Pascal, Pascal's or PASCAL may refer to:
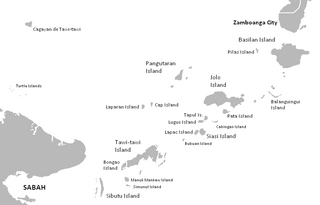
The Sulu Archipelago is a chain of islands in the Pacific Ocean, in the southwestern Philippines. The archipelago forms the northern limit of the Celebes Sea and southern limit of the Sulu Sea. The Sulu Archipelago islands are within the Mindanao island group, consisting of the provinces of Basilan, Sulu, and Tawi-Tawi; hence the archipelago is sometimes referred to as Basulta, derived from the first syllables of the three provinces.

The Sulu Sea is a body of water in the southwestern area of the Philippines, separated from the South China Sea in the northwest by Palawan and from the Celebes Sea in the southeast by the Sulu Archipelago. Borneo is found to the southwest and Visayas to the northeast.

Sulu, officially the Province of Sulu, is a province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM).

Jolo is a volcanic island in the southwest Philippines and the primary island of the province of Sulu, on which the capital of the same name is situated. It is located in the Sulu Archipelago, between Borneo and Mindanao, and has a population of approximately 500,000 people.

Jolo, officially the Municipality of Jolo, is a 1st class municipality and capital of the province of Sulu, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 137,266 people.
The Philippine Campaign Medal is a medal of the United States Armed Forces which was created to denote service of U.S. military men in the Philippine–American War between the years of 1899 and 1913. Although a single service medal, the Philippine Campaign Medal was issued under separate criteria for both the United States Army and the U.S. Navy.
The Battle of Bud Dajo may refer to:

Francisco de Sande Picón was the third Spanish governor and captain-general of the Philippines from August 25, 1575 to April 1580. He established the Royal City of Nueva Cáceres, now known as Naga City.
Yolo or YOLO may refer to:

The Jolo Group of Volcanoes, more commonly referred to as the Jolo Group, are an active group of volcanoes in the island of Jolo in Southern Philippines. The Global Volcanism Program lists Jolo as one of the active volcanoes in the Philippines while the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) collectively list the group as Bud Dajo, one of the cinder cones on the island.
Our Lady of Mount Carmel Cathedral or Cathedral of Our Lady of Carmel may refer to:

The Spanish–Moro conflict was a series of battles in the Philippines lasting over several centuries. It began during the Spanish Philippines and lasted until the Spanish–American War, when Spain finally began to subjugate the Moro people after centuries of attempts to do so. Spain ultimately conquered portions of the Mindanao and Jolo islands and turned the Sultanate of Sulu into a protectorate, establishing geographic dominance over the region until the Spanish-American War. Moro resistance continued.
The 2000 Sipadan kidnappings was a hostage crisis in Sabah, Malaysia, and the southern Philippines that began with the seizing of twenty-one hostages from the dive resort island of Sipadan at approximately 6:15 p.m. on 23 April 2000, by up to six Abu Sayyaf (ASG) bandits. Taken hostage were 10 tourists from Europe and the Middle East and 11 Malaysian resort workers, 19 non-Filipino nationals in total. The hostages were taken to an Abu Sayyaf base in Jolo, Sulu.

The Japanese Invasion of Davao and on Jolo in the Sulu Archipelago on 19 December 1941 was one in a series of advance landings made by Imperial Japanese forces as first step in their invasion of the Philippines. The purpose was to cut off the possibility of reinforcements reaching Luzon from the south and to complete the encirclement of American forces there, with the secondary purpose of establishing a base from which the IJA 16th Army could launch an invasion of British North Borneo and the Netherlands Indies. The first invasion of the Philippines was at Batan Island on 8 December 1941. This was followed by Vigan, Aparri, Legaspi, Davao, and Jolo over the next few days
The battle of Jolo, also referred to as the burning of Jolo or the siege of Jolo, was a military confrontation between the Moro National Liberation Front (MNLF) and the government of the Philippines in February 1974 in the municipality of Jolo, in the southern Philippines.

Panyalam or panyam, is a traditional Filipino-Bangsamoro fried rice pancake. It is made with ground glutinous rice, muscovado, and coconut milk mixed into a batter that is deep-fried.

In the morning of January 27, 2019, two bombs exploded at the Roman Catholic Cathedral of Our Lady of Mount Carmel in Jolo, Sulu, Philippines. Twenty people were killed and 102 others injured. The bombings took place a week after the autonomy plebiscite held on January 21 for the creation of Bangsamoro. It is believed that the Abu Sayyaf carried out the attacks, and the Islamic State claimed responsibility. President Rodrigo Duterte responded by issuing an "all-out war" directive against the Abu Sayyaf. The bombings were widely condemned by other countries and organizations.
2019 Sulu bombings may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.










