Iron sulfate may refer to:
- Ferrous sulfate, Iron(II) sulfate, FeSO4
- Ferric sulfate, Iron(III) sulfate, Fe2(SO4)3
Iron sulfate may refer to:

Sulfuric acid or sulphuric acid, known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water.

The mineral pyrite, or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula FeS2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.

In chemistry, the adjective Ferrous indicates a compound that contains iron(II), meaning iron in its +2 oxidation state, possibly as the divalent cation Fe2+. It is opposed to "ferric" or iron(III), meaning iron in its +3 oxidation state, such as the trivalent cation Fe3+. This usage has been largely replaced by the IUPAC nomenclature, which calls for the oxidation state being indicated by Roman numerals in parentheses, such as iron(II) oxide for ferrous oxide (FeO), iron(III) oxide for ferric oxide (Fe2O3), and iron(II,III) oxide for the oxide Fe3O4 that contains both forms of iron.
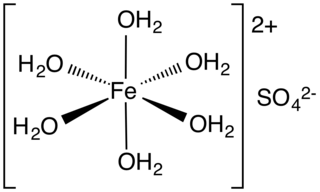
Iron(II) sulfate (British English: iron(II) sulphate) or ferrous sulfate denotes a range of salts with the formula FeSO4·xH2O. These compounds exist most commonly as the heptahydrate (x = 7) but several values for x are known. The hydrated form is used medically to treat iron deficiency, and also for industrial applications. Known since ancient times as copperas and as green vitriol (vitriol is an archaic name for sulfate), the blue-green heptahydrate (hydrate with 7 molecules of water) is the most common form of this material. All the iron(II) sulfates dissolve in water to give the same aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry and is paramagnetic. The name copperas dates from times when the copper(II) sulfate was known as blue copperas, and perhaps in analogy, iron(II) and zinc sulfate were known respectively as green and white copperas.

Jarosite is a basic hydrous sulfate of potassium and ferric iron (Fe-III) with a chemical formula of KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6. This sulfate mineral is formed in ore deposits by the oxidation of iron sulfides. Jarosite is often produced as a byproduct during the purification and refining of zinc and is also commonly associated with acid mine drainage and acid sulfate soil environments.

Vitriol is the general chemical name encompassing a class of chemical compound comprising sulfates of certain metals – originally, iron or copper. Those mineral substances were distinguished by their color, such as green vitriol for hydrated iron(II) sulfate and blue vitriol for hydrated copper(II) sulfate.
Iron(II) sulfide or ferrous sulfide is one of a family chemical compounds and minerals with the approximate formula FeS. Iron sulfides are often iron-deficient non-stoichiometric. All are black, water-insoluble solids.

