
Gornji Vakuf-Uskoplje is a town and municipality located in Central Bosnia Canton of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, an entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina.

The 7th Muslim Brigade was an elite all-volunteer brigade of the 3rd Corps of the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It served as the ARBiH's primary assault brigade in Central Bosnia, and was headquartered in Zenica. The brigade's manpower largely came from the cities of Zenica, Travnik, and Kakanj; however, there were soldiers from all over Bosnia who served in its ranks. During the war, the brigade liberated over 1,100 km2 of territory, including multiple cities, as well as numerous villages and mountains. Some of the most notable combat actions of the 7th Muslim brigade include the liberation of Vareš, Fojnica, Bugojno, Kakanj, and Travnik from the hands of HVO forces, as well as the defence of Mt. Igman and the liberation of liberation of Mt. Vlašić (Opaljenik), Teslić-Šerić (Jezera), Nabožić (Ilijaš), and Vozuća and the Ozren pocket from VRS forces.
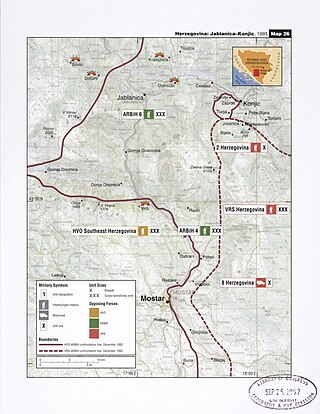
Operation Neretva '93 was an Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) operation against the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) in September 1993 on a 200 km long front from Gornji Vakuf to south of Mostar, one of its largest of the year, during the Croat–Bosniak War. The ARBiH made limited gains in the area of northern Herzegovina and around Mostar, but did not achieve a breakthrough to the southern Neretva, where the HVO retained control. The operation was halted in October. During the operation, dozens of Croat civilians were killed in the Grabovica and Uzdol massacres.

The Bosnian offensive on Sarajevo in 1995 was a military offensive executed by Bosnian Muslim forces (ARBiH) against Serb forces (VRS) in an attempt to break the Siege of Sarajevo during the Bosnian War. The Bosnian Muslim forces were superior in manpower, but not in heavy weapons, key items for Trench Warfare. This lack of weapons eventually led to commander Rasim Delić to stop the offensive due to heavy losses.

Operation Shield 94 refers to the offensive in Western Bosnia from the 4 November to 20 November 1994, the key goal was to fully destroy the 5th Corps, and to recapture lands lost during Operation Grmeć 94. It resulted in a decisive Serbian victory.

The Attack on Teslić was an attempt by the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) to take Teslić and the surrounding settlements from the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) in October 1994 during the Bosnian War. All attacks on the city were successfully defended by the VRS. After the signing of the Washington Agreement in late march 1994, which ended the Croat-Bosniak War in the Tešanj-Maglaj enclave, the ARBiH saved significant forces that were on the front lines against the 111th Croatian Defence Council (HVO) brigade from Žepče and transferred them to the Serb front line towards Teslić.

The Operation Autumn '94, also called the Second Mitrovdan offensive was an operation carried out by the ARBiH against the VRS during the Bosnian War, with the goal of taking control over Podvelež and Velež, south-east of Mostar.
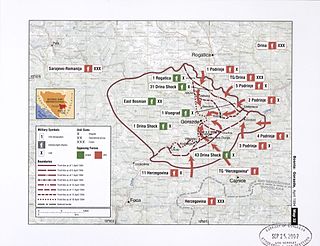
Operation Star 94 is the code name for the operation of the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) in the spring of 1994, in Gornje Podrinje. The goal of the operation was to force the political leadership of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina to negotiate the signing of an armistice by capturing Goražde.

The Battle of Azići was one of the battles in the Siege of Sarajevo in 1993. The VRS made its first step in the operation in the suburbs in early December 1992, breaking through the suburb of Otes, some 15 kilometers west of central Sarajevo. In the middle of February, the Sarajevo-Romanijan Corps started the second part of the campaign, attacked Aziće, the troops of the 1st Ilidžan Infantry Brigade attacked with support tanks and armored personnel carriers of the 1st Sarajevo Mechanized Brigade.

Operation Brana 94 was the name of the operation of the joint forces of the 3rd Corps of the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH), which began on June 1, 1994, from the direction of Zavidović and with shorter interruptions that lasted until 5 July 1994. In the end, the Serbs, with far fewer soldiers, managed to defend Vozuća.

The Brčko offensive was a response by the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) to expand the Corridor near Brčko due to many Croatian Defence Council (HVO) attacks. The HVO forces from the settlement south of Brčko and Orašje aimed to cut off the corridor. At the end of 1992, the focus of the fighting in the Posavina Corridor shifted to its narrowest sector near Brčko. The Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) and HVO forces, including units from Orašje, launched several attacks that temporarily cut off the corridor northwest of Brčko. The Army of Republika Srpska retaliated with an attack to widen the corridor, succeeding in doing so.
The Battle of Foča took place from April 8 to 17 in 1992, when Bosnian Serbs and Serb volunteers from Montenegro invaded Foča and fought with the Territorial Defence Force of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (TORBIH). It was the site of one of the first battles in this war, along with the Siege of Sarajevo, Operation Višegrad, the Battle of Zvornik and the Battle of Kupres.

The Offensive on Teslić (1994) was the initial assault by the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) on the town of Teslić during the Bosnian War.

The Treskavica Front was a crucial zone for the Siege of Sarajevo during the Bosnian War. In mid-July 1995, the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) started a series of offensives on the Treskavica mountain range, causing heavy fighting. The Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) initially had success in pushing back Bosnian Serb troops at various times, but it always resulted in counter-offensives by the Army of Republika Srpska.
Operation Bosanska Krajina was the code name of the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) offensive during the Bosnian War which aimed to capture the municipalities of Prijedor, Sanski Most and Ključ. The offensive was also the response of the VRS to the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) attack on the city of Prijedor. The operation ended with the victory of the VRS and the beginning of the siege of Bihać.

The attack on Stolice was an attempt by the ARBiH to control the positions of the VRS on Mountain Majevica. At first, the ARBiH suppressed the VRS, and a week later, the ARBiH attacked the VRS positions again, with which the VRS retaliated with a counterattack up to the top of Velika Jelica and returned part of the southern territory. The defense of Stolica and Banj brdo was carried out by the East Bosnian Corps of the Army of Republika Srpska.

The Battle of Grbavica was one of the many battles fought between the VRS and the ARBiH in the siege of Sarajevo. The year 1993 was the most difficult year for Grbavica, she was constantly attacked. Until the end of the war, Grbavica remained part of Republika Srpska, but was later given to the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina by the Dayton Agreement.
Ledenice offensive was Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) attack to break the defense of the 107th Cavalry Motorized Brigade near Gradačac and to put pressure on the ARBiH.

The Mala Kladuša offensive were series of fighting between the NOZB and ARBiH to recapture villages east of Velika Kladuša. This offensive was after the successful Operation Spider, in which the Autonomous Province of Western Bosnia was re-established. The goal was to eliminate the 5th Corps from the Mala Kladuša-Podzvizd region.

The Operation Sword–1 was first phase of a bigger operation called "Sword 95" during the 1995 Bosnian War and Inter-Bosnian Muslim War. The goal of Sword 1 was to make APZB double in size and to return its largest village Šturlić. And after that to be declared a republic. The goal of Sword 2 was to occupy Cazin because it was in the middle of the Bihać enclave, and that would put a lot of pressure on 5th Corps. But due to operation Storm, this phase did not start.

















