Related Research Articles
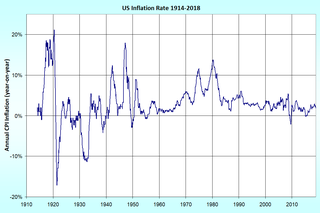
In economics, inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation reflects a reduction in the purchasing power per unit of money – a loss of real value in the medium of exchange and unit of account within the economy. The measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index, usually the consumer price index, over time. The opposite of inflation is deflation.
This aims to be a complete article list of economics topics:
IPI or ipi may refer to:

The Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia, also known as the Philadelphia Fed and the Philly Fed – headquartered at 10 N. Independence Mall West at Arch Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, with an additional entrance at N. 7th Street – is responsible for the Third District of the Federal Reserve, which covers eastern and central Pennsylvania, the nine southern counties of New Jersey, and Delaware. Its geographical territory is by far the smallest in the system, and its population base is the second-smallest. The current President of the Philadelphia Fed is Patrick T. Harker.
Capacity planning is the process of determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands for its products. In the context of capacity planning, design capacity is the maximum amount of work that an organization is capable of completing in a given period. Effective capacity is the maximum amount of work that an organization is capable of completing in a given period due to constraints such as quality problems, delays, material handling, etc.
Capacity utilization or capacity utilisation is the extent to which an enterprise or a nation uses its installed productive capacity. It is the relationship between output that is produced with the installed equipment, and the potential output which could be produced with it, if capacity was fully used.
Economic planning is a mechanism for the allocation of resources between and within organizations which is held in contrast to the market mechanism. As an allocation mechanism for socialism, economic planning replaces factor markets with a direct allocation of resources within a single or interconnected group of socially-owned organizations.
The Conference Board Leading Economic Index is an American economic leading indicator intended to forecast future economic activity. It is calculated by The Conference Board, a non-governmental organization, which determines the value of the index from the values of ten key variables. These variables have historically turned downward before a recession and upward before an expansion.
Industrial production is a measure of output of the industrial sector of the economy. The industrial sector includes manufacturing, mining, and utilities. Although these sectors contribute only a small portion of gross domestic product (GDP), they are highly sensitive to interest rates and consumer demand. This makes industrial production an important tool for forecasting future GDP and economic performance. Industrial production figures are also used by central banks to measure inflation, as high levels of industrial production can lead to uncontrolled levels of consumption and rapid inflation.The Industrial productions came about during the Industrial revolution.
A wind power forecast corresponds to an estimate of the expected production of one or more wind turbines in the near future. By production is often meant available power for wind farm considered. Forecasts can also be expressed in terms of energy, by integrating power production over each time interval.
Construction activity has increased due to recent tax incentives. Romania is becoming an increasingly popular choice for British property investors, according to recent research from Currencies Direct. The latest Global Emerging Markets Index from the foreign exchange company shows that Romania has made the top ten for the first time, reaching number nine. The monthly index is based on the number of foreign exchange transfers undertaken by the firm to emerging market regions for property purchases. According to Currencies Direct, Romania has seen significant increases in house prices in recent years and its interest rate has dropped from a level of 154 per cent in 1997 to 8.9 per cent in 2005.

Industry was 40,5% of China’s gross domestic product (GDP) in 2017. Industry contributed 46.8 percent of GDP in 2010 and occupied 27 percent of the workforce in 2007. As of 2015, the manufacturing industrial sectors contribute 40% of China's GDP. The manufacturing sector produced 44.1 percent of GDP in 2004 and accounted for 11.3 percent of total employment in 2006. China is the world’s leading manufacturer of chemical fertilizers, cement, and steel. Prior to 1978, most output was produced by state-owned enterprises. As a result of the economic reforms that followed, there was a significant increase in production by enterprises sponsored by local governments, especially townships and villages, and, increasingly, by private entrepreneurs and foreign investors, but by 1990 the state sector accounted for about 70 percent of output. By 2002 the share in gross industrial output by state-owned and state-holding industries had decreased with the state-run enterprises themselves accounting for 46 percent of China’s industrial output. In November, 2012 the State Council of the People's Republic of China mandated a "social risk assessment" for all major industrial projects. This requirement followed mass public protests in some locations for planned projects or expansions.
The Survey of Professional Forecasters (SPF) is a quarterly survey of macroeconomic forecasts for the economy of the United States issued by the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia. It is the oldest such survey in the United States.

James Brian Bullard is the chief executive officer and 12th president of the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, positions he has held since 2008. He is currently serving a term that began on March 1, 2016. In 2014, he was named the 7th most influential economist in the world.
The mineral industry of Russia is one of the world's leading mineral industries and accounts for a large percentage of the Commonwealth of Independent States' production of a range of mineral products, including metals, industrial minerals, and mineral fuels. In 2005, Russia ranked among the leading world producers or was a significant producer of a vast range of mineral commodities, including aluminum, arsenic, cement, copper, magnesium compounds and metals, nitrogen, palladium, silicon, nickel and vanadium.
Pakistan ranked as number 43-44 among the countries of the world in nominal GDP, 26th in GDP with purchasing power parity and number 55 in the world in factory output.
The Livingston Survey is a biannual survey about the economy of the United States conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia.
The Greenbook of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors is a book with projections of various economic indicators for the economy of the United States produced by the Federal Reserve Board before each meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee. The projections are referred to as Greenbook projections or Greenbook forecasts. Many of the variables projected coincide with variables covered in the Survey of Professional Forecasters.
References
- ↑ "Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization - G.17". Federal Reserve Bulletin. Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. Retrieved 27 April 2011.
- ↑ "Industrial Production Index". FRED Database. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. Retrieved 27 April 2011.