A double salt is a salt that contains more than one different cation or anion. Examples of double salts include alums (with the general formula MIMIII[SO4]2·12H2O) and Tutton's salts (with the general formula [MI]2MII[SO4]2·6H2O). Other examples include potassium sodium tartrate, ammonium iron(II) sulfate (Mohr's salt), potassium uranyl sulfate (used to discover radioactivity) and bromlite BaCa(CO3)2. The fluorocarbonates contain fluoride and carbonate anions. Many coordination complexes form double salts.
A Nitrate Test is a chemical test used to determine the presence of nitrate ion in solution. Testing for the presence of nitrate via wet chemistry is generally difficult compared with testing for other anions, as almost all nitrates are soluble in water. In contrast, many common ions give insoluble salts, e.g. halides precipitate with silver, and sulfate precipitate with barium.
Acid sulfate soils are naturally occurring soils, sediments or organic substrates that are formed under waterlogged conditions. These soils contain iron sulfide minerals or their oxidation products. In an undisturbed state below the water table, acid sulfate soils are benign. However, if the soils are drained, excavated or exposed to air by a lowering of the water table, the sulfides react with oxygen to form sulfuric acid.
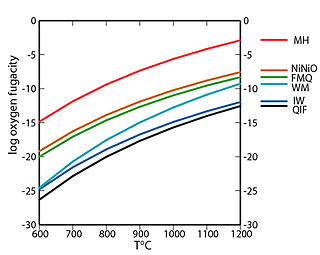
In geology, a redox buffer is an assemblage of minerals or compounds that constrains oxygen fugacity as a function of temperature. Knowledge of the redox conditions (or equivalently, oxygen fugacities) at which a rock forms and evolves can be important for interpreting the rock history. Iron, sulfur, and manganese are three of the relatively abundant elements in the Earth's crust that occur in more than one oxidation state. For instance, iron, the fourth most abundant element in the crust, exists as native iron, ferrous iron (Fe2+), and ferric iron (Fe3+). The redox state of a rock affects the relative proportions of the oxidation states of these elements and hence may determine both the minerals present and their compositions. If a rock contains pure minerals that constitute a redox buffer, then the oxygen fugacity of equilibration is defined by one of the curves in the accompanying fugacity-temperature diagram.
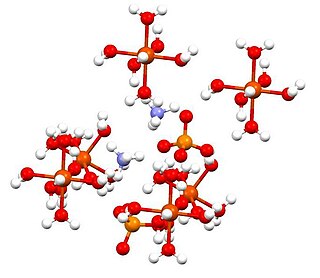
Ammonium iron(II) sulfate, or Mohr's salt, is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2(H2O)6. Containing two different cations, Fe2+ and NH4+, it is classified as a double salt of ferrous sulfate and ammonium sulfate. It is a common laboratory reagent because it is readily crystallized, and crystals resist oxidation by air. Like the other ferrous sulfate salts, ferrous ammonium sulfate dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. Its mineral form is mohrite.

Potassium ferrioxalate, also called potassium trisoxalatoferrate or potassium tris(oxalato)ferrate(III) is a chemical compound with the formula K
3[Fe(C
2O
4)
3]. It often occurs as the trihydrate K3[Fe(C2O4)3]·3H2O. Both are crystalline compounds, lime green in colour.

Iron(III) sulfate (or ferric sulfate), is a family of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe2(SO4)3(H2O)n. A variety of hydrates are known, including the most commonly encountered form of "ferric sulfate". Solutions are used in dyeing as a mordant, and as a coagulant for industrial wastes. Solutions of ferric sulfate are also used in the processing of aluminum and steel.

Ammonium iron(III) sulfate, NH4Fe(SO4)2·12 H2O, or NH4[Fe(H2O)6](SO4)2·6 H2O, also known as ferric ammonium sulfate (FAS) or iron alum, is a double salt in the class of alums, which consists of compounds with the general formula AB(SO4)2 · 12 H2O. It has the appearance of weakly violet, octahedrical crystals. There has been some discussion regarding the origin of the crystals' colour, with some ascribing it to impurities in the compound, and others claiming it to be a property of the crystal itself.

Green rust is a generic name for various green crystalline chemical compounds containing iron(II) and iron(III) cations, the hydroxide (HO−
) anion, and another anion such as carbonate (CO2−
3), chloride (Cl−
), or sulfate (SO2−
4), in a layered double hydroxide structure. The most studied varieties are
Copper phosphate may refer to :
Iron(II) selenate (ferrous selenate) is an inorganic compound with the formula FeSeO4. It has anhydrous and several hydrate forms. The pentahydrate has the structure, [Fe(H2O)4]SeO4•H2O, isomorphous to the corresponding iron(II) sulfate. Heptahydrate is also known, in form of unstable green crystalline solid.
Gallium(III) sulfate refers to the chemical compound, a salt, with the formula Ga2(SO4)3, or its hydrates Ga2(SO4)3·xH2O. Gallium metal dissolves in sulfuric acid to form solutions containing [Ga(OH2)6]3+ and SO42− ions. The octadecahydrate Ga2(SO4)3·18H2O crystallises from these solutions at room temperature. This hydrate loses water in stages when heated, forming the anhydrate Ga2(SO4)3 above 150 °C and completely above 310 °C. Anhydrous Ga2(SO4)3 is isostructural with iron(III) sulfate, crystallizing in the rhombohedral space group R3.