Invasion of Sakhalin may refer to:
- Mongol invasions of Sakhalin (1264–1308), during the period of the Mongol Empire
- Japanese invasion of Sakhalin (1905), during the Russo-Japanese War
- Soviet invasion of South Sakhalin (1945), during World War II
Invasion of Sakhalin may refer to:

Sakhalin is the northernmost island of the Japanese archipelago and the largest island of the Russian Federation. It is situated in the North Pacific Ocean between 45°50' and 54°24' N, and is sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin, which is about one third the size of Honshu, is just off the Russian Pacific coast, and just north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. The population of Sakhalin Island was 497,973 as of the 2010 census, made up of mostly ethnic Russians and a smaller Korean community. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks and Nivkhs. Derived from the Manchu word Sahaliyan, the island of Sakhalin was home to indigenous peoples including the Ainu. Certain elements of the Sakhalin Ainu were once tributaries of the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties for periods of time from the 14th to 18th centuries. Sakhalin was later claimed by both Russia and Japan over the course of the 19th and 20th centuries. These disputes sometimes involved military conflicts and divisions of the island between the two powers. In 1875, Japan ceded its claims to Russia in exchange for the northern Kuril Islands. In 1905, following the Russo-Japanese War, the island was divided, with the south going to Japan. Russia has held all of the island since seizing the Japanese portion—as well as all the Kuril Islands—in the final days of World War II in 1945. Japan no longer claims any of Sakhalin, although it does still claim the southern Kuril Islands. Most Ainu on Sakhalin moved to Hokkaido, 43 kilometres (27 mi) to the south across the La Pérouse Strait, when the Japanese were displaced from the island in 1949.
Sino-Japanese War most often refers to:

The Russian Far East is a region in North Asia which includes the Far Eastern Federal District, the easternmost territory of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean.

The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands is a volcanic archipelago in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast that stretches approximately 1,300 km (810 mi) northeast from Hokkaido, Japan to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the north Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many minor rocks. It consists of the Greater Kuril Chain and the Lesser Kuril Chain. The total land area is 10,503.2 square kilometres (4,055.3 sq mi), and the total population is 19,434.

Hōjō Tokimune of the Hōjō clan was the eighth shikken of the Kamakura shogunate, known for leading the Japanese forces against the invasion of the Mongols and for spreading Zen Buddhism. He was the eldest son of Tokiyori, fifth shikken (regent) of the Kamakura shogunate and de facto ruler of Japan. From birth, Hojo was seen as the tokuso (head) of the clan Hojo and rigorously groomed to become his father’s successor. In 1268 AD, at the age of 18, he became shikken himself.
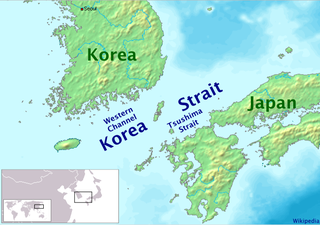
The Korea Strait is a sea passage in East Asia between Korea and Japan, connecting the East China Sea, the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan in the northwest Pacific Ocean. The strait is split by the Tsushima Island into the Western Channel and the Tsushima Strait or Eastern Channel.

Sakhalin Oblast is a federal subject of Russia comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian Far East. The oblast has an area of 87,100 square kilometers (33,600 sq mi). Its administrative center and largest city is Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk. As of the 2010 Census, the oblast has a population of 497,973. Besides people from other parts of the former Soviet Union and the Korean Peninsula, the oblast is home to Nivkhs and Ainu, with the latter having lost their language in Sakhalin recently. Sakhalin is rich in natural gas and oil, and is Russia's fourth wealthiest federal subject and wealthiest oblast. It borders Khabarovsk Krai to the west and Kamchatka Krai to the north, along with Hokkaido, Japan to the south.

Tsushima Strait or Eastern Channel is a channel of the Korea Strait, which lies between Korea and Japan, connecting the Sea of Japan, the Yellow Sea, and the East China Sea.

Karafuto Prefecture, commonly known as South Sakhalin, was a prefecture of Japan located in Sakhalin from 1907 to 1949.

The Mongol invasions of Japan, which took place in 1274 and 1281, were major military efforts taken by Kublai Khan of the Yuan dynasty to conquer the Japanese archipelago after the submission of the Korean kingdom of Goryeo to vassaldom. Ultimately a failure, the invasion attempts are of macro-historical importance because they set a limit on Mongol expansion and rank as nation-defining events in the history of Japan. The invasions are referred to in many works of fiction and are the earliest events for which the word kamikaze is widely used, originating in reference to the two typhoons faced by the Yuan fleets.

The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire, which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history. In addition, Mongol expeditions may have spread the bubonic plague across much of Eurasia, helping to spark the Black Death of the 14th century.

Relations between the Soviet Unionand Japan between the Communist takeover in 1917 and the collapse of Communism in 1991 tended to be hostile. Japan had sent troops to counter the Bolshevik presence in Russia's Far East during the Russian Civil War, and both countries had been in opposite camps during World War II and the Cold War. In addition, territorial conflicts over the Kuril Islands and South Sakhalin were a constant source of tension. These, with a number of smaller conflicts, prevented both countries from signing a peace treaty after World War II, and even today matters remain unresolved.
Invasion of Russia can refer to:

This article discusses the political divisions and vassals of the Mongol Empire. Through invasions and conquests the Mongols established a vast empire that included many political divisions, vassals and tributary states. It was the largest contiguous land empire in history. However, after the death of Möngke Khan, the Toluid Civil War and subsequent wars had led to the fragmentation of the Mongol Empire. By 1294, the empire had fractured into four autonomous khanates, including the Golden Horde in the northwest, the Chagatai Khanate in the middle, the Ilkhanate in the southwest, and the Yuan dynasty in the east based in modern-day Beijing, although the Yuan emperors held the nominal title of Khagan of the empire.
Battle of Beijing may refer to multiple battles fought in what is now Beijing:

The Invasion of South Sakhalin, also called the Battle of Sakhalin, was the Soviet invasion of the Japanese territorial portion of Sakhalin Island known as Karafuto Prefecture. The invasion was part of the Soviet–Japanese War, a massive campaign of the Second World War.

From 1264 to 1308, the Mongol Empire made several incursions into the island of Sakhalin off the east coast of Siberia to aid their Nivkh allies against the Ainu, who had been expanding north from Hokkaido. The Ainu put up a tenacious resistance, even launching a counter-attack on Mongol positions on the continent across the Strait of Tartary in 1297, but finally capitulated to the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China in 1308.

The Ainu languages, sometimes also known as Ainuic, are a small language family, often portrayed as a language isolate, historically spoken by the Ainu people of northern Japan and neighboring islands.

During the Soviet-Japanese War in August 1945, the Soviet Union made plans to invade Hokkaido, the northernmost of Japan's four main Home Islands. Opposition from the United States and doubts within the Soviet high command caused the plans to be canceled before the invasion could begin.