
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum around 700 nanometers, to 1 millimeter (300 GHz). Black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is almost all at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, with properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon.

A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network for interconnecting electronic devices within an individual person's workspace. A PAN provides data transmission among devices such as computers, smartphones, tablets and personal digital assistants. PANs can be used for communication among the personal devices themselves, or for connecting to a higher level network and the Internet where one master device takes up the role as gateway.

A personal digital assistant (PDA), also known as a handheld PC, is a variety mobile device which functions as a personal information manager. PDAs have been mostly displaced by the widespread adoption of highly capable smartphones, in particular those based on iOS and Android.

The Infrared Data Association (IrDA) is an industry-driven interest group that was founded in 1993 by around 50 companies. IrDA provides specifications for a complete set of protocols for wireless infrared communications, and the name "IrDA" also refers to that set of protocols. The main reason for using the IrDA protocols had been wireless data transfer over the "last one meter" using point-and-shoot principles. Thus, it has been implemented in portable devices such as mobile telephones, laptops, cameras, printers, and medical devices. Main characteristics of this kind of wireless optical communication is physically secure data transfer, line-of-sight (LOS) and very low bit error rate (BER) that makes it very efficient.

In electronics, a remote control or clicker is an electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operate devices such as a television set, DVD player or other home appliance. A remote control can allow operation of devices that are out of convenient reach for direct operation of controls. They function best when used from a short distance. This is primarily a convenience feature for the user. In some cases, remote controls allow a person to operate a device that they otherwise would not be able to reach, as when a garage door opener is triggered from outside.

Wireless communication is the transfer of information between two or more points that do not use an electrical conductor as a medium by which to perform the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications include the use of other electromagnetic wireless technologies, such as light, magnetic, or electric fields or the use of sound.
OBEX is a communications protocol that facilitates the exchange of binary objects between devices. It is maintained by the Infrared Data Association but has also been adopted by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group and the SyncML wing of the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA). One of OBEX's earliest popular applications was in the Palm III. This PDA and its many successors use OBEX to exchange business cards, data, even applications.

Open Palmtop Integrated Environment (OPIE) was an open-source graphical user interface for PDAs and other devices running Linux. It is a fork of Trolltech's Qtopia environment.
The Psion Series 7 is a subnotebook computer from Psion that was released in 2000. In size it is fairly original — larger than a palmtop or handheld machine, but smaller than a laptop computer. It was the first of the Psion series to have a full color screen — and the last. It has a leather-bound clam-shell design, with a touch-sensitive, VGA-resolution LCD screen and QWERTY keyboard. Internally it boasts a 132.71 MHz StrongARM SA-1100 processor, 16 MB of RAM and 16 MB of internal ROM.
CEBus(r), short for Consumer Electronics Bus, also known as EIA-600, is a set of electrical standards and communication protocols for electronic devices to transmit commands and data. It is suitable for devices in households and offices to use, and might be useful for utility interface and light industrial applications.
OMA Device Management is a device management protocol specified by the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) Device Management (DM) Working Group and the Data Synchronization (DS) Working Group. The current approved specification of OMA DM is version 1.2.1, the latest modifications to this version released in June 2008. The candidate release 2.0 was scheduled to be finalized in September 2013.

Sybase iAnywhere, is a subsidiary of Sybase specializing in mobile computing, management and security and enterprise database software. SQL Anywhere, formerly known as SQL Anywhere Studio or Adaptive Server Anywhere (ASA), is the company's flagship relational database management system (RDBMS). SQL Anywhere powers popular applications such as Intuit, Inc.'s QuickBooks, and the devices of 140,000 census workers during the 2010 United States Census. The product's customers include Brinks, Kodak, Pepsi Bottling Group (PBG), MICROS Systems, Inc. and the United States Navy. In August 2008.
Consumer IR, consumer infrared, or CIR is a class of devices employing the infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum for wireless communications. CIR ports are commonly found in consumer electronics devices such as television remote controls, PDAs, laptops, and computers.
CEN ISO/IEEE 11073 Health informatics - Medical / health device communication standards enable communication between medical, health care and wellness devices and external computer systems. They provide automatic and detailed electronic data capture of client-related and vital signs information, and of device operational data.

An infrared blaster is a device that emulates an infrared remote control to autonomously control a device that is normally controlled only by keypresses on its remote control. The most common use of an IR blaster is to allow a recording device, such as a DVR or VCR, to change the channel on an external tuner, such as a cable box or satellite television receiver. This way, the receiving device can automatically select the correct channel to record before starting the recording process. Two other common uses are to extend infrared signals in order to place remote-controlled products behind closed doors and to allow mobile devices to control infrared devices.
Infrared lamps are electrical devices which emit infrared radiation. Infrared lamps are commonly used in radiant heating for industrial processes and building heating. Infrared LEDs are used for communication over optical fibers and in remote control devices. Infrared lamps are also used for some night vision devices where visible light would be objectionable. Infrared lamp sources are used in certain scientific and industrial instrument for chemical analysis of liquids and gases; for example, the pollutant sulfur dioxide in air can be measured using its infrared absorption characteristics.
vMessage is a file format used for the storage and exchange of short messages, typically SMS messages, between mobile devices and desktop computers. The format is used by multiple vendors, including Nokia, Siemens, and Palm, Inc., and is similar to the commonly used vCard format. vCard is used within the format to embed contact information for the sender of the message.
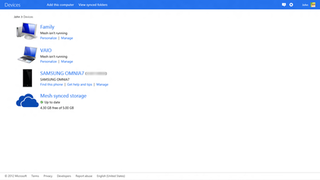
Windows Live Devices was an online device management service as part of Windows Live which will allow users to centrally access and manage the synchronization of files stored on their computers, mobile devices, as well as other peripherals such as digital photo frames. Windows Live Devices also allows users to remotely access their computers from the internet using a web browser.

A portable data terminal, or shortly PDT, is an electronic device that is used to enter or retrieve data via wireless transmission. They have also been called enterprise digital assistants (EDA), data capture mobile devices, batch terminals or just portables.










