Josiah Tattnall may refer to:
- Josiah Tattnall (politician) (1765–1803), American politician
- Josiah Tattnall Sr. (b. 1740), British colonist
- Josiah Tattnall III (1794–1871), American naval officer
Josiah Tattnall may refer to:

Tattnall County is a county located in the southeast portion of the U.S. state of Georgia, located within the Magnolia Midlands, a part of the Historic South region. As of the 2020 census, the population was 22,842. The county seat is Reidsville. Tattnall County was created on December 5, 1801, from part of Montgomery County, Georgia by the Georgia General Assembly.

Reidsville is a city in, and county seat of, Tattnall County, Georgia. The population was 2,515 in 2020. The Georgia State Prison is near Reidsville.

USS Tattnall (DDG-19) was a Charles F. Adams-class guided missile-armed destroyer of the United States Navy. She was named for Commodore Josiah Tattnall III USN (1794–1871) – also commandant of the CSS Virginia, and an admiral in the Confederate States Navy – who made the adage "blood is thicker than water" a part of American history.
Josiah Quincy may refer to:

USS Tattnall (DD–125) was a Wickes-class destroyer in the United States Navy during World War II. She was the first ship named for Captain Josiah Tattnall III.

Commodore Josiah Tattnall was a United States Navy officer during the War of 1812, the Second Barbary War and the Mexican–American War. He later served in the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War.
The fourth USS Spitfire was a sidewheel gunboat in the United States Navy during the Mexican–American War.

CSSResolute was a tugboat built in 1858 at Savannah Georgia as the Ajax which served in the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War.
CSS Savannah, later called Old Savannah and Oconee, was a gunboat in the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War.
Josiah Tattnall was an American planter, soldier and politician from Savannah, Georgia. He represented Georgia in the U.S. Senate from 1796 to 1799, and was the 25th Governor of Georgia in 1801 and 1802. Born near Savannah, Georgia, at Bonaventure Plantation in the early 1760s to Mary Mullryne and Josiah Tattnall, he studied at Eton School before joining Anthony Wayne's troops at Ebenezer during the American Revolutionary War. After the war, he was elected brigadier general of the 1st Regiment in the Georgia Militia. He helped to rescind the Yazoo land fraud of 1795. He died in Nassau, New Providence.
Edward Fenwick Tattnall was an American politician, soldier and lawyer.
Josiah Tattnall was a British emigrant to colonial America who became notable for his acts in support of the Crown during his time in Savannah in the Province of Georgia.
Josiah is a masculine given name derived from the Hebrew Yoshi-yahu (Hebrew: יֹאשִׁיָּהוּ, Modern: Yošiyyáhu, Tiberian: Yôšiyyāhû, "Yahweh has healed".
Tattnall may refer to:
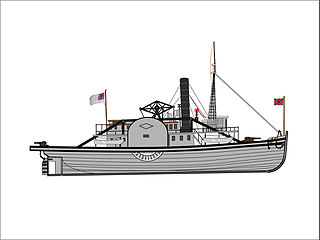
CSS Sampson, sometimes spelled Samson, was employed as a tugboat, prior to her purchase by the Confederate Government in 1861.
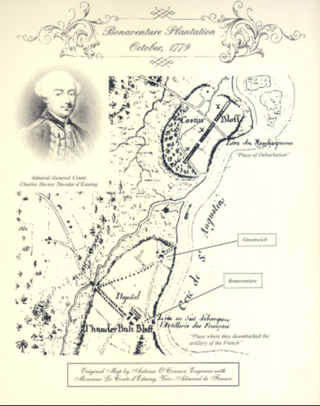
Bