The phrase Jesuit missions usually refers to a Jesuit missionary enterprise in a particular area, involving a large number of Jesuit priests and brothers, and lasting over a long period of time.
The phrase Jesuit missions usually refers to a Jesuit missionary enterprise in a particular area, involving a large number of Jesuit priests and brothers, and lasting over a long period of time.

Francis Xavier, venerated as Saint Francis Xavier, was a Navarrese Catholic missionary and saint who was a co-founder of the Society of Jesus.

The Society of Jesus abbreviated SJ, also known as the Jesuits, is a religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The society is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 nations. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. Jesuits also give retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian ministries, and promote ecumenical dialogue.

Guarani are a group of culturally-related indigenous peoples of South America. They are distinguished from the related Tupi by their use of the Guarani language. The traditional range of the Guarani people is in present-day Paraguay between the Paraná River and lower Paraguay River, the Misiones Province of Argentina, southern Brazil once as far east as Rio de Janeiro, and parts of Uruguay and Bolivia.

The Canadian Martyrs, also known as the North American Martyrs, were eight Jesuit missionaries from Sainte-Marie among the Hurons. They were ritually tortured and killed on various dates in the mid-17th century in Canada, in what is now southern Ontario, and in upstate New York, during the warfare between the Iroquois and the Huron. They have subsequently been canonized and venerated as martyrs by the Catholic Church.

The Mission is a 1986 British period drama film about the experiences of a Jesuit missionary in 18th-century South America. Directed by Roland Joffé and written by Robert Bolt, the film stars Robert De Niro, Jeremy Irons, Ray McAnally, Aidan Quinn, Cherie Lunghi, and Liam Neeson.

The Jesuit missions among the Guarani were a type of settlement for the Guaraní people in an area straddling the borders of present-day Paraguay, Brazil, and Argentina. The reductions were established by the Jesuit Order of the Catholic Church early in the 17th century and wound up in the late 18th century after the expulsion of the Jesuit order from the Americas. The reductions have been called an experiment in "socialist theocracy" or a rare example of "benign colonialism". Detractors have said that 'the Jesuits took away the Indians' freedom, forced them to radically change their lifestyle, physically abused them, and subjected them to disease."

The suppression of the Jesuits was the removal of all members of the Society of Jesus from most of the countries of Western Europe and their colonies beginning in 1759, and the abolishment of the order by the Holy See in 1773. The Jesuits were serially expelled from the Portuguese Empire (1759), France (1764), the Two Sicilies, Malta, Parma, the Spanish Empire (1767) and Austria and Hungary (1782).

Regimini militantis Ecclesiae was the papal bull promulgated by Pope Paul III on September 27, 1540, which gave a first approval to the Society of Jesus, also known as the Jesuits, but limited the number of its members to sixty.

The Revolt of the Comuneros was a series of uprisings by settlers in Paraguay in the Viceroyalty of Peru against the Spanish authorities from 1721–1725 and 1730–1735. The underlying cause of the unrest was strong anti-Jesuit feelings among the Paraguayans and dislike for any governor seen as favoring the Jesuits. In the resumption of the revolt in 1730, economic issues came to fore as well. The rebel organization split in its second phase, as the rural poor and the urban elite each formed their own factions with similar grievances against the Jesuits, but incompatible politics. Paraguay had an unusually strong tradition of self-rule; the colonists did not have a tradition of strict obedience to everything the Spanish Crown's governor decreed. This independence helped push the revolt forward.
Gaspar Coelho was a Portuguese Jesuit missionary. He replaced Francisco Cabral as the Superior and Vice-Provincial of the Jesuit mission in Japan during the late 16th century. He catalyzed the disfavor of Toyotomi Hideyoshi against the Jesuit mission in Japan in 1587.
The General Congregation is an assembly of the Jesuit representatives from all parts of the world, and serves as the highest authority in the Society of Jesus. A General Congregation (GC) is always summoned on the death or resignation of the administrative head of the order, called the Superior General or Father General, to choose his successor, and it may be called at other times if circumstances warrant. A smaller congregation of worldwide representatives meets every three years to discuss internal business and to decide the need for a general congregation.

Sacred Heart Church is a Roman Catholic church and parish in Wimbledon, South West London initially run by the Jesuits, that serves the Catholic community of Wimbledon and surrounding areas. It is in the Archdiocese of Southwark and is situated next to Wimbledon College and Donhead Preparatory School. The main entrance to the church is on Edge Hill road, but the church can also be accessed from the adjacent Darlaston Road.

São Miguel das Missões is a municipality in Rio Grande do Sul state, southern Brazil. Important 17th century Spanish Jesuit mission ruins are located in the municipality. San Miguel Mission is within Santo Ângelo Microregion, and the Riograndense Northwest Mesoregion. The city covers 1,246 square kilometres (481 sq mi) and had a population of 7,683 residents.
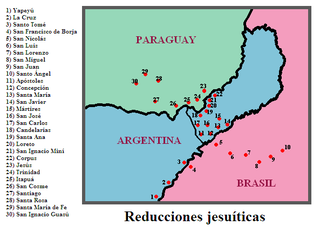
The Guarani War of 1756, also called the War of the Seven Reductions, took place between the Guaraní tribes of seven Jesuit Reductions and joint Spanish-Portuguese forces. It was a result of the 1750 Treaty of Madrid, which set a line of demarcation between Spanish and Portuguese colonial territory in South America.

The Ajacán Mission was a Spanish attempt in 1570 to establish a Jesuit mission in the vicinity of the Virginia Peninsula to bring Christianity to the Virginia Indians. The effort to found St. Mary's Mission predated the founding of the English settlement at Jamestown, Virginia, by about 36 years. In February 1571, the entire party was massacred by Indians except for Alonso de Olmos. The following year, a Spanish party from Florida went to the area, rescued Alonso, and killed an estimated 20 Indians.
Missionary work of the Catholic Church has often been undertaken outside the geographically defined parishes and dioceses by religious orders who have people and material resources to spare, and some of which specialized in missions. Eventually, parishes and dioceses would be organized worldwide, often after an intermediate phase as an apostolic prefecture or apostolic vicariate. Catholic mission has predominantly been carried out by the Latin Church in practice.

The Jesuit Missions of Chiquitos are located in Santa Cruz department in eastern Bolivia. Six of these former missions collectively were designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1990. Distinguished by a unique fusion of European and Amerindian cultural influences, the missions were founded as reductions or reducciones de indios by Jesuits in the 17th and 18th centuries to convert local tribes to Christianity.

Jesuit missions in North America were attempted in the late 16th century, established early in the 17th century, faltered at the beginning of the 18th, disappeared during the suppression of the Society of Jesus around 1763, and returned around 1830 after the restoration of the Society. The missions were established as part of the colonial drive of France and Spain during the period, the "saving of souls" being an accompaniment of the constitution of Nouvelle-France and early New Spain. The efforts of the Jesuits in North America were paralleled by their China missions on the other side of the world, and in South America. They left written documentation of their efforts, in the form of The Jesuit Relations.

The history of the missions of the Jesuits in China is part of the history of relations between China and the Western world. The missionary efforts and other work of the Society of Jesus, or Jesuits, between the 16th and 17th century played a significant role in continuing the transmission of knowledge, science, and culture between China and the West, and influenced Christian culture in Chinese society today.