An information resource may refer to:
- Resource (computer science), any component of limited availability in a computer system
- Web resource, a data source accessible at the World Wide Web
An information resource may refer to:

The Dublin Core, also known as the Dublin Core Metadata Element Set (DCMES), is a set of fifteen "core" elements (properties) for describing resources. This fifteen-element Dublin Core has been formally standardized as ISO 15836, ANSI/NISO Z39.85, and IETF RFC 5013. The Dublin Core Metadata Initiative (DCMI), which formulates the Dublin Core, is a project of the Association for Information Science and Technology (ASIS&T), a non-profit organization. The core properties are part of a larger set of DCMI Metadata Terms. "Dublin Core" is also used as an adjective for Dublin Core metadata, a style of metadata that draws on multiple Resource Description Framework (RDF) vocabularies, packaged and constrained in Dublin Core application profiles.
File or filing may refer to:
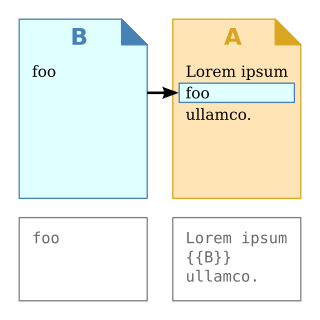
In computer science, transclusion is the inclusion of part or all of an electronic document into one or more other documents by reference via hypertext. Transclusion is usually performed when the referencing document is displayed, and is normally automatic and transparent to the end user. The result of transclusion is a single integrated document made of parts assembled dynamically from separate sources, possibly stored on different computers in disparate places.
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. In 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people used a browser. The most used browser is Google Chrome, with a 65% global market share on all devices, followed by Safari with 18%.
Input may refer to:

In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource.
Directory may refer to:
String or strings may refer to:
An application program is a computer program designed to carry out a specific task other than one relating to the operation of the computer itself, typically to be used by end-users. Word processors, media players, and accounting software are examples. The collective noun "application software" refers to all applications collectively. The other principal classifications of software are system software, relating to the operation of the computer, and utility software ("utilities").
About may refer to:
Distribution may refer to:
Open source products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product.

Alan Emtage is a Bajan-Canadian computer scientist who conceived and implemented the first version of Archie, a pre-Web Internet search engine for locating material in public FTP archives. It is widely considered the world's first Internet search engine.
Top-down may refer to:
Comment may refer to:
The FAO geopolitical ontology is an ontology developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) to describe, manage and exchange data related to geopolitical entities such as countries, territories, regions and other similar areas.
Software categories are groups of software. They allow software to be understood in terms of those categories, instead of the particularities of each package. Different classification schemes consider different aspects of software.
Transparency, transparence or transparent most often refer to:
UBY is a large-scale lexical-semantic resource for natural language processing (NLP) developed at the Ubiquitous Knowledge Processing Lab (UKP) in the department of Computer Science of the Technische Universität Darmstadt . UBY is based on the ISO standard Lexical Markup Framework (LMF) and combines information from several expert-constructed and collaboratively constructed resources for English and German.