
Biotite is a common phyllosilicate mineral within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula K(Mg,Fe)
3AlSi
3O
10(F,OH)
2. More generally, it refers to the dark mica series, primarily a solid-solution series between the iron-endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more aluminous end-members include siderophyllite. Biotite was named by J.F.L. Hausmann in 1847 in honor of the French physicist Jean-Baptiste Biot, who performed early research into the many optical properties of mica.

Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the processes of mineral origin and formation, classification of minerals, their geographical distribution, as well as their utilization.

Titanite, or sphene (from the Greek sphenos (σφηνώ), meaning wedge), is a calcium titanium nesosilicate mineral, CaTiSiO5. Trace impurities of iron and aluminium are typically present. Also commonly present are rare earth metals including cerium and yttrium; calcium may be partly replaced by thorium.

A waveplate or retarder is an optical device that alters the polarization state of a light wave travelling through it. Two common types of waveplates are the half-wave plate, which shifts the polarization direction of linearly polarized light, and the quarter-wave plate, which converts linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light and vice versa. A quarter-wave plate can be used to produce elliptical polarization as well.

Pleochroism is an optical phenomenon in which a substance has different colors when observed at different angles, especially with polarized light.

Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent. The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.
Petrography is a branch of petrology that focuses on detailed descriptions of rocks. Someone who studies petrography is called a petrographer. The mineral content and the textural relationships within the rock are described in detail. The classification of rocks is based on the information acquired during the petrographic analysis. Petrographic descriptions start with the field notes at the outcrop and include macroscopic description of hand specimens. However, the most important tool for the petrographer is the petrographic microscope. The detailed analysis of minerals by optical mineralogy in thin section and the micro-texture and structure are critical to understanding the origin of the rock. Electron microprobe analysis of individual grains as well as whole rock chemical analysis by atomic absorption, X-ray fluorescence, and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy are used in a modern petrographic lab. Individual mineral grains from a rock sample may also be analyzed by X-ray diffraction when optical means are insufficient. Analysis of microscopic fluid inclusions within mineral grains with a heating stage on a petrographic microscope provides clues to the temperature and pressure conditions existent during the mineral formation.

In optical mineralogy and petrography, a thin section is a laboratory preparation of a rock, mineral, soil, pottery, bones, or even metal sample for use with a polarizing petrographic microscope, electron microscope and electron microprobe. A thin sliver of rock is cut from the sample with a diamond saw and ground optically flat. It is then mounted on a glass slide and then ground smooth using progressively finer abrasive grit until the sample is only 30 μm thick. The method involved using the Michel-Lévy interference colour chart. Typically quartz is used as the gauge to determine thickness as it is one of the most abundant minerals.

Extinction is a term used in optical mineralogy and petrology, which describes when cross-polarized light dims, as viewed through a thin section of a mineral in a petrographic microscope. Isotropic minerals, opaque (metallic) minerals, or amorphous materials (glass) show no light. Anisotropic minerals will show one extinction for each 90 degrees of stage rotation.

A petrographic microscope is a type of optical microscope used in petrology and optical mineralogy to identify rocks and minerals in thin sections. The microscope is used in optical mineralogy and petrography, a branch of petrology which focuses on detailed descriptions of rocks. The method is called "polarized light microscopy" (PLM). Depending on the grade of observation required, petrological microscopes are derived from conventional brightfield microscopes of similar basic capabilities by:
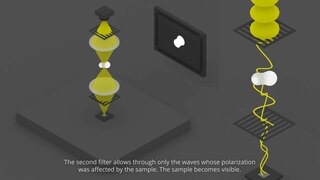
Polarized light microscopy can mean any of a number of optical microscopy techniques involving polarized light. Simple techniques include illumination of the sample with polarized light. Directly transmitted light can, optionally, be blocked with a polariser orientated at 90 degrees to the illumination. More complex microscopy techniques which take advantage of polarized light include differential interference contrast microscopy and interference reflection microscopy. Scientists will often use a device called a polarizing plate to convert natural light into polarized light.

Marrite (mar'-ite) is depicted by the chemical formula PbAgAsS3. It is the arsenic equivalent of mineral freieslebenite (PbAgSbS3), but also displays close polyhedral characteristics with sicherite and diaphorite. Marrite was named in honor of geologist John Edward Marr (1857–1933) of Cambridge, England.

Amicite has a general formula of K2Na2Al4Si4O16·5(H2O). The name is in honor of Giovan Battista Amici (1786–1863) a physicist, optician, and inventor of microscope optical elements.
Gabrielite is a rare thallium sulfosalt mineral with a chemical formula of Tl6Ag3Cu6(As,Sb)9S21 or Tl2AgCu2As3S7.

Nambulite is a lithium bearing manganese silicate mineral with formula: (Li,Na)Mn4Si5O14(OH). It is named after the mineralogist, Matsuo Nambu (born 1917) of Tohoko University, Japan, who is known for his research in manganese minerals. The mineral was first discovered in the Funakozawa Mine of northeastern Japan, a metasedimentary manganese ore.

Eveite is a manganese arsenate mineral in the olivenite group. Its chemical formula is Mn2AsO4OH. It is found only in Långban, Filipstad, Värmland, Sweden and at the Sterling Mine in New Jersey, United States. It is a dimorph of sarkinite and is isostructural with adamite. The name, for the biblical "Eve", comes from its structural similarities to adamite and is also a reference to its apple-green color. It can also be pale yellow. Eveite is an orthorhombic mineral, which means it has three crystallographic axes of unequal lengths which are at 90° to one another.

















