In digital logic and computing, a counter is a device which stores the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock. The most common type is a sequential digital logic circuit with an input line called the clock and multiple output lines. The values on the output lines represent a number in the binary or BCD number system. Each pulse applied to the clock input increments or decrements the number in the counter.
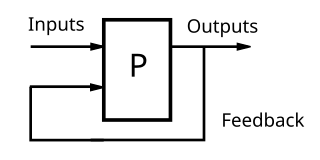
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to feed back into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled carefully when applied to feedback systems:
Simple causal reasoning about a feedback system is difficult because the first system influences the second and second system influences the first, leading to a circular argument. This makes reasoning based upon cause and effect tricky, and it is necessary to analyze the system as a whole. As provided by Webster, feedback in business is the transmission of evaluative or corrective information about an action, event, or process to the original or controlling source.

Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals.
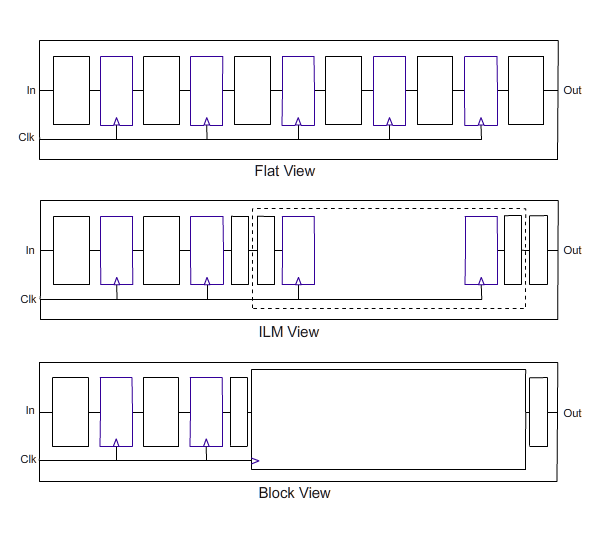
A shift register is a type of digital circuit using a cascade of flip-flops where the output of one flip-flop is connected to the input of the next. They share a single clock signal, which causes the data stored in the system to shift from one location to the next. By connecting the last flip-flop back to the first, the data can cycle within the shifters for extended periods, and in this form they were used as a form of computer memory. In this role they are very similar to the delay-line memory systems and were widely used in the late 1960s and early 1970s to replace that form of memory.
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits at the register-transfer level of abstraction. It is also used in the verification of analog circuits and mixed-signal circuits, as well as in the design of genetic circuits. In 2009, the Verilog standard was merged into the SystemVerilog standard, creating IEEE Standard 1800-2009. Since then, Verilog is officially part of the SystemVerilog language. The current version is IEEE standard 1800-2017.
In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, and most commonly, digital logic circuits.
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer: the layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. The physical layer provides an electrical, mechanical, and procedural interface to the transmission medium. The shapes and properties of the electrical connectors, the frequencies to broadcast on, the line code to use and similar low-level parameters, are specified by the physical layer.
In automata theory, sequential logic is a type of logic circuit whose output depends on the present value of its input signals and on the sequence of past inputs, the input history. This is in contrast to combinational logic, whose output is a function of only the present input. That is, sequential logic has state (memory) while combinational logic does not.

An application-specific integrated circuit is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficiency video codec. Application-specific standard product chips are intermediate between ASICs and industry standard integrated circuits like the 7400 series or the 4000 series. ASIC chips are typically fabricated using metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, as MOS integrated circuit chips.
In digital circuit design, register-transfer level (RTL) is a design abstraction which models a synchronous digital circuit in terms of the flow of digital signals (data) between hardware registers, and the logical operations performed on those signals.
Asynchronous circuit is a sequential digital logic circuit that does not use a global clock circuit or signal generator to synchronize its components. Instead, the components are driven by a handshaking circuit which indicates a completion of a set of instructions. Handshaking works by simple data transfer protocols. Many synchronous circuits were developed in early 1950s as part of bigger asynchronous systems. Asynchronous circuits and theory surrounding is a part of several steps in integrated circuit design, a field of digital electronics engineering.
Clock skew is a phenomenon in synchronous digital circuit systems in which the same sourced clock signal arrives at different components at different times due to gate or, in more advanced semiconductor technology, wire signal propagation delay. The instantaneous difference between the readings of any two clocks is called their skew.

In electronic engineering, ground bounce is a phenomenon associated with transistor switching where the gate voltage can appear to be less than the local ground potential, causing the unstable operation of a logic gate.

Integrated circuit design, or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits, or ICs. ICs consist of miniaturized electronic components built into an electrical network on a monolithic semiconductor substrate by photolithography.
In digital electronic design a clock domain crossing (CDC), or simply clock crossing, is the traversal of a signal in a synchronous digital circuit from one clock domain into another. If a signal does not assert long enough and is not registered, it may appear asynchronous on the incoming clock boundary.
The Timing closure in VLSI design and electronics engineering is the process by which a logic design of a clocked synchronous circuit consisting of primitive elements such as combinatorial logic gates and sequential logic gates is modified to meet its timing requirements. Unlike in a computer program where there is no explicit delay to perform a calculation, logic circuits have intrinsic and well defined delays to propagate inputs to outputs.

In integrated circuit design, physical design is a step in the standard design cycle which follows after the circuit design. At this step, circuit representations of the components of the design are converted into geometric representations of shapes which, when manufactured in the corresponding layers of materials, will ensure the required functioning of the components. This geometric representation is called integrated circuit layout. This step is usually split into several sub-steps, which include both design and verification and validation of the layout.

The EnCore microprocessor family is a configurable and extendable implementation of a compact 32-bit RISC instruction set architecture - developed by the PASTA Research Group at the University of Edinburgh School of Informatics. The following are key features of the EnCore microprocessor family:

In electronics, flip-flops and latches are circuits that have two stable states that can store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will output its state. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.
Low Power flip-flops are flip-flops that are designed for low-power electronics, such as smartphones and notebooks. A flip-flop, or latch, is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information.