A management system is a set of policies, processes and procedures used by an organization to ensure that it can fulfill the tasks required to achieve its objectives. These objectives cover many aspects of the organization's operations. For instance, an environmental management system enables organizations to improve their environmental performance and an occupational health and safety management system (OHSMS) enables an organization to control its occupational health and safety risks, etc.

Hazard analysis and critical control points, or HACCP, is a systematic preventive approach to food safety from biological, chemical, and physical hazards in production processes that can cause the finished product to be unsafe and designs measures to reduce these risks to a safe level. In this manner, HACCP attempts to avoid hazards rather than attempting to inspect finished products for the effects of those hazards. The HACCP system can be used at all stages of a food chain, from food production and preparation processes including packaging, distribution, etc. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) require mandatory HACCP programs for juice and meat as an effective approach to food safety and protecting public health. Meat HACCP systems are regulated by the USDA, while seafood and juice are regulated by the FDA. All other food companies in the United States that are required to register with the FDA under the Public Health Security and Bioterrorism Preparedness and Response Act of 2002, as well as firms outside the US that export food to the US, are transitioning to mandatory hazard analysis and risk-based preventive controls (HARPC) plans.
Facility management is a professional management discipline focused upon the efficient and effective delivery of support services for the organizations that it serves. The ISO defines FM as the "organizational function which integrates people, place and process within the built environment with the purpose of improving the quality of life of people and the productivity of the core business."
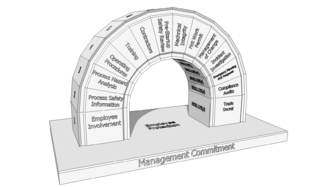
Process safety managementsystem is a regulation promulgated by the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). A process is any activity or combination of activities including any use, storage, manufacturing, handling or the on-site movement of highly hazardous chemicals (HHCs) as defined by OSHA and the Environmental Protection Agency.
In general, compliance means conforming to a rule, such as a specification, policy, standard or law. Regulatory compliance describes the goal that organizations aspire to achieve in their efforts to ensure that they are aware of and take steps to comply with relevant laws, policies, and regulations. Due to the increasing number of regulations and need for operational transparency, organizations are increasingly adopting the use of consolidated and harmonized sets of compliance controls. This approach is used to ensure that all necessary governance requirements can be met without the unnecessary duplication of effort and activity from resources.
An information technology audit, or information systems audit, is an examination of the management controls within an Information technology (IT) infrastructure. The evaluation of obtained evidence determines if the information systems are safeguarding assets, maintaining data integrity, and operating effectively to achieve the organization's goals or objectives. These reviews may be performed in conjunction with a financial statement audit, internal audit, or other form of attestation engagement.

The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) is a joint initiative to combat corporate fraud. It was established in the United States by five private sector organizations, dedicated to guide executive management and governance entities on relevant aspects of organizational governance, business ethics, internal control, enterprise risk management, fraud, and financial reporting. COSO has established a common internal control model against which companies and organizations may assess their control systems. COSO is supported by five supporting organizations: the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA), the American Accounting Association (AAA), the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA), and Financial Executives International (FEI).
IEC standard 61511 is a technical standard which sets out practices in the engineering of systems that ensure the safety of an industrial process through the use of instrumentation. Such systems are referred to as Safety Instrumented Systems. The title of the standard is "Functional safety - Safety instrumented systems for the process industry sector".
Risk Based Inspection (RBI) is an Optimal maintenance business process used to examine equipment such as pressure vessels, heat exchangers and piping in industrial plants. RBI is a decision-making methodology for optimizing inspection plans.The RBI concept lies in that the risk of failure can be assessed in relation to a level that is acceptable, and inspection and repair used to ensure that the level of risk is below that acceptance limit. It examines the Health, Safety and Environment (HSE) and business risk of ‘active’ and ‘potential’ Damage Mechanisms (DMs) to assess and rank failure probability and consequence. This ranking is used to optimize inspection intervals based on site-acceptable risk levels and operating limits, while mitigating risks as appropriate. RBI analysis can be qualitative, quantitative or semi-quantitative in nature.
Internal control, as defined in accounting and auditing, is a process for assuring of an organization's objectives in operational effectiveness and efficiency, reliable financial reporting, and compliance with laws, regulations and policies. A broad concept, internal control involves everything that controls risks to an organization.
Information security management (ISM) describes controls that an organization needs to implement to ensure that it is sensibly protecting the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of assets from threats and vulnerabilities. By extension, ISM includes information risk management, a process which involves the assessment of the risks an organization must deal with in the management and protection of assets, as well as the dissemination of the risks to all appropriate stakeholders. This of course requires proper asset identification and valuation steps, including evaluating the value of confidentiality, integrity, availability, and replacement of assets. As part of information security management, an organization may implement an information security management system and other best practices found in the ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 27002, and ISO/IEC 27035 standards on information security.
Nuclear knowledge management (NKM) is knowledge management as applied in the nuclear technology field. It supports the gathering and sharing of new knowledge and the updating of the existing knowledge base. Knowledge management is of particular importance in the nuclear sector, owing to the rapid development and complexity of nuclear technologies and their hazards and security implications. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) launched a nuclear knowledge management programme in 2002.

The Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement is an agency under the United States Department of the Interior. Established in 2011, BSEE is the lead agency in charge of improving safety and ensuring environmental protection relating to the offshore energy industry, mainly natural gas and oil, on the United States Outer Continental Shelf (OCS). The agency exercises the safety and environmental enforcement functions formerly under the Minerals Management Service including the authority to inspect, investigate, summon witnesses and produce evidence, levy penalties, cancel or suspend activities, and oversee safety, response, and removal preparedness.
Integrity Management Plan is a documented and systematic approach to ensure the long-term integrity of an asset or assets.
Asset Integrity Management Systems (AIMS) outline the ability of an asset to perform its required function effectively and efficiently whilst protecting health, safety and the environment and the means of ensuring that the people, systems, processes, and resources that deliver integrity are in place, in use and will perform when required over the whole life-cycle of the asset. Originally developed in the UK Asset Integrity Management was the result of a collaboration between the HSE and leading oil and gas operators resulting in a series of reports and workshops, the outcome being a group of documents called Key Programmes, currently publicly available.

IT risk management is the application of risk management methods to information technology in order to manage IT risk, i.e.:
Piping corrosion circuit or Corrosion loop / Piping Circuitization and Corrosion Modelling. This is carried out as part of either a Risk Based Inspection analysis (RBI) or Materials Operating Envelope analysis (MOE). It is the systematization of the piping components versus failure modes analysis into materials operating envelope. It groups piping materials / chemical make-up into systems / sub systems and assigns corrosion mechanisms. These are then monitored over the operating lifetime of the facility. This analysis is performed on circuit inspection results to determine and optimize circuit corrosion rates and measured thickness/dates for circuit components. Corrosion Circuits are utilized in the Integrity Management Plan (IMP) which forms a part of the overall Asset integrity management system and is an integral part of any RBI analysis. Many times a "system" will be a broad overview of the facilities process flow, broken by stream constituents, while a circuit level analysis breaks systems into smaller "circuits" that group common metallurgies, equal temperatures and pressures, and expected damage mechanisms.
Permit To Work (PTW) refers to management systems used to ensure that work is done safely and efficiently. These are used in hazardous industries and involve procedures to request, review, authorise, document and most importantly, de-conflict tasks to be carried out by front line workers. Permit to work is an essential part of control of work (COW), the integrated management of business critical maintenance processes. Control of work is made up of permit to work, hazard identification and risk assessment (RA), and isolation management (IM).

The Civil Aviation Authority of Fiji (CAAF) is the national aviation authority in the Republic of Fiji and is responsible for discharging functions on behalf of the Government of Fiji under the States responsibility to the Convention on International Civil Aviation, also known as the Chicago Convention on International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). CAAF regulates the activities of airport operators, air traffic control and air navigation service providers, airline operators, pilots and air traffic controllers, aircraft engineers, technicians, airports, airline contracting organisations and international air cargo operators in Fiji.
2 Offshore Information Sheet 4/2006 Offshore Installations (Safety Case) Regulations 2005 Regulation 13 Thorough Review of a Safety Case (Revised and reissued July 2008)
3 Structural integrity management framework for fixed jacket structures Prepared by Atkins Limited for the Health and Safety Executive 2009 Research Report RR684
6 Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management Systems Ccps, Center for Chemical Process Safety (CCPS) - Technology & Engineering - 2011 - 250 pages






