Related Research Articles

Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is most often used by the government of a single country to measure its economic health. Due to its complex and subjective nature, this measure is often revised before being considered a reliable indicator.

In economics, the Gini coefficient, also known as the Gini index or Gini ratio, is a measure of statistical dispersion intended to represent the income inequality, the wealth inequality, or the consumption inequality within a nation or a social group. It was developed by Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini.
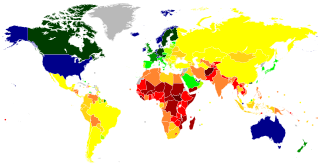
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
A variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region, including gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), net national income (NNI), and adjusted national income. All are specially concerned with counting the total amount of goods and services produced within the economy and by various sectors. The boundary is usually defined by geography or citizenship, and it is also defined as the total income of the nation and also restrict the goods and services that are counted. For instance, some measures count only goods & services that are exchanged for money, excluding bartered goods, while other measures may attempt to include bartered goods by imputing monetary values to them.
The Human Poverty Index (HPI) was an indication of the poverty of community in a country, developed by the United Nations to complement the Human Development Index (HDI) and was first reported as part of the Human Development Report in 1997. It is developed by United Nations Development Program which also publishes indexes like HDI It was considered to better reflect the extent of deprivation in deprived countries compared to the HDI. In 2010, it was supplanted by the UN's Multidimensional Poverty Index.
The Carstairs index is an index of deprivation used in spatial epidemiology to identify Socio-economic confounding.
The Indices of deprivation 2004 is a deprivation index at the small area level, created by the British Department for Communities and Local Government(DCLG).
The Gender Development Index (GDI) is an index designed to measure gender equality.
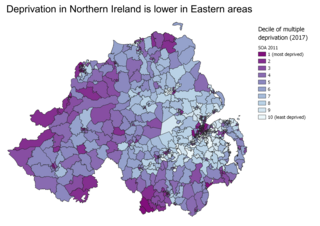
Indices of multiple deprivation (IMD) are widely-used datasets within the UK to classify the relative deprivation of small areas. Multiple components of deprivation are weighted with different strengths and compiled into a single score of deprivation.
The Indices of deprivation 2007 is a deprivation index at the small area level, created by the British Department for Communities and Local Government (DCLG) and released on 12 June 2007. It follows the Indices of deprivation 2004 (ID2004) and because much of the datasets are the same or similar between indices, it allows for a comparison of 'relative deprivation' of an area between the two indices. Deprivation Index=H-Value/H-L

The Child Development Index (CDI) is an index combining performance measures specific to children—education, health and nutrition—to produce a score on a scale of 0 to 100. A zero score would be the best. The higher the score, the worse children are faring.
The Scottish index of multiple deprivation (SIMD) is a statistical tool used by local authorities, the Scottish government, the NHS and other government bodies in Scotland to support policy and decision making. It won the Royal Statistical Society's Excellence in Official Statistics Awards in 2017.
Contextual value added (CVA) is a statistic that was used by the government of the United Kingdom to assess the performance of schools. It was superseded by expected progress and then Progress 8
The Families and Children Study (FACS) is a longitudinal study collecting information about families with dependent children in Great Britain, managed by the Department for Work and Pensions (DWP).

Multidimensional Poverty Indices use a range of indicators to calculate a summary poverty figure for a given population, in which a larger figure indicates a higher level of poverty. This figure considers both the proportion of the population that is deemed poor, and the 'breadth' of poverty experienced by these 'poor' households, following the Alkire & Foster 'counting method'. The method was developed following increased criticism of monetary and consumption based poverty measures, seeking to capture the deprivations in non-monetary factors that contribute towards well-being. While there is a standard set of indicators, dimensions, cutoffs and thresholds used for a 'Global MPI', the method is flexible and there are many examples of poverty studies that modify it to best suit their environment. The methodology has been mainly, but not exclusively, applied to developing countries.

The Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI) is an economic research centre within the Oxford Department of International Development at the University of Oxford, England, that was established in 2007.
The OECD Better Life Index, created in May 2011 by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, is an initiative pioneering the development of economic indicators which better capture multiple dimensions of economic and social progress.

The Gender Inequality Index (GII) is an index for the measurement of gender disparity that was introduced in the 2010 Human Development Report 20th anniversary edition by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). According to the UNDP, this index is a composite measure to quantify the loss of achievement within a country due to gender inequality. It uses three dimensions to measure opportunity cost: reproductive health, empowerment, and labor market participation. The new index was introduced as an experimental measure to remedy the shortcomings of the previous indicators, the Gender Development Index (GDI) and the Gender Empowerment Measure (GEM), both of which were introduced in the 1995 Human Development Report.
The Townsend index is a measure of material deprivation within a population. It was first described by sociologist Peter Townsend in 1988.