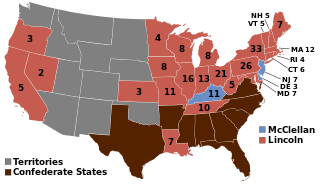
The 1864 United States presidential election was the 20th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 8, 1864. Near the end of the American Civil War, incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 212–21 in the electoral college, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats.

Mathew B. Brady was an American photographer. Known as one of the earliest and most famous photographers in American history, he is best known for his scenes of the Civil War. He studied under inventor Samuel Morse, who pioneered the daguerreotype technique in America. Brady opened his own studio in New York City in 1844, and went on to photograph U.S. presidents John Quincy Adams, Abraham Lincoln, Millard Fillmore, Martin Van Buren, and other public figures.

The American Civil War was the most widely covered conflict of the 19th century. The images would provide posterity with a comprehensive visual record of the war and its leading figures, and make a powerful impression on the populace. Something not generally known by the public is the fact that roughly 70% of the war's documentary photography was captured by the twin lenses of a stereo camera. The American Civil War was the first war in history whose intimate reality would be brought home to the public, not only in newspaper depictions, album cards and cartes-de-visite, but in a popular new 3D format called a "stereograph," "stereocard" or "stereoview." Millions of these cards were produced and purchased by a public eager to experience the nature of warfare in a whole new way.

Titian Ramsay Peale was an American artist, naturalist, and explorer from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He was a scientific illustrator whose paintings and drawings of wildlife are known for their beauty and accuracy.

A tintype, also known as a melanotype or ferrotype, is a photograph made by creating a direct positive on a thin sheet of metal, colloquially called 'tin', coated with a dark lacquer or enamel and used as the support for the photographic emulsion. It was introduced in 1853 by Adolphe Alexandre Martin in Paris, like the daguerreotype was fourteen years before by Daguerre. The daguerreotype was established and most popular by now, though the primary competition for the tintype would have been the ambrotype, that shared the same collodion process, but on a glass support instead of metal. Both found unequivocal, if not exclusive, acceptance in North America. Tintypes enjoyed their widest use during the 1860s and 1870s, but lesser use of the medium persisted into 1930s and it has been revived as a novelty and fine art form in the 21st century. It has been described as the first "truly democratic" medium for mass portraiture.

Montgomery Cunningham Meigs was a career United States Army officer and military and civil engineer, who served as Quartermaster General of the U.S. Army during and after the American Civil War. Although a Southerner from Georgia, Meigs strongly opposed secession and supported the Union. His record as Quartermaster General was regarded as outstanding, both in effectiveness and in ethical probity, and Secretary of State William H. Seward viewed Meigs' leadership and contributions as key factors in the Union victory in the war.

Alexander Gardner was a Scottish photographer who immigrated to the United States in 1856, where he began to work full-time in that profession. He is best known for his photographs of the American Civil War, U.S. President Abraham Lincoln, and of the conspirators and the execution of the participants in the Lincoln assassination plot.

War photography involves photographing armed conflict and its effects on people and places. Photographers who participate in this genre may find themselves placed in harm's way, and are sometimes killed trying to get their pictures out of the war arena.

James Robertson (1813–1888) was an English gem and coin engraver who worked in the Mediterranean region, and who became a pioneering photographer working in the Crimea and possibly India. He is noted for his Orientalist photographs and for being one of the first war photographers.
Documentary photography usually refers to a popular form of photography used to chronicle events or environments both significant and relevant to history and historical events as well as everyday life. It is typically undertaken as professional photojournalism, or real life reportage, but it may also be an amateur, artistic, or academic pursuit.

Timothy H. O'Sullivan was an American photographer widely known for his work related to the American Civil War and the Western United States.

James "Spider" Martin was an American photographer known for his work documenting the American Civil Rights Movement in 1965, specifically Bloody Sunday and other incidents from the Selma to Montgomery marches.

Thomas C. Roche was a photographer known for his photographs of the American Civil War.

Jeremiah Gurney was an American daguerreotype photographer operating in New York.

Presidents of the United States have frequently appeared on U.S. postage stamps since the mid-19th century. The United States Post Office Department released its first two postage stamps in 1847, featuring George Washington on one, and Benjamin Franklin on the other. The advent of presidents on postage stamps has been definitive to U.S. postage stamp design since the first issues were released and set the precedent that U.S. stamp designs would follow for many generations.
The practice and appreciation of photographyin the United States began in the 19th century, when various advances in the development of photography took place and after daguerreotype photography was introduced in France in 1839. The earliest commercialization of photography was made in the country when Alexander Walcott and John Johnson opened the first commercial portrait gallery in 1840. In 1866, the first color photograph was taken. Only in the 1880s, would photography expand to a mass audience with the first easy-to-use, lightweight Kodak camera, issued by George Eastman and his company.

George Norman Barnard was an American photographer most well known for his photographs from the American Civil War era. He is often noted as G. N. Barnard.

In the 1864 U.S. presidential election, the Democrats nominated Union Army General George McClellan for U.S. President and Ohio U.S. Representative George Pendleton for U.S. Vice President. During the campaign, McClellan vowed to do a better job of prosecuting the Union Army effort in the American Civil War than incumbent U.S. President Abraham Lincoln did. Ultimately, the McClellan-Pendleton ticket lost to the National Union ticket of Abraham Lincoln and former U.S. Senator Andrew Johnson.

Photography in India refers to both historical as well as to contemporary photographs taken in modern-day India.

A Harvest of Death is the title of a photograph taken by Timothy H. O'Sullivan, sometime between July 4 and 7, 1863. It shows the bodies of soldiers killed at the Battle of Gettysburg during the American Civil War, stretched out over part of the battlefield.



















