Iron nitrate may refer to:
- Iron(II) nitrate, Fe(NO3)2, a green compound that is unstable to heat
- Iron(III) nitrate (or ferric nitrate), Fe(NO3)3, a pale violet compound that has a low melting point
Iron nitrate may refer to:

In chemistry, iron(III) refers to the element iron in its +3 oxidation state. In ionic compounds (salts), such an atom may occur as a separate cation (positive ion) denoted by Fe3+.

Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Fe2O3. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4), which also occurs naturally as the mineral magnetite. As the mineral known as hematite, Fe2O3 is the main source of iron for the steel industry. Fe2O3 is readily attacked by acids. Iron(III) oxide is often called rust, and to some extent this label is useful, because rust shares several properties and has a similar composition; however, in chemistry, rust is considered an ill-defined material, described as Hydrous ferric oxide.
Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
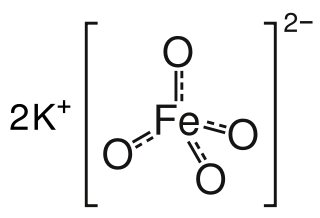
Potassium ferrate is the chemical compound with the formula K2FeO4. This purple salt is paramagnetic, and is a rare example of an iron(VI) compound. In most of its compounds, iron has the oxidation state +2 or +3 (Fe2+ or Fe3+). Reflecting its high oxidation state, FeO42− is a powerful oxidizing agent.
Iron sulfide or Iron sulphide can refer to range of chemical compounds composed of iron and sulfur.

Iron-oxidizing bacteria are chemotrophic bacteria that derive energy by oxidizing dissolved ferrous iron. They are known to grow and proliferate in waters containing iron concentrations as low as 0.1 mg/L. However, at least 0.3 ppm of dissolved oxygen is needed to carry out the oxidation.
Iron sulfate may refer to:
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry is a systematic method of naming inorganic chemical compounds, as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry. Ideally, every inorganic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous formula can be determined. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry.
Iron(III) oxide-hydroxide or ferric oxyhydroxide is the chemical compound of iron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula FeO(OH).
A solubility chart is a chart with a list of ions and how, when mixed with other ions, they can become precipitates or remain aqueous.
A nitrate test is a chemical test used to determine the presence of nitrate ion in solution. Testing for the presence of nitrate via wet chemistry is generally difficult compared with testing for other anions, as almost all nitrates are soluble in water. In contrast, many common ions give insoluble salts, e.g. halides precipitate with silver, and sulfate precipitate with barium.
Microbial metabolism is the means by which a microbe obtains the energy and nutrients it needs to live and reproduce. Microbes use many different types of metabolic strategies and species can often be differentiated from each other based on metabolic characteristics. The specific metabolic properties of a microbe are the major factors in determining that microbe's ecological niche, and often allow for that microbe to be useful in industrial processes or responsible for biogeochemical cycles.

Iron(III) nitrate, or ferric nitrate, is the chemical compound with the formula Fe(NO3)3.

Cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl or (C4H4)Fe(CO)3 is an organoiron compound with the formula Fe(C4H4)(CO)3. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It has been used in organic chemistry as a precursor for cyclobutadiene, which is an elusive species in the free state.
Iron chloride can refer to

Barium ferrate is the chemical compound of formula BaFeO4. This is a rare compound containing iron in the +6 oxidation state. The ferrate(VI) ion has two unpaired electrons, making it paramagnetic. It is isostructural with BaSO4, and contains the tetrahedral [FeO4]2− anion.
Iron(III) chromate is the iron(III) salt of chromic acid with the chemical formula Fe2(CrO4)3.

Green rust is a generic name for various green crystalline chemical compounds containing iron(II) and iron(III) cations, the hydroxide (HO−
) anion, and another anion such as carbonate (CO2−
3), chloride (Cl−
), or sulfate (SO2−
4), in a layered double hydroxide structure. The most studied varieties are

Iron(III) pyrophosphate is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula Fe4(P2O7)3.