
The Office of National Assessments (ONA) was an Australian statutory intelligence agency established by the Office of National Assessments Act 1977 as an independent statutory body directly accountable to the Prime Minister of Australia as a portfolio agency of the Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. ONA provided all-source assessments on international political, strategic and economic developments to the Prime Minister and the National Security Committee of Cabinet. ONA also played a coordination role in the Australian Intelligence Community through evaluating foreign intelligence products, convening the National Intelligence Coordination Committee, and developing relationships with intelligence agencies around world.
The Boland Amendment is a term describing three U.S. legislative amendments between 1982 and 1984, all aimed at limiting U.S. government assistance to the Contras in Nicaragua. The first Boland Amendment was part of the House Appropriations Bill of 1982, which was attached as a rider to the Defense Appropriations Act of 1983, named for the Massachusetts Democrat, Representative Edward Boland, who authored it. The House of Representatives passed the Defense Appropriations Act 411–0 on December 8, 1982 and it was signed by President Ronald Reagan on December 21, 1982. The amendment outlawed U.S. assistance to the Contras for the purpose of overthrowing the Nicaraguan government, while allowing assistance for other purposes.

The New Zealand Security Intelligence Service is New Zealand's primary national intelligence agency, responsible for national security and foreign intelligence.

The Government Communications Security Bureau (GCSB) is the public-service department of New Zealand charged with promoting New Zealand's national security by collecting and analysing information of an intelligence nature.
Three anti-terrorism bills were enacted in the Australian Parliament in 2004 by the Howard Coalition government with the support of the Labor Opposition. These were the Anti-terrorism Bill 2004, the Anti-terrorism Bill 2004 and the Anti-terrorism Bill 2004.
The Australian Protective Service (APS) was an Australian Commonwealth law enforcement agency which existed between 1984 and 2004. The APS was created by the separation of the Protective Service component of the Australian Federal Police (AFP) into a new agency based upon recommendations contained in the Stewart Royal Commission of Inquiry into Drug Trafficking. It was initially responsible for protecting personnel and property of the Australian government; foreign diplomatic missions and Internationally Protected Persons (IPPs); and the provision of custodial services at immigration detention centres. From 1990 the APS commenced providing Counter Terrorist First Response duties at certain security-designated airports including the specialist Bomb Appraisal Officer function and, following the terrorist attacks of 11 September 2001, deployed Air Security Officers on board Australian registered commercial aircraft. Close Personal Protection (CPP), or bodyguard, functions were never provided by the APS; where this has been a Commonwealth responsibility, the function is provided by the AFP.
The Parliamentary Joint Committee on Intelligence and Security (PJCIS) is a joint committee of the Parliament of Australia which oversees Australia's primary agencies of the Australian Intelligence Community: Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO), the Australian Secret Intelligence Service (ASIS), the Australian Signals Directorate (ASD), the Defence Intelligence Organisation (DIO), the Australian Geospatial-Intelligence Organisation (DIGO), and the Office of National Assessments (ONA).

The Intelligence Services Act 1994 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
The Australian Intelligence Community (AIC) and the National Intelligence Community (NIC) or National Security Community of the Australian Government are the collectives of statutory intelligence agencies, policy departments, and other government agencies concerned with protecting and advancing the national security and national interests of the Commonwealth of Australia. The intelligence and security agencies of the Australian Government have evolved since the Second World War and the Cold War and saw transformation and expansion during the Global War on Terrorism in response to current international and domestic security issues such as terrorism, violent extremism, cybersecurity, transnational crime, counter-proliferation, support to military operations, and Pacific regional instability.
Title V: Removing obstacles to investigating terrorism is the fifth of ten titles which comprise the USA PATRIOT Act, an anti-terrorism bill passed in the United States after the September 11, 2001 attacks. It contains 8 sections regarding the capture and prosecution of terrorists.

The Foreign Intelligence Service, or Serviciul de Informații Externe (SIE) in Romanian, is, under Law no. 1/1998, "the state body specialized in foreign intelligence concerning the national security and the safeguarding of Romania and its interests".
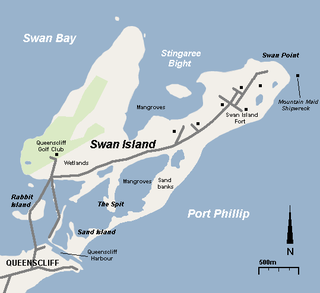
Swan Island is a 1.4 km2 sand barrier island which, with Duck Island and the Edwards Point spit, separate Swan Bay from Port Phillip in Victoria, Australia. It lies close to and north of the town of Queenscliff at the eastern end of the Bellarine Peninsula, and is an official bounded locality of the Borough of Queenscliffe.
The Inspector-General of Intelligence and Security (IGIS) is an independent statutory office holder in the Commonwealth of Australia responsible for reviewing the activities of the six intelligence agencies which collectively comprise the Australian Intelligence Community (AIC). With own motion powers in addition to considering complaints or requests from ministers, IGIS is a key element of the accountability regime for Australia’s intelligence and security agencies.

The Australian Security Intelligence Organisation Act 1979 is an Act of the Parliament of Australia which replaced the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation Act 1956, which had established the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) as a statutory body. ASIO is the counter-intelligence and security agency of Australia, which had been established in 1949 by Prime Minister Ben Chifley's Directive for the Establishment and Maintenance of a Security Service under the executive power of the Constitution, under the control of the Director-General of Security and responsible to the Attorney-General.
William ("Bill") Thomas Robertson was one of the founders of the Australian Secret Intelligence Service (ASIS), formed in 1952 though its existence was kept secret, and served as the agency's fourth Director-General from 1968 until he was sacked by Prime Minister Gough Whitlam in controversial circumstances in 1975. He also served in World War II as an infantry officer and the chief of staff of an Australian and two British divisions.
The Secret Intelligence Service (SIS), commonly known as MI6, is the foreign intelligence service of the government of the United Kingdom, tasked mainly with the covert overseas collection and analysis of human intelligence (HUMINT) in support of the UK's national security. SIS is a member of the country's intelligence community and its Chief is accountable to the country's Foreign Secretary.

The Telecommunications Amendment Act 2015 is an Australian law that amends the Telecommunications Act 1979 and the Telecommunications Act 1997 to introduce a statutory obligation for Australian telecommunication service providers to retain, for a period of two years, particular types of telecommunications data (metadata) and introduces certain reforms to the regimes applying to the access of stored communications and telecommunications data under the TIA Act.










