
Transport in India consists of transport by land, water and air. Road transport is the primary mode of transport for most Indian citizens, and India's road transport systems are among the most heavily used in the world.

The Royal Canal is a canal originally built for freight and passenger transportation from Dublin to Longford in Ireland. It is one of two canals from Dublin to the River Shannon and was built in direct competition to the Grand Canal. The canal fell into disrepair in the late 20th century, but much of it has since been restored for navigation. The length of the canal to the River Shannon was reopened on 1 October 2010, but a final spur branch, to Longford Town, remains closed.

The Itsukaichi Line is a railway line operated by East Japan Railway Company in Tokyo, Japan. It links Musashi-Itsukaichi Station in the city of Akiruno with Haijima Station in the city of Akishima. From there, some trains travel through to Tachikawa Station via the Ōme Line, and select weekend/holiday services continue from Tachikawa along the Chūō Line to Tokyo Station. This line can only accommodate trains of 4- or 6-car lengths.

The Boyne Navigation is a series of canals running 31 km (19 mi) roughly parallel to the River Boyne from Oldbridge to Navan in County Meath, in Ireland. The navigation was once used by horse-drawn boats travelling between Navan, Slane and the port of Drogheda; however is now derelict. The Boyne Navigation branch of the Inland Waterways Association of Ireland have an agreement with An Taisce – The National Trust for Ireland giving it a license to carry out restoration work on the navigation to return it to a usable waterway.

The Scottish Inland Waterways Association (SIWA) was a registered charity and association of canal societies and individual canal enthusiasts in Scotland.

The Inland Waterways Association of Ireland is a registered charity and a limited company in the Republic of Ireland and also operates in Northern Ireland. It was founded in 1954 to campaign for the conservation and development of the waterways and their preservation as working navigations. As of 2008, the association had approximately 4,400 members which were organised in twenty branches.

Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is the statutory authority in charge of the waterways in India. It was constituted under IWAI Act-1985 by the Parliament of India. Its headquarters is located in Noida, Uttar Pradesh.

The West Coast Canal or National Waterway No 3 is a 205 km (127 mi) long inland navigational route located in Kerala, India, which runs from Kollam to Kottapuram. It was declared a National Waterway in 1993. In addition to the main stretch, Champakara and Udyogmandal canals are navigable and connect the industrial centers of Kochi to Kochi port Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) under the Ministry of Shipping is coordinating the task for developing, monitoring and administering national waterways. It is the first National Waterway in the country with 24-hour navigation facilities along the entire stretch. It has been extended to Kozhikode by the National Waterways Act, 2016. The National Waterway 3 mainly passes through the previous Thiruvananthapuram–Shoranur canal.

Iwai Station is a passenger railway station in the city of Minamibōsō, Chiba Prefecture, Japan, operated by the East Japan Railway Company.
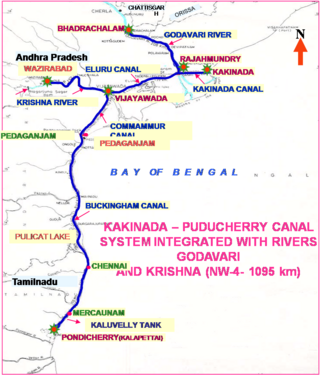
National Waterway 4 (NW-4) is a 1,095 kilometres (680 mi) long waterway in India. It has been declared as an Indian National Waterway and is currently under development. It connects the Indian states of Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and the union territory of Puducherry. The NW-4 runs along the Coromandal Coast through Kakinada, Eluru, Commanur, Buckingham Canals and also through part of Krishna and Godavari rivers in South India. It was declared a National Waterway on 24 November 2008 under the Provisions of National Waterways Bill, 2006. It is being developed by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI), and was scheduled for completion by 2013. The National Waterways Act, 2016 has extended the length of NW-4 from 1,095 km (680 mi) to 2,890 km (1,800 mi) by connecting the Krishna and Godavari Rivers. The Project would be undertaken in 3 phases with first phase beginning in October, 2017 and to be completed by June, 2019

The National Waterway 1 (NW-1) or Ganga-Bhagirathi-Hooghly river system is located in India and runs from Prayagraj in Uttar Pradesh to Haldia in West Bengal via Patna and Bhagalpur in Bihar across the Ganges river. It is 1,620 km (1,010 mi) long, making it the longest waterway in India. It is of prime importance amongst all the national waterways considering its locational advantages. The NW-1 passes through West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh and serves major cities and their industrial hinterlands like;
National Waterways 6 is a waterway between Lakhipur and Bhanga of the Barak River.
The Iwai Rebellion was a rebellion against the Yamato court that took place in Tsukushi Province, Japan in 527 AD. The rebellion was named after its leader, Iwai, who is believed by historians to have been a powerful governor of Tsukushi. The rebellion was quelled by the Yamato court, and played an important part in the consolidation of early Japan. The main record of the rebellion can be found in the Nihon Shoki, although it is also mentioned in Kojiki and other historical sources.

Thoppilkadavu or Thoppilkkadavu is one of the neighbourhoods of the city of Kollam, located on the shores of Ashtamudi Lake in Kerala, India. It is an integral part of Kollam city. Presence of Ashtamudi Lake is increasing the importance of Thoppilkadavu as one of the tourism hotspots in the city. Thoppilkadavu is the western endpoint of Asramam Link Road in the city.

The Sagarmala Programme is an initiative by the Government of India to enhance the performance of the country's logistics sector. The programme envisages unlocking the potential of waterways and the coastline to minimize infrastructural investments required to meet these targets.
The Haldia Multi-Modal Terminal is a barge terminal in Port City Haldia in East Midnapore district of West Bengal and a small barrier set for small ships. The terminal is built near the Haldia Port. The terminal will be built as a river port with 61 acres of land. The terminal is built by Inland Waterways Authority of India by help of West Bengal and the Calcutta Port Trust.
Varanasi Multi-Modal Terminal or Varanasi Port is an Inland river port situated in the city of Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh. The port is located on the Ganges river. This port is built under the government's Jal Marg Vikas project. The port has provided a direct link with the Port of Kolkata and Haldia Port.
Water transport in India has played a significant role in the country's economy and is indispensable to foreign trade. India is endowed with an extensive network of waterways in the form of rivers, canals, backwaters, creeks and a long coastline accessible through the seas and oceans. It has the largest carrying capacity of any form of transport and is most suitable for carrying bulky goods over long distances. It is one of the cheapest mode of transport in India, as it takes advantage of natural track and does not require huge capital investment in construction and maintenance except in the case of canals. Its fuel efficiency contributes to lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact due to carbon. India has 14500 km of inland waterways. Out of which only 5685 km are navigable by mechanized vessels.












