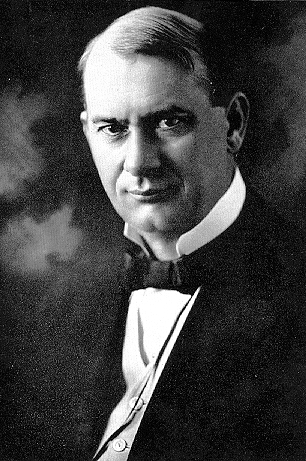Jehovah's Witnesses is a nontrinitarian, millenarian, restorationist Christian denomination. In 2023, the group reported approximately 8.6 million members involved in evangelism, with around 20.5 million attending the annual Memorial of Christ's death. Jehovah's Witnesses believe that the destruction of the present world system at Armageddon is imminent, and the establishment of God's kingdom over earth is the only solution to all of humanity's problems.

The New World Translation of the Holy Scriptures is a translation of the Bible published by the Watch Tower Bible and Tract Society; it is used and distributed by Jehovah's Witnesses. The New Testament portion was released first, in 1950, as the New World Translation of the Christian Greek Scriptures, with the complete New World Translation of the Bible released in 1961.
Jehovah's Witnesses' practices are based on the biblical interpretations of Charles Taze Russell (1852–1916), founder of the Bible Student movement, and of successive presidents of the Watch Tower Society, Joseph Franklin Rutherford and Nathan Homer Knorr. Since 1976, practices have also been based on decisions made at closed meetings of the group's Governing Body. The group disseminates instructions regarding activities and acceptable behavior through The Watchtower magazine and through other official publications, and at conventions and congregation meetings.
A religious order is a subgroup within a larger confessional community with a distinctive high-religiosity lifestyle and clear membership. Religious orders often trace their lineage from revered teachers, venerate their founders, and have a document describing their lifestyle called a rule of life. Such orders exist in many of the world's religions.

Jehovah's Witnesses have been criticized by adherents of mainstream Christianity, members of the medical community, former Jehovah's Witnesses, and commentators with regard to their beliefs and practices. The Jehovah's Witness movement's leaders have been accused of practicing doctrinal inconsistencies and making doctrinal reversals, making failed predictions, mistranslating the Bible, harshly treating former Jehovah's Witnesses, and leading the Jehovah's Witness movement in an authoritarian and coercive manner. Jehovah's Witnesses have also been criticized because they reject blood transfusions, even in life-threatening medical situations, and for failing to report cases of sexual abuse to the authorities. Many of the claims are denied by Jehovah's Witnesses and some have also been disputed by courts and religious scholars.
This is an index page of Wikipedia articles related to the topic of religion.
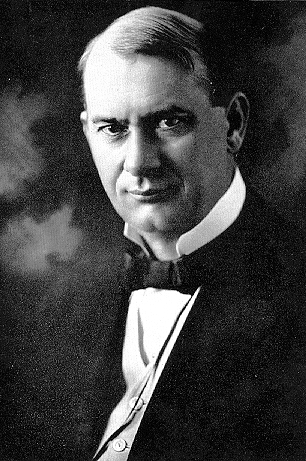
Joseph Franklin Rutherford, also known as Judge Rutherford, was an American religious leader and the second president of the incorporated Watch Tower Bible and Tract Society. He played a primary role in the organization and doctrinal development of Jehovah's Witnesses, which emerged from the Bible Student movement established by Charles Taze Russell.

A Kingdom Hall is a place of worship used by Jehovah's Witnesses. The term was first suggested in 1935 by Joseph Franklin Rutherford, then president of the Watch Tower Society, for a building in Hawaii. Rutherford's reasoning was that these buildings would be used for "preaching the good news of the Kingdom".
There are various names of God, many of which enumerate the various qualities of a Supreme Being. The English word god is used by multiple religions as a noun to refer to different deities, or specifically to the Supreme Being, as denoted in English by the capitalized and uncapitalized terms God and god. Ancient cognate equivalents for the biblical Hebrew Elohim, one of the most common names of God in the Bible, include proto-Semitic El, biblical Aramaic Elah, and Arabic ilah. The personal or proper name for God in many of these languages may either be distinguished from such attributes, or homonymic. For example, in Judaism the tetragrammaton is sometimes related to the ancient Hebrew ehyeh. It is connected to the passage in Exodus 3:14 in which God gives his name as אֶהְיֶה אֲשֶׁר אֶהְיֶה, where the verb may be translated most basically as "I am that I am", "I shall be what I shall be", or "I shall be what I am". In the passage, YHWH, the personal name of God, is revealed directly to Moses.
The Watch Tower Bible and Tract Society produces a significant amount of printed and electronic literature, primarily for use by Jehovah's Witnesses. Their best known publications are the magazines, The Watchtower and Awake!
Jehovah's Witnesses teach that the League of Nations and the United Nations were set up as a counterfeit of God's Kingdom. Joseph F. Rutherford, second president of the Watch Tower Society, condemned politicians, business leaders and clergy in their support of the League of Nations. Jehovah's Witnesses believe that the United Nations will soon destroy all other religions, and then turn against Jehovah's Witnesses. Jehovah's Witness representatives have sought the services of UN bodies such as the United Nations Department of Public Information and the United Nations Human Rights Committee.
Jehovah's Witnesses believe that the Bible prohibits Christians from accepting blood transfusions. Their literature states that, "'abstaining from ... blood' means not accepting blood transfusions and not donating or storing their own blood for transfusion." The belief is based on an interpretation of scripture that differs from other Christian denominations. It is one of the doctrines for which Jehovah's Witnesses are best known.
Jehovah's Witnesses employ various levels of congregational discipline as formal controls administered by congregation elders. Members who engage in conduct that is considered inappropriate may be counseled privately by elders, and congregational responsibilities may be withheld or restricted.

Christian pacifism is the theological and ethical position according to which pacifism and non-violence have both a scriptural and rational basis for Christians, and affirms that any form of violence is incompatible with the Christian faith. Christian pacifists state that Jesus himself was a pacifist who taught and practiced pacifism and that his followers must do likewise. Notable Christian pacifists include Martin Luther King Jr., Leo Tolstoy, Adin Ballou, Dorothy Day, Ammon Hennacy, and brothers Daniel and Philip Berrigan.
Yahweh is a reconstruction of the name of the God mentioned in the Hebrew Bible.

Christianity is the predominant religion in Paraguay, with Catholicism being its largest denomination. Before the arrival of Spanish missionaries, the people residing in the territory of modern day Paraguay practiced a variety of religions.

Christianity is the largest religion in Nauru, with Nauru Congregational Church being the largest denomination, encompassing 35.71% of the population as of the 2011 census.
Jah is an abbreviated form of Jehovah, a name of God.
The beliefs of Jehovah's Witnesses are based on the Bible teachings of Charles Taze Russell—founder of the Bible Student movement—and successive presidents of the Watch Tower Society, Joseph Franklin Rutherford, and Nathan Homer Knorr. Since 1976, all doctrinal decisions have been made by the Governing Body of Jehovah's Witnesses, a group of elders at the denomination's headquarters. These teachings are disseminated through The Watchtower magazine and other publications of Jehovah's Witnesses, and at conventions and congregation meetings.