Summary
Headquartered in San Ramon, California, the IMTC was formed in September 1994 through a merger of The Consortium for Audiographics Teleconferencing Standards, Inc. (CATS) and the Multimedia Communications Community of Interest (MCCOI). CATS, formed in 1993, focused on the T.120 standards suite for multipoint data conferencing. MCCOI, also formed in 1993, focused on the ITU-T H.320 (ISDN) and H.324 (POTS) standards suites for multipoint video communications. In December 1995, the IMTC merged with the Personal Conferencing Work Group, Inc. (PCWG). The PCWG had also focused on multimedia teleconferencing standards as well as the needs of users of products and services in this category.
The IMTC initiated formal standards initiatives and testing programs (aka Plug fests) to improve interoperability of the products and services in the ecosystem.
From the mid-1990s, as the rich-media communications concept extended beyond traditional switched networks to include Internet Protocol (IP) networks, the IMTC acted as an industry convergence point for Voice, Data, and Video over IP. At that time IMTC's efforts resulted in the promulgation of the ITU-T H.323 (packet-based video) standard, agreement on the initial Voice over IP (VoIP) Implementation Framework, and the first integrated interoperability tests involving the ITU-T T.120, H.320, H.324, H.323 standards and emerging IETF requests for comments (RFCs) such as session initiation protocol (SIP).
Today, the IMTC retains its focus on addressing rich-media deployment obstacles and interoperability in wide area and enterprise networks. The initiatives IMTC sponsors now include 3GPP, packet switched streaming techniques, enterprise network address translation and wireless/mobility. Its efforts enable service providers and vendors to create more compatible rich-media products, applications and services, which in turn facilitate the widespread adoption of the offerings by protecting end-users' capital investments and meeting usability expectations.
Past contribution
In the mid-1990s, IMTC's Standards First! initiatives spurred the creation of the ITU-T T.120, H.320, H.324, and H.323 standards that led to the first cross-protocol switched and packet interoperability test sessions (later branded as SuperOp!).
In the mid/late-1990s IMTC released a Voice over IP Implementation Agreement, which specified dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) data transfer and reproduction, and IP-specific needs such as directory services and dynamic IP address resolution mechanisms to support multi-party voice and voice-band calls over IP networks.
Test suites and procedures developed by the IMTC in the late 1990s demonstrated the viability of connecting gatekeepers, gateways, proxies, MCUs, endpoints and network components into integrated rich-media sessions and interoperability and interworking between IP networks and switched-circuit networks including H.323, SIP, the iNOW! Profile, and the T.120, H.320, H.324 M, H.248/Megaco, and H.450 protocols.
More recently IMTC has begun to highlight the interoperability of multimedia offerings for mobile phone users. These offerings are based on the 3GPP specifications for streaming, and interacting with, multimedia content (such as newscasts) on demand and in real-time over 3G wireless networks. They support offline file exchange (which involves raw codec bitstreams, packetized bitstreams and the 3GPP/MPEG-4 file format) and virtual streaming over the Internet and include streaming servers, multimedia terminals and content-creation tools in the value chain.
Structure
The IMTC is structured as an open organization, and is controlled by its Voting Members. The IMTC's Board of Directors, which oversees the management of the corporation and establishes its operating policies, is elected annually by the Voting Members. Any Voting Member can submit a candidate in these elections. Voting Members also ratify the IMTC's annual budget and any changes to IMTC's corporate by-laws, ensuring that a majority ratifies any changes to member rights and privileges.
The IMTC also follows a defined consensus decision-making process. Specifications and recommendations that require product development work, and issues which commit the IMTC to a specific course of action, are balloted within the membership for majority approval. All members are encouraged to participate, voice opinions and help resolve issues. This reflects IMTC's strong commitment to an inclusive, open structure and a "make things happen" environment.
H.263 is a video compression standard originally designed as a low-bit-rate compressed format for videoconferencing. It was standardized by the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) in a project ending in 1995/1996. It is a member of the H.26x family of video coding standards in the domain of the ITU-T.
Quality of service (QoS) is the description or measurement of the overall performance of a service, such as a telephony or computer network or a cloud computing service, particularly the performance seen by the users of the network. To quantitatively measure quality of service, several related aspects of the network service are often considered, such as packet loss, bit rate, throughput, transmission delay, availability, jitter, etc.
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating real-time sessions that include voice, video and messaging applications. SIP is used for signaling and controlling multimedia communication sessions in applications of Internet telephony for voice and video calls, in private IP telephone systems, in instant messaging over Internet Protocol (IP) networks as well as mobile phone calling over LTE (VoLTE).
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), also called IP telephony, is a method and group of technologies for the delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet. The terms Internet telephony, broadband telephony, and broadband phone service specifically refer to the provisioning of communications services over the Internet, rather than via the public switched telephone network (PSTN), also known as plain old telephone service (POTS).
The Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) is a standards body which develops open standards for the mobile phone industry. It is not a formal government-sponsored standards organization like the ITU, but a forum for industry stakeholders to agree on common specifications for products and services.
Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband (AMR-WB) is a patented wideband speech audio coding standard developed based on Adaptive Multi-Rate encoding, using similar methodology as algebraic code excited linear prediction (ACELP). AMR-WB provides improved speech quality due to a wider speech bandwidth of 50–7000 Hz compared to narrowband speech coders which in general are optimized for POTS wireline quality of 300–3400 Hz. AMR-WB was developed by Nokia and VoiceAge and it was first specified by 3GPP.
The IP Multimedia Subsystem or IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) is a standardised architectural framework for delivering IP multimedia services. Historically, mobile phones have provided voice call services over a circuit-switched-style network, rather than strictly over an IP packet-switched network. Alternative methods of delivering voice (VoIP) or other multimedia services have become available on smartphones, but they have not become standardized across the industry. IMS is an architectural framework that provides such standardization.

