Publications
Jeff Prosise is the author of the book Programming Windows with MFC, published by Microsoft Press. His book is about the MFC, a C++ based proprietary programming library for Microsoft Windows. This book, along with Charles Petzold's popular Programming Windows book are considered to be 'bibles' in Windows programming. While Petzold's book is known as the 'Windows API bible', Prosise's book is often referred to as the 'MFC bible'.
Some of his other publications are Programming Microsoft .NET, Programming Windows with C# and How Computer Graphics Work (co-author Gary Suen). His previous books, published back in the 1980s and 1990s, included PC Magazine DOS 6 Techniques And Utilities, PC Magazine DOS 6 Memory Management With Utilities, and Windows Desktop Utilities.
The Windows API, informally WinAPI, is Microsoft's core set of application programming interfaces (APIs) available in the Microsoft Windows operating systems. The name Windows API collectively refers to several different platform implementations that are often referred to by their own names ; see the versions section. Almost all Windows programs interact with the Windows API. On the Windows NT line of operating systems, a small number use the Native API.
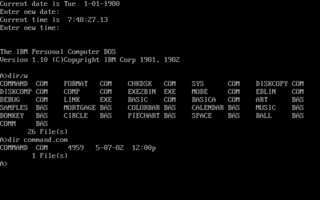
IBM PC DOS, an acronym for IBM personal computer disk operating system, is a discontinued operating system for the IBM Personal Computer, manufactured and sold by IBM from the early 1980s into the 2000s.

Microsoft Visual C++ (MSVC) is a compiler from Microsoft for the C, C++, and C++/CLI programming languages. MSVC is proprietary software; it was originally a standalone product but later became a part of Visual Studio and made available in both trialware and freeware forms. It features tools for developing and debugging C++ code, especially code written for the Windows API, DirectX and .NET.
Microsoft Foundation Class Library (MFC) is a C++ object-oriented library for developing desktop applications for Windows.
Peter Norton is an American programmer, software publisher, author, and philanthropist. He is best known for the computer programs and books that bear his name and portrait. Norton sold his PC software business to Symantec Corporation in 1990.

In computing, the fdisk command-line utility provides disk-partitioning functions - for example: preparatory to defining file systems. fdisk features in the DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, and Microsoft Windows operating systems, and in certain ports of FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonFly BSD and macOS for compatibility reasons. In versions of the Windows NT operating-system line from Windows 2000 onwards, fdisk is replaced by a more advanced tool called diskpart. Similar utilities exist for Unix-like systems, for example, BSD disklabel.

In DOS memory management, conventional memory, also called base memory, is the first 640 kilobytes of the memory on IBM PC or compatible systems. It is the read-write memory directly addressable by the processor for use by the operating system and application programs. As memory prices rapidly declined, this design decision became a limitation in the use of large memory capacities until the introduction of operating systems and processors that made it irrelevant.
CodeView is a standalone debugger created by David Norris at Microsoft in 1985 as part of its development toolset. It originally shipped with Microsoft C 4.0 and later. It also shipped with Visual Basic for MS-DOS, Microsoft BASIC PDS, and a number of other Microsoft language products. It was one of the first debuggers on the DOS platform that was full-screen oriented, rather than line-oriented.

Microsoft Diagnostics (MSD) was a software tool developed by Microsoft to assist in the diagnostics of 1990s-era computers. Users primarily deployed this tool to provide detailed technical information about the user's software and hardware and to print the gathered information, usually for use by support technicians in troubleshooting and resolving problems. The assumptions made by the program were valid until the late 1990s: it does not handle plug-and-play USB or other new technologies that appeared around 2000.
John Socha-Leialoha is a software developer best known for creating Norton Commander, the first orthodox file manager. The original Norton Commander was written for DOS. Over the years, Socha's design for file management has been extended and cloned many times.

Charles Petzold is an American programmer and technical author on Microsoft Windows applications. He is also a Microsoft Most Valuable Professional and was named one of Microsoft's seven Windows Pioneers.

Mark Eugene Russinovich is a Spanish-born American software engineer who serves as CTO of Microsoft Azure. He was a cofounder of software producers Winternals before it was acquired by Microsoft in 2006.

In computing, ATTRIB is a command in Intel ISIS-II, DOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS that allows the user to change various characteristics, or "attributes" of a computer file or directory. The command is also available in the EFI shell.
In computing, sys is a command used in many operating system command-line shells and also in Microsoft BASIC.
The DOS API is an API which originated with 86-DOS and is used in MS-DOS/PC DOS and other DOS-compatible operating systems. Most calls to the DOS API are invoked using software interrupt 21h. By calling INT 21h with a subfunction number in the AH processor register and other parameters in other registers, various DOS services can be invoked. These include handling keyboard input, video output, disk file access, program execution, memory allocation, and various other activities. In the late 1980s, DOS extenders along with the DOS Protected Mode Interface (DPMI) allow the programs to run in either 16-bit or 32-bit protected mode and still have access to the DOS API.
This article presents a timeline of events in the history of 16-bit x86 DOS-family disk operating systems from 1980 to 2020. Non-x86 operating systems named "DOS" are not part of the scope of this timeline.

MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and some operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS". MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatible personal computers during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system.
Mitchell Waite is an American computer programmer, author of programming books and publisher of books mobile apps. His first book "Projects in Sight, Sound and Sensation" was published in 1974. He studied nuclear physics at Sonoma State University during 1971–1975.
The command-line tool exe2bin is a post-compilation utility program available on MS-DOS and other operating systems.







