Project management is the practice of initiating, planning, executing, controlling, and closing the work of a team to achieve specific goals and meet specific success criteria at the specified time.The primary challenge of project management is to achieve all of the project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, quality and budget. The secondary—and more ambitious—challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives.

Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globally. Its headquarters are in Dallas, Texas, United States. TI is one of the top-10 semiconductor companies worldwide, based on sales volume. Texas Instruments's focus is on developing analog chips and embedded processors, which account for more than 80% of their revenue. TI also produces TI digital light processing technology and education technology products including calculators, microcontrollers and multi-core processors. To date, TI has more than 45,000 patents worldwide.
Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American global aerospace, defense, security and advanced technologies company with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It is headquartered in North Bethesda, Maryland, in the Washington, DC, area. Lockheed Martin employs approximately 100,000 people worldwide as of December 2017.

Sales are activities related to selling or the number of goods or services sold in a given time period.
The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is an iterative software development process framework created by the Rational Software Corporation, a division of IBM since 2003. RUP is not a single concrete prescriptive process, but rather an adaptable process framework, intended to be tailored by the development organizations and software project teams that will select the elements of the process that are appropriate for their needs. RUP is a specific implementation of the Unified Process.
Synopsys is an American EDA company. Majority of their products include tools used in the design of an application-specific integrated circuit. Products include logic synthesis, behavioral synthesis, place and route, static timing analysis, formal verification, hardware description language simulators as well as transistor-level circuit simulation. The simulators include development and debugging environments which assist in the design of the logic for chips and computer systems. In recent years Synopsys has also expanded into the application security market.
Agile software development is an approach to software development under which requirements and solutions evolve through the collaborative effort of self-organizing and cross-functional teams and their customer(s)/end user(s). It advocates adaptive planning, evolutionary development, early delivery, and continual improvement, and it encourages rapid and flexible response to change.

The V-model is a graphical representation of a systems development lifecycle. It is used to produce rigorous development lifecycle models and project management models. The V-model falls into three broad categories, the German V-Modell, a general testing model and the US government standard.
Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) is a process level improvement training and appraisal program. Administered by the CMMI Institute, a subsidiary of ISACA, it was developed at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU). It is required by many United States Department of Defense (DoD) and U.S. Government contracts, especially in software development. CMU claims CMMI can be used to guide process improvement across a project, division, or an entire organization. CMMI defines the following maturity levels for processes: Initial, Managed, Defined, Quantitatively Managed, and Optimizing. Version 2.0 was published in 2018. CMMI is registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office by CMU.
Purchasing is a business or organization attempting to acquire goods or services to accomplish its goals. Although there are several organizations that attempt to set standards in the purchasing process, processes can vary greatly between organizations. Typically the word purchasing is not used interchangeably with the word procurement, since procurement typically includes expediting, supplier quality, and transportation and logistics (T&L) in addition to purchasing.

The Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF) is an architecture framework for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) that provides visualization infrastructure for specific stakeholders concerns through viewpoints organized by various views. These views are artifacts for visualizing, understanding, and assimilating the broad scope and complexities of an architecture description through tabular, structural, behavioral, ontological, pictorial, temporal, graphical, probabilistic, or alternative conceptual means.
Integrated logistic support (ILS) is an integrated and iterative process for developing materiel and a support strategy that optimizes functional support, leverages existing resources, and guides the system engineering process to quantify and lower life cycle cost and decrease the logistics footprint, making the system easier to support. Although originally developed for military purposes, it is also widely used in commercial product support or customer service organisations.
The Defence Logistics Organisation (DLO) was a key element of the UK Ministry of Defence, responsible for supporting the armed forces throughout the various stages of an operation or exercise; from training, deployment, in-theatre training and conduct of operations, through to recovery and recuperation ready for redeployment.
The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) defines a Process Area as, "A cluster of related practices in an area that, when implemented collectively, satisfies a set of goals considered important for making improvement in that area." Both CMMI for Development v1.3 and CMMI for Acquisition v1.3 identify 22 process areas, whereas CMMI for Services v1.3 identifies 24 process areas. Many of the process areas are the same in these three models.
Scrum is an agile process framework for managing complex knowledge work, with an initial emphasis on software development, although it has been used in other fields and is slowly starting to be explored for other complex work, research and advanced technologies. It is designed for teams of ten or fewer members, who break their work into goals that can be completed within timeboxed iterations, called sprints, no longer than one month and most commonly two weeks, then track progress and re-plan in 15-minute time-boxed stand-up meetings, called daily scrums.
The Joint Capabilities Integration and Development System (JCIDS), is the formal United States Department of Defense (DoD) process which defines acquisition requirements and evaluation criteria for future defense programs. JCIDS was created to replace the previous service-specific requirements generation system that allowed redundancies in capabilities and failed to meet the combined needs of all US military services. In order to correct these problems, JCIDS is intended to guide the development of requirements for future acquisition systems to reflect the needs of all four services by focusing the requirements generation process on needed capabilities as requested or defined by one of the US combatant commanders. In an ideal implementation of the JCIDS process, regional and functional combatant commanders give early and continuous feedback into the acquisition and sustainment processes to ensure their current and evolving requirements are known and met.
Rational Rhapsody, a modeling environment based on UML, is a visual development environment for systems engineers and software developers creating real-time or embedded systems and software. Rational Rhapsody uses graphical models to generate software applications in various languages including C, C++, Ada, Java and C#.
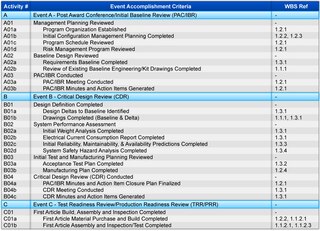
In the United States Department of Defense, the Integrated Master Plan (IMP) and the Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) are important program management tools that provide significant assistance in the planning and scheduling of work efforts in large and complex materiel acquisitions. The IMP is an event-driven plan that documents the significant accomplishments necessary to complete the work and ties each accomplishment to a key program event. The IMP is expanded to a time-based IMS to produce a networked and multi-layered schedule showing all detailed tasks required to accomplish the work effort contained in the IMP. The IMS flows directly from the IMP and supplements it with additional levels of detail——both then form the foundations to implement an Earned Value Management System.

Military acquisition is the bureaucratic management and procurement process dealing with a nation's investments in the technologies, programs, and product support necessary to achieve its national security strategy and support its armed forces. Its objective is to acquire products that satisfy specified needs and provide measurable improvement to mission capability at a fair and reasonable price.
In the United States military integrated acquisition lifecycle the Technical section has multiple acquisition "Technical Reviews". Technical reviews and audits assist the acquisition and the number and types are tailored to the acquisition. Overall guidance flows from the Defense Acquisition Guidebook chapter 4, with local details further defined by the review organizations. Typical topics examined include adequacy of program/contract metrics, proper staffing, risks, budget, and schedule.