The Gateway Control Protocol is an implementation of the media gateway control protocol architecture for providing telecommunication services across a converged internetwork consisting of the traditional public switched telephone network (PSTN) and modern packet networks, such as the Internet. H.248 is the designation of the recommendations developed by the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) and Megaco is a contraction of media gateway control protocol used by the earliest specifications by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The standard published in March 2013 by ITU-T is entitled H.248.1: Gateway control protocol: Version 3.
A session border controller (SBC) is a network element deployed to protect SIP based voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) networks.

Microsoft NetMeeting is a discontinued VoIP and multi-point videoconferencing client included in many versions of Microsoft Windows. It uses the H.323 protocol for videoconferencing, and is interoperable with OpenH323-based clients such as Ekiga, OpenH323, and Internet Locator Service (ILS) as reflector. It also uses a slightly modified version of the T.120 Protocol for whiteboarding, application sharing, and file transfers.
The next-generation network (NGN) is a body of key architectural changes in telecommunication core and access networks. The general idea behind the NGN is that one network transports all information and services by encapsulating these into IP packets, similar to those used on the Internet. NGNs are commonly built around the Internet Protocol, and therefore the term all IP is also sometimes used to describe the transformation of formerly telephone-centric networks toward NGN.

A VoIP phone or IP phone uses voice over IP technologies for placing and transmitting telephone calls over an IP network, such as the Internet, instead of the traditional public switched telephone network (PSTN).
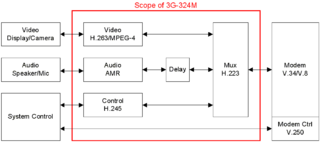
3G-324M is the 3GPP umbrella protocol for video telephony in 3G mobile networks.
Text over IP is a means of providing a real-time text (RTT) service that operates over IP-based networks. It complements Voice over IP (VoIP) and Video over IP.

H.323 is a Recommendation from the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) that defines the protocols to provide audio-visual communication sessions on any packet network. The H.323 standard addresses call signaling and control, multimedia transport and control, and bandwidth control for point-to-point and multi-point conferences.
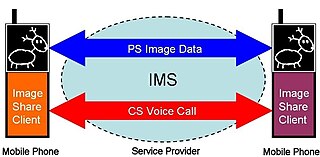
Image Share is a service for sharing images between users during a mobile phone call. It has been specified for use in a 3GPP-compliant cellular network by the GSM Association in the PRD IR.79 Image Share Interoperability Specification.
The 3GPP/NGN IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) multimedia telephony service (MMTel) is a global standard based on the IMS, offering converged, fixed and mobile real-time multimedia communication using the media capabilities such as voice, real-time video, text, file transfer and sharing of pictures, audio and video clips. With MMTel, users have the capability to add and drop media during a session. You can start with chat, add voice, add another caller, add video, share media and transfer files, and drop any of these without losing or having to end the session. MMTel is one of the registered ICSI feature tags.
International Mobile Telecommunications-Advanced are the requirements issued by the ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 2008 for what is marketed as 4G mobile phone and Internet access service.
Total conversation is an ITU standard of simultaneous video, voice and text service in telecommunications. Total conversation allows people in two or more locations to: (a) see each other, (b) hear each other, and (c) conduct a text interaction with each other, or choose to communicate with any combination of those three modes and to do so in real-time.

The media gateway control protocol architecture is a methodology of providing telecommunication services using decomposed multimedia gateways for transmitting telephone calls between an Internet Protocol network and traditional analog facilities of the public switched telephone network (PSTN). The architecture was originally defined in RFC 2805 and has been used in several prominent voice over IP (VoIP) protocol implementations, such as the Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) and Megaco (H.248), both successors to the obsolete Simple Gateway Control Protocol (SGCP).





