Bromine is a chemical element with symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest halogen, and is a fuming red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured gas. Its properties are thus intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος ("stench"), referencing its sharp and disagreeable smell.

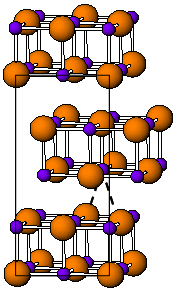
Potassium bromide (KBr) is a salt, widely used as an anticonvulsant and a sedative in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with over-the-counter use extending to 1975 in the US. Its action is due to the bromide ion. Potassium bromide is used as a veterinary drug, as an antiepileptic medication for dogs.

Sodium bromide is an inorganic compound with the formula NaBr. It is a high-melting white, crystalline solid that resembles sodium chloride. It is a widely used source of the bromide ion and has many applications.

The Barbier reaction is an organometallic reaction between an alkyl halide, a carbonyl group and a metal. The reaction can be performed using magnesium, aluminium, zinc, indium, tin, samarium, barium or their salts. The reaction product is a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol. The reaction is similar to the Grignard reaction but the crucial difference is that the organometallic species in the Barbier reaction is generated in situ, whereas a Grignard reagent is prepared separately before addition of the carbonyl compound. Unlike many Grignard reagents, the organometallic species generated in a Barbier reaction are unstable, necessitating their immediate usage. Barbier reactions are nucleophilic addition reactions that involve relatively inexpensive, water insensitive metals or metal compounds. For this reason it is possible in many cases to run the reaction in water, making the procedure part of green chemistry. In contrast, Grignard reagents and organolithium reagents are highly moisture sensitive and must be used under an inert atmosphere without the presence of water. The Barbier reaction is named after Victor Grignard's teacher Philippe Barbier.

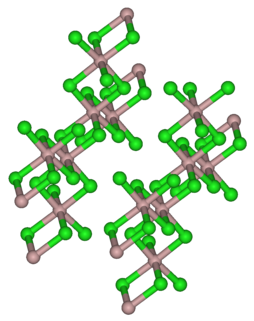
Iron(III) bromide is the chemical compound with the formula FeBr3. Also known as ferric bromide, this red-brown odorless compound is used as a Lewis acid catalyst in the halogenation of aromatic compounds. It dissolves in water to give acidic solutions.
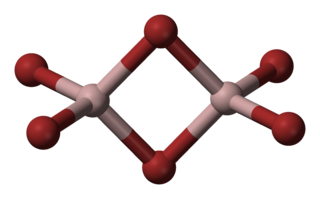
Aluminium bromide is any chemical compound with the empirical formula AlBrx. Aluminium tribromide is the most common form of aluminium bromide. It is a colorless, sublimable hygroscopic solid; hence old samples tend to be hydrated, mostly as aluminium tribromide hexahydrate (AlBr3·6H2O).

Lithium bromide (LiBr) is a chemical compound of lithium and bromine. Its extreme hygroscopic character makes LiBr useful as a desiccant in certain air conditioning systems.

Zinc bromide (ZnBr2) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ZnBr2. It is a colourless salt that shares many properties with zinc chloride (ZnCl2), namely a high solubility in water forming acidic solutions, and solubility in organic solvents. It is hygroscopic and forms a dihydrate ZnBr2 · 2H2O.

Aluminium iodide is any chemical compound containing only aluminium and iodine. Invariably, the name refers to a compound of the composition AlI
3, formed by the reaction of aluminium and iodine or the action of HI on Al metal. The hexahydrate is obtained from a reaction between metallic aluminum or aluminum hydroxide with hydrogen iodide or hydroiodic acid. Like the related chloride and bromide, AlI
3 is a strong Lewis acid and will absorb water from the atmosphere. It is employed as a reagent for the scission of certain kinds of C-O and N-O bonds. It cleaves aryl ethers and deoxygenates epoxides.

Gold(III) bromide is a dark-red to black crystalline solid. It has the empirical formula AuBr3, but exists primarily as a dimer with the molecular formula Au2Br6 in which two gold atoms are bridged by two bromine atoms. It is commonly referred to as gold(III) bromide, gold tribromide, and rarely but traditionally auric bromide, and sometimes as digold hexabromide. As is similar with the other gold halides, this compound is unique for being a coordination complex of a group 11 transition metal that is stable in an oxidation state of three whereas copper or silver complexes persist in oxidation states of one or two.

Gallium(III) bromide (GaBr3) is a chemical compound, and one of four Gallium trihalides.
The thallium halides include monohalides, where thallium has oxidation state +1, trihalides where thallium generally has oxidation state +3 and some intermediate halides with mixed +1 and +3 oxidation states. These materials find use in specialized optical settings, such as focusing elements in research spectrophotometers. Compared to the more common zinc selenide-based optics, materials such as thallium bromoiodide enable transmission at longer wavelengths. In the infrared, this allows for measurements as low as 350 cm−1 (28 µm), whereas zinc selenide is opaque by 21.5 µm and ZnSe optics are generally only usable to 650 cm−1 (15 µm).
There are three sets of indium halides, the trihalides, the monohalides, and several intermediate halides.
In the monohalides the oxidation state of indium is +1 and their proper names are indium(I) fluoride, indium(I) chloride, indium(I) bromide and indium(I) iodide.
Barium bromide is the chemical compound with the formula BaBr2. Like barium chloride, it dissolves well in water and is toxic in aqueous solution.

Cobalt(II) bromide (CoBr2) is an inorganic compound. In its anhydrous form, it is a green solid that is soluble in water, used primarily as a catalyst in some processes.

Mercury(II) bromide or mercuric bromide is the chemical compound composed of mercury and bromine with the formula HgBr2. This white crystalline solid is a laboratory reagent. Like mercury(II) chloride, it is extremely toxic.

Diphenylzinc is an organozinc compound. It is commonly used as the synthetic equivalent of a Ph− synthon. Solvent-free diphenylzinc exists as dimeric PhZn(μ-Ph)2ZnPh molecules in solid state.