New Orleans, before being sold in Jamaica in 1815.

USS Enterprise vs Flambeau was a single ship action fought in October 1800 during the Quasi-War, and the final battle between French and American forces. During the action, USS Enterprise defeated the French brig Flambeau off the leeward side of the island of Dominica in the Caribbean Sea. Although Enterprise was outgunned by Flambeau, she was still able to take her as a prize after a short battle. The battle helped bring to fame Enterprise's commanding officer, John Shaw, who added the capture of Flambeau to his already long list of French prizes.

HMS Peruvian was an 18-gun Cruizer-class brig-sloop launched in 1808 at Parson's Yard, Warsash, England. She was the first naval vessel built at that yard. Peruvian captured two American privateers and participated in an expedition up the Penobscot River during the War of 1812. Then she claimed Ascension Island for Great Britain in 1815. She was broken up in 1830.

HMS Charybdis was a Royal Navy Cruizer-class brig-sloop built by Mark Richards and John Davidson at Hythe, and launched in 1809. She captured two American prizes during the War of 1812 before she was laid up in 1815 and sold in 1819. She apparently then became the whaler Greenwich, which made three voyages for Samuel Enderby & Sons and one for Daniel Bennett & Son. She was wrecked in the Seychelles in 1833 on her fourth whaling voyage.
HMS Whiting was a Royal Navy Ballahoo-class schooner of four 12-pounder carronades and a crew of 20. The prime contractor for the vessel was Goodrich & Co., in Bermuda, and she was launched in 1805. She was a participant at the Battle of Basque Roads. A French privateer captured her at the beginning of the War of 1812, shortly after the Americans had captured and released her in the first naval incident of the war.
HMS Paz was a Spanish naval schooner that the British Royal Navy captured at Monte Video on 3 February 1807. She served on the River Plate, North Sea, and North American Stations, where she captured numerous privateers and merchant vessels. The Navy sold her in 1816.
HMS Magnet was an American brig captured in 1812. HMS Magnet served during the War of 1812 as a prison ship at Halifax, Nova Scotia. The Royal Navy eventually renamed her Attentive, possibly in 1814 when the Navy acquired Sir Sydney Smith, which it renamed Magnet. Then as Attentive she served as a store ship, still apparently on the Halifax station, before she sailed to Britain in 1816. She was broken up in January 1817.

HMS Doterel, was an 18-gun Cruizer-class brig-sloop of the British Royal Navy. Launched on 6 October 1808, she saw action in the Napoleonic Wars and in the War of 1812. In February 1809 she took part in the Battle of Les Sables-d'Olonne, then in April the Battle of Basque Roads. She was laid up in 1827 at Bermuda, but not broken up until 1855.
Tartar was an unsuccessful American privateer schooner during the War of 1812. She was launched in 1813 and was driven ashore and destroyed on her maiden voyage at the end of the year, not having captured anything.
At least six vessels, including two belonging to the British Royal Navy, have borne the name Little Belt, a translation from the Danish of Lillebælt, the name of the strait that separates Funen from the Danish mainland and that links the Kattegat to the Baltic Sea. The merchant vessels and the second Royal Navy vessel were named to commemorate HMS Little Belt, which was one of the protagonists in the Little Belt affair, or perhaps the affair itself.
Albion was launched at Topsham, Devon, in 1800. She spent most of her career sailing between London and Jamaica. After 1814 she held a license from the British East India Company to trade with India, but she does not appear to have availed herself of the option. In 1814 the American privateer Brutus captured Albion, but the British recaptured her within a few days. She was condemned at Charleston, South Carolina, and broken up in 1816.
HMS Plumper was launched in 1807. She captured three small American privateers early in the War of 1812 but was wrecked in December 1812.
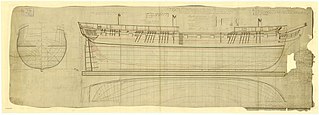
HMS Barrosa was launched in 1812 for the Royal Navy and served during the War of 1812 during which she captured several prices. After the war she spent a decade or so (1823–1833) on harbour duties. The navy sold Barrosa in 1841.
HMS Racer was the American schooner Independence, launched in 1811 in New York, that the British Royal Navy captured in 1812 and took into service. She was wrecked in the Florida Straits on 10 October 1814.
Several vessels have been named Morning Star for the Morning Star:
HMS Redbridge was the French schooner Aristotle, built in America. The Royal Navy took her into service as HMS Redbridge in 1807 and renamed her HMS Variable in 1808. She was sold in 1814.
Sarah Ann was a United States privateer commissioned at Baltimore in 1812. She captured a British merchantman in a single-ship action before HMS Rhodian captured Sarah Ann on 16 September 1812.



