Life
Johann Christian von Boyneburg was born into a family whose members had often been in the official Hessian state service. His father was the council and aristocratic marshal Johann Berthold von Boineburg-Lengsfeld († 1640) and his mother Barbara Sibylla von Buttlar († 1624).
In 1648 he married Anna Christine († 1689), daughter of the president of the Hessian court of law Kuno Quirin Schütz von Holzhausen.
Johann Christian von Boyneburg became the Hessian ambassador at the Swedish court, later a privy councillor (Geheimrat) and in 1650 first government minister. In 1656 he converted to the Catholic faith.
Von Boyneburg motivated Leibniz to move to Frankfurt. Leibniz also became the teacher of Boyneburg's son Philipp Wilhelm.

Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat who is credited, alongside Sir Isaac Newton, with the creation of calculus in addition to many other branches of mathematics, such as binary arithmetic and statistics. Leibniz has been called the "last universal genius" due to his vast expertise across fields, which became a rarity after his lifetime with the coming of the Industrial Revolution and the spread of specialized labor. He is a prominent figure in both the history of philosophy and the history of mathematics. He wrote works on philosophy, theology, ethics, politics, law, history, philology, games, music, and other studies. Leibniz also made major contributions to physics and technology, and anticipated notions that surfaced much later in probability theory, biology, medicine, geology, psychology, linguistics and computer science.

Christian Wolff was a German philosopher. Wolff is characterized as one of the most eminent German philosophers between Leibniz and Kant. His life work spanned almost every scholarly subject of his time, displayed and unfolded according to his demonstrative-deductive, mathematical method, which some deem the peak of Enlightenment rationality in Germany.
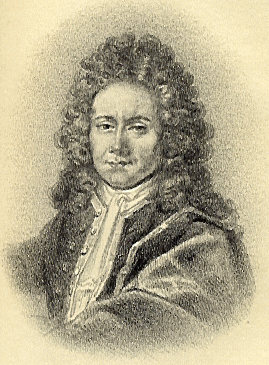
Johann Ernst Elias Bessler, known as Orffyreus or Orffyré, was a German entrepreneur who claimed to have built several perpetual motion machines. Those claims generated considerable interest and controversy among some of the leading natural philosophers of the day, including Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Johann Bernoulli, John Theophilus Desaguliers, and Willem 's Gravesande. The modern scientific consensus is that Bessler perpetrated a deliberate fraud, although the details of this have not been satisfactorily explained.

Angelus Silesius, OFM, born Johann Scheffler, was a German Catholic priest, physician, mystic and religious poet. Born and raised a Lutheran, he began to read the works of medieval mystics while studying in the Netherlands and became acquainted with the works of the German mystic Jacob Böhme through Böhme's friend Abraham von Franckenberg. Silesius's display of his mystic beliefs caused tension with Lutheran authorities and led to his eventual conversion to Catholicism in 1653, wherein he adopted the name Angelus and the epithet Silesius ("Silesian"). He entered the Franciscans and was ordained a priest in 1661. Ten years later, in 1671, he retired to a Jesuit house where he remained for the rest of his life.

Johann Helfrich von Müller was an engineer in the Hessian army who conceived the difference engine in 1786, an idea that later evolved into modern computers. In 1784, he was responsible for an improved adding machine based on principles of Leibniz's stepped reckoner.

The Berlin Observatory is a German astronomical institution with a series of observatories and related organizations in and around the city of Berlin in Germany, starting from the 18th century. It has its origins in 1700 when Gottfried Leibniz initiated the "Brandenburg Society of Science″ which would later (1744) become the Prussian Academy of Sciences. The Society had no observatory but nevertheless an astronomer, Gottfried Kirch, who observed from a private observatory in Berlin. A first small observatory was furnished in 1711, financing itself by calendrical computations.

Acta Eruditorum was the first scientific journal of the German-speaking lands of Europe, published from 1682 to 1782.
Friedrich Karl of Limburg Stirum, was Count of Limburg Styrum and Bronckhorst, and Sovereign Lord of Gemen.

Johann Wolfgang von Goethe was a German polymath, who is widely regarded as the greatest and most influential writer in the German language. His work has had a profound and wide-ranging influence on Western literary, political, and philosophical thought from the late 18th century to the present day. A poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic, his works include plays, poetry and aesthetic criticism, as well as treatises on botany, anatomy, and color.

Johann Friedrich Karl von Ostein was the Archbishop of Mainz, Elector of Mainz and Prince-Bishop of Worms.

Johann Valentin Tischbein was a German painter from the Tischbein family of artists.

Elisabeth of Hesse was Hereditary Princess of Saxony in 1519-1537 by marriage to John of Saxony. After the death of her husband, she managed her Wittum, the Saxon districts of Rochlitz and Kriebstein between 1537 and 1547, earning her the name Elisabeth of Rochlitz. She allowed for the spread of Protestantism in her territories. She acted as mediator between her Catholic mother and Lutheran brother, and as the nurse of Maurice of Saxony.

Jestädt is a borough of the Municipality of Meinhard in the Werra-Meißner-Kreis in the State of Hesse of Germany.

Christian Seybold was a German painter in the Baroque style. He is best known for his detailed, realistic character heads and portraits, which sometimes stood out from the idealized ones preferred at that time. Most of his works can be classified as tronies.
Gotthelf Leberecht Glaeser was a German painter of the Biedermeier movement.

Johann Georg Christian Kestner was a German lawyer and archivist. He is also notable as the model for Lotte's husband Albert in The Sorrows of Young Werther by Goethe, with Kestner's fiancée Charlotte Buff used as the model for Lotte herself.
Christian Johann Christoph Schreiber was a German theologian, philologist, philosopher, and poet. He was also the Superintendent of the dioceses of Lengsfeld and Dermbach. He was connected in friendship or correspondence to writers and philosophers of his time, and published poetry, sermons, historical and philosophical works.

Friedrich Moritz Christian Pfeiffer was a German jurist and politician.
Johann PeterBoßler [ˈbɔslɐ] also written Bossler and Bosler was a German master gunsmith and hunting arms manufacturer. He was in the service of the House of Hesse-Darmstadt and is considered an outstanding figure in the history of hunting in Hesse-Darmstadt.
Count Johann Franz Heinrich Carl von Ostein was a German lawyer, Imperial Privy Councilor and Imperial Ambassador.














