Institutional Investor may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Institutional Investor. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Institutional Investor may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Institutional Investor. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
A hedge fund is an investment fund that pools capital from accredited investors or institutional investors and invests in a variety of assets, often with complicated portfolio-construction and risk management techniques. It is administered by a professional investment management firm, and often structured as a limited partnership, limited liability company, or similar vehicle. Hedge funds are generally distinct from mutual funds and regarded as alternative investments, as their use of leverage is not capped by regulators, and distinct from private equity funds, as the majority of hedge funds invest in relatively liquid assets. However, funds which operate similarly to hedge funds but are regulated similarly to mutual funds are available and known as liquid alternative investments.
The primary market is the part of the capital market that deals with the issuance and sale of equity-backed securities to investors directly by the issuer. Investor buy securities that were never traded before. Primary markets create long term instruments through which corporate entities raise funds from the capital market. It is also known as the New Issue Market (NIM).
To invest is to allocate money in the expectation of some benefit in the future.
Initial public offering (IPO) or stock market launch is a type of public offering in which shares of a company are sold to institutional investors and usually also retail (individual) investors. An IPO is underwritten by one or more investment banks, who also arrange for the shares to be listed on one or more stock exchanges. Through this process, colloquially known as floating, or going public, a privately held company is transformed into a public company. Initial public offerings can be used to raise new equity capital for companies, to monetize the investments of private shareholders such as company founders or private equity investors, and to enable easy trading of existing holdings or future capital raising by becoming publicly traded.
Private equity (PE) typically refers to investment funds, generally organized as limited partnerships, that buy and restructure companies that are not publicly traded.

The money market is a component of the economy which provides short-term funds. The money market deals in short-term loans, generally for a period of less than or equal to 365 days.

Venture capital (VC) is a type of financing that is provided by firms or funds to small, early-stage, emerging firms that are deemed to have high growth potential, or which have demonstrated high growth. Venture capital firms or funds invest in these early-stage companies in exchange for equity, or an ownership stake, in those companies. Venture capitalists take on the risk of financing risky start-ups in the hopes that some of the firms they support will become successful. Because startups face high uncertainty, VC investments have high rates of failure. The start-ups are usually based on an innovative technology or business model and they are usually from the high technology industries, such as information technology (IT), clean technology or biotechnology.
A certificate of deposit (CD) is a time deposit, a financial product commonly sold by banks, thrift institutions, and credit unions.

The secondary market, also called the aftermarket and follow on public offering is the financial market in which previously issued financial instruments such as stock, bonds, options, and futures are bought and sold. Another frequent usage of "secondary market" is to refer to loans which are sold by a mortgage bank to investors such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
An institutional investor is an entity which pools money to purchase securities, real property, and other investment assets or originate loans. Institutional investors include banks, credit unions, insurance companies, pensions, hedge funds, REITs, investment advisors, endowments, and mutual funds. Operating companies which invest excess capital in these types of assets may also be included in the term. Activist institutional investors may also influence corporate governance by exercising voting rights in their investments.
Investment management is the professional asset management of various securities and other assets in order to meet specified investment goals for the benefit of the investors. Investors may be institutions or private investors.

Euromoney Institutional Investor PLC is one of Europe's largest business and financial information companies which has interests in business and financial publishing and event organization. It is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index. It was formerly 49% owned by the Daily Mail and General Trust Group until the stake was spun-off in 2019.

Perella Weinberg Partners L.P. is an independent, privately owned, global financial services firm providing corporate advisory and asset management services to clients around the world. Founded in 2006 by Joseph R. Perella, Peter Weinberg, Terry Meguid and several other partners from financial institutions, the firm is a private partnership with approximately 650 employees. It is headquartered in New York City with offices in London, Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Denver, San Francisco, Calgary, and Houston.

There are two basic financial market participant categories, Investor vs. Speculator and Institutional vs. Retail. Action in financial markets by central banks is usually regarded as intervention rather than participation.

Socially responsible investing (SRI), or social investment, also known as sustainable, socially conscious, "green" or ethical investing, is any investment strategy which seeks to consider both financial return and social/environmental good to bring about social change regarded as positive by proponents.
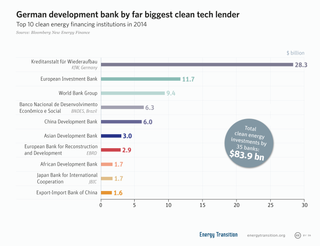
A development finance institution (DFI) also known as a development bank or development finance company (DFC) is a financial institution that provides risk capital for economic development projects on non commercial basis. They are often established and owned by governments or charitable institutions to provide funds for projects that would otherwise not be able to get funds from commercial lenders. Some development banks include socially responsible investing and impact investing criteria into their mandates. Governments often use development banks to form part of their development aid or economic development initiatives.
Private equity real estate is a term used in investment finance to refer to a specific subset of the real estate investment asset class. Private equity real estate refers to one of the four quadrants of the real estate capital markets, which include private equity, private debt, public equity and public debt.

Institutional Investor magazine is a monthly periodical published by Euromoney Institutional Investor. It was founded in 1967 by Gilbert E. Kaplan. A separate international edition of the magazine was established in 1976 for readers in Europe and Asia. Capital Cities Communications purchased the magazine in 1984. The Walt Disney Company bought Capital Cities in 1996 and sold the magazine to Euromoney a year later. Institutional Investor has offices in New York City, London and Hong Kong.
Impact investing refers to investments "made into companies, organizations, and funds with the intention to generate a measurable, beneficial social or environmental impact alongside a financial return". Impact investments provide capital to address social and/or environmental issues.