Related Research Articles

James Harold Wilson, Baron Wilson of Rievaulx, was a British statesman and Labour Party politician who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1964 to 1970 and again from 1974 to 1976. He was Leader of the Labour Party from 1963 to 1976, Leader of the Opposition twice from 1963 to 1964 and again from 1970 to 1974, and a Member of Parliament (MP) from 1945 to 1983. Wilson is the only Labour leader to have formed administrations following four general elections.

Leonard James Callaghan, Baron Callaghan of Cardiff, commonly known as Jim Callaghan, was a British statesman and Labour Party politician who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1976 to 1979 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1976 to 1980. Callaghan is the only person to have held all four Great Offices of State, having also served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1964 to 1967, Home Secretary from 1967 to 1970 and Foreign Secretary from 1974 to 1976. He was a Member of Parliament (MP) from 1945 to 1987.

The Winter of Discontent was the period between November 1978 and February 1979 in the United Kingdom characterised by widespread strikes by private, and later public, sector trade unions demanding pay rises greater than the limits Prime Minister James Callaghan and his Labour Party government had been imposing, against Trades Union Congress (TUC) opposition, to control inflation. Some of these industrial disputes caused great public inconvenience, exacerbated by the coldest winter in 16 years, in which severe storms isolated many remote areas of the country.

Gerard Fitt, Baron Fitt was a politician from Northern Ireland. He was a founder and the first leader of the Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP), a social democratic and Irish nationalist party.

The Central Bank of Ireland is the Irish member of the Eurosystem and had been the monetary authority for Ireland from 1943 to 1998, issuing the Irish pound. It is also the country's main financial regulatory authority, and since 2014 has been Ireland's national competent authority within European Banking Supervision.

Anthony Perrinott Lysberg Barber, Baron Barber, was a British Conservative politician who served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1970 to 1974.

The Hot Autumn of 1969–70 is a term used for a series of large strikes in the factories and industrial centers of Northern Italy, in which workers demanded better pay and better conditions. During 1969 and 1970 there were over 440 hours of strikes in the region. The decrease in the flow of labour migration from Southern Italy had resulted in nearly full employment levels in the northern part of the country, meaning that the workforce there now had the leverage to start exercising its influence.
Thomas Murphy, also known as Slab, is an Irish republican, believed to be a former Chief of Staff of the Provisional Irish Republican Army. His farm straddles County Armagh and County Louth on the border between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. In December 2015, Murphy was found guilty on nine counts of tax evasion following a lengthy investigation by the Criminal Assets Bureau of the Republic of Ireland. In February 2016, Murphy was jailed and sentenced to 18 months in prison. One of three brothers, Murphy is a lifelong bachelor who lived on the Louth side of his farm before his imprisonment.

The economic history of the Republic of Ireland effectively began in 1922, when the then Irish Free State won independence from the United Kingdom. The state was plagued by poverty and emigration until the 1960s when an upturn led to the reversal of long term population decline. However, global and domestic factors combined in the 1970s and 1980s to return the country to poor economic performance and emigration. The 1990s, however saw the beginning of unprecedented economic success, in a phenomenon known as the "Celtic Tiger", which continued until the 2008 global financial crisis, specifically the post-2008 Irish economic downturn. It also led to Ireland becoming the most indebted state in the European Union. As of 2015, the Republic has returned to growth, and was the fastest growing economy for that year. In May 2023, Irish unemployment was at a record low of 3.8%.

The Dublin lock-out was a major industrial dispute between approximately 20,000 workers and 300 employers that took place in Dublin, Ireland. The dispute, lasting from 26 August 1913 to 18 January 1914, is often viewed as the most severe and significant industrial dispute in Irish history. Central to the dispute was the workers' right to unionise.
The Gdańsk Agreement was an accord reached between the government of the Polish People's Republic and the striking shipyard workers in Gdańsk, Poland. The accord, signed in late August 1980 by government representative Mieczysław Jagielski and strike leader Lech Wałęsa, led to the creation of the trade union Solidarity and was an important milestone in the end of Communist rule in Poland.

The Union of Construction, Allied Trades and Technicians (UCATT) was a British and Irish trade union, operating in the construction industry. It was founded in 1971, and merged into Unite on 1 January 2017.

The New Industrial State is a 1967 book by John Kenneth Galbraith. Three revised editions appeared in 1972, 1978 and 1985.
Gerald McCarthy is an Irish former hurling manager and player. In his playing career he was known for his intelligent anticipation, his ability to find open space and his overhead striking of the ball. A versatile player who lined out in no less than eight different positions, McCarthy made his name as an attacking midfielder and as a centre-forward. He is widely regarded to be one of the most skilful and stylish players of his generation and as one of the greatest players in the history of the sport.

The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939 that affected many countries across the world. It became evident after a sharp decline in stock prices in the United States, the largest economy in the world at the time, leading to a period of economic depression. The economic contagion began around September 1929 and led to the Wall Street stock market crash of October. This crisis marked the start of a prolonged period of economic hardship characterized by high unemployment rates and widespread business failures.

The post-2008 Irish banking crisis was when a number of Irish financial institutions faced almost imminent collapse due to insolvency during the Great Recession. In response, the Irish government instigated a €64 billion bank bailout. This then led to a number of unexpected revelations about the business affairs of some banks and business people. Ultimately, added onto the deepening recession in the country, the banks' bailout was the primary reason for the Irish government requiring IMF assistance and a total restructuring of the government occurred as result.
The Cork county hurling team represents Cork in hurling and is governed by Cork GAA, the county board of the Gaelic Athletic Association. The team competes in the three major annual inter-county competitions: the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship, the Munster Senior Hurling Championship, and the National Hurling League.
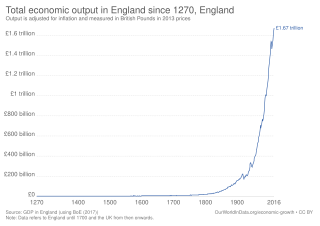
The economic history of the United Kingdom relates the economic development in the British state from the absorption of Wales into the Kingdom of England after 1535 to the modern United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland of the early 21st century.

On 8 November 2016, the Government of India announced the demonetisation of all ₹500 and ₹1,000 banknotes of the Mahatma Gandhi Series. It also announced the issuance of new ₹500 and ₹2,000 banknotes in exchange for the demonetised banknotes. Prime Minister Narendra Modi said that this decision would curtail the shadow economy, increase cashless transactions and reduce the use of illicit and counterfeit cash to fund illegal activity and terrorism.

The Cork county football team represents Cork in men's Gaelic football and is governed by Cork GAA, the county board of the Gaelic Athletic Association. The team competes in the three major annual inter-county competitions; the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship, the Munster Senior Football Championship and the National Football League.
References
- ↑ Antoine E. Murphy (March 1978). "Money in an economy without banks: The case of Ireland". The Manchester School. 46 (1): 41–50. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9957.1978.tb00151.x.
- ↑ "How six-month bank strike rocked the nation". Irish Independent. December 29, 1999. Archived from the original on August 2, 2012.
- ↑ Brendan Keenan (August 5, 2010). "It's 1970: Industrial unrest and a jobless rate of 7pc are key concerns". Irish Independent.