Commission or commissioning may refer to:
Development or developing may refer to:
Seismic risk refers to the risk of damage from earthquake to a building, system, or other entity. Seismic risk has been defined, for most management purposes, as the potential economic, social and environmental consequences of hazardous events that may occur in a specified period of time. A building located in a region of high seismic hazard is at lower risk if it is built to sound seismic engineering principles. On the other hand, a building located in a region with a history of minor seismicity, in a brick building located on fill subject to liquefaction can be as high or higher risk.
Program management or programme management is the process of managing several related projects, often with the intention of improving an organization's performance. In practice and in its aims, program management is often closely related to systems engineering, industrial engineering, change management, and business transformation. In the defense sector, it is the dominant approach to managing very large projects. Because major defense programs entail working with contractors, it is often called acquisition management, indicating that the government buyer acquires goods and services by means of contractors.
Global means of or referring to a globe and may also refer to:
The Environment Agency (EA) is a non-departmental public body, established in 1995 and sponsored by the United Kingdom government's Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA), with responsibilities relating to the protection and enhancement of the environment in England.

The Driving Standards Agency (DSA) was an executive agency of the UK Department for Transport (DfT).
Enterprise architecture (EA) is the most reputed discipline that: i) defines, organises, standardizes, and documents the whole architecture and all important elements of the respective organisation, covering relevant domains such as business, digital, physical, or organisational; and ii) the relations and interactions between elements that belong to those domains, such as processes, functions, applications, events, data, or technologies.

Business process re-engineering (BPR) is a business management strategy, originally pioneered in the early 1990s, focusing on the analysis and design of workflows and business processes within an organization. BPR aimed to help organizations fundamentally rethink how they do their work in order to improve customer service, cut operational costs, and become world-class competitors.
Lean government refers to the application of lean production principles and methods to both identify and then implement the most efficient, value added way to provide government services. Government agencies have found that when Lean is implemented, they see an improved understanding of how their own processes work, that it facilitates the quick identification and implementation of improvements and that it builds a culture of continuous improvement.
Reconstruction may refer to:
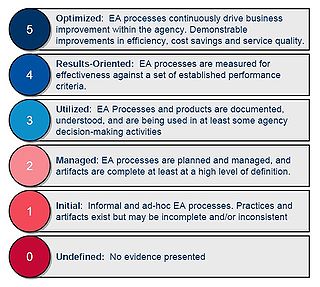
The Enterprise Architecture Assessment Framework (EAAF) is created by the US Federal government Office of Management and Budget (OMB) to allow federal agencies to assess and report their enterprise architecture activity and maturity, and to advance the use of enterprise architecture in the federal government.
Business process management (BPM) is the discipline in which people use various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and automate business processes. Any combination of methods used to manage a company's business processes is BPM. Processes can be structured and repeatable or unstructured and variable. Though not required, enabling technologies are often used with BPM.

The IBM Center for The Business of Government is an independent business think tank that focuses on management issues in the U.S. Federal government. Founded in 2002, the Center is located in Washington, D.C.
Improvement is the process of a thing moving from one state to a state considered to be better, usually through some action intended to bring about that better state. The concept of improvement is important to governments and businesses, as well as to individuals.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.



