Indo-Aryan refers to:
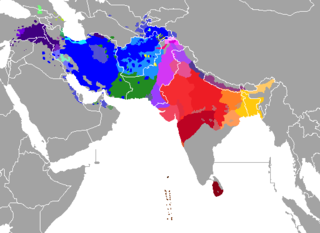
The Indo-Iranian languages constitute the largest and southeasternmost extant branch of the Indo-European language family. They include over 300 languages, spoken by around 1.5 billion speakers, predominantly in South Asia, West Asia and parts of Central Asia.
The Aryan race is a pseudoscientific historical race concept that emerged in the late-19th century to describe people who descend from the Proto-Indo-Europeans as a racial grouping. The terminology derives from the historical usage of Aryan, used by modern Indo-Iranians as an epithet of "noble". Anthropological, historical, and archaeological evidence does not support the validity of this concept.
Marathi may refer to:

The Indo-Aryan languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated east of the Indus river in Bangladesh, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and Nepal. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages.
Indian Languages may refer to:
Gujarati may refer to:
Indo-Iranian may refer to:

Bundeli or Bundelkhandi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Bundelkhand region of central India. It belongs to the Central Indo-Aryan languages and is part of the Western Hindi subgroup.

The Dardic languages, or Hindu-Kush Indo-Aryan languages, are a group of several Indo-Aryan languages spoken in northern Pakistan, northwestern India and parts of northeastern Afghanistan. This region has sometimes been referred to as Dardistan.
The term Aryan language appears in works published in the 19th century and 20th century to mean very old Indo-European languages:

Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryans were the Indo-Iranian speaking pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and introduced the Proto-Indo-Aryan language. The early Indo-Aryan peoples were known to be closely related and belonging to the same Indo-Iranian group that have resided north of the Indus River; an evident connection in cultural, linguistic, and historical ties. Today, Indo-Aryan speakers are found south of the Indus, across the modern-day regions of Bangladesh, Nepal, eastern-Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and northern-India.
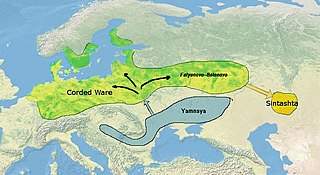
The Indo-Iranian peoples, also known as Ā́rya or Aryans from their self-designation, were a group of Indo-European speaking peoples who brought the Indo-Iranian languages to major parts of Eurasia in waves from the first part of the 2nd millennium BC onwards. They eventually branched out into the Iranian peoples and Indo-Aryan peoples.
The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages. These are the predominant languages of today's Bangladesh, Maldives, Nepal, North India, Eastern Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
Aryan languages may refer to:
Aryan was a self-designation by Indo-Iranian people.
Indigenous Aryanism, also known as the Indigenous Aryans theory (IAT) and the Out of India theory (OIT), is the conviction that the Aryans are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent, and that the Indo-European languages radiated out from a homeland in India into their present locations. It is a "religio-nationalistic" view on Indian history, and propagated as an alternative to the established migration model, which considers the Pontic–Caspian steppe to be the area of origin of the Indo-European languages.
The phoneme inventory of the Marathi language is similar to that of many other Indo-Aryan languages. An IPA chart of all contrastive sounds in Marathi is provided below.

The Vedic period, or the Vedic age, is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas, was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the end of the urban Indus Valley Civilisation and a second urbanisation, which began in the central Indo-Gangetic Plain c. 600 BCE. The Vedas are liturgical texts which formed the basis of the influential Brahmanical ideology, which developed in the Kuru Kingdom, a tribal union of several Indo-Aryan tribes. The Vedas contain details of life during this period that have been interpreted to be historical and constitute the primary sources for understanding the period. These documents, alongside the corresponding archaeological record, allow for the evolution of the Indo-Aryan and Vedic culture to be traced and inferred.
Aryan, or Arya in Proto-Indo-Iranian, is a term originating from the ethno-cultural self-designation of the Indo-Iranians. It stood in contrast to nearby outsiders, whom they designated as non-Aryan. In ancient India, the term was used by the Indo-Aryan peoples of the Vedic period, both as an endonym and in reference to a region called "Aryavarta", where their culture emerged. Similarly, according to the Avesta, the Iranian peoples used the term to designate themselves as an ethnic group and to refer to a region called "Airyanem Vaejah", which was their mythical homeland. The word stem also forms the etymological source of place names like Alania and Iran.
Kholosi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in two villages in southern Iran that was first described in 2008. At its current status, the language is considered endangered. In 2008, it was only spoken in the neighboring villages of Kholus and Gotav. As it is located on the Iranian Plateau and surrounded by Iranian languages, it draws heavily from them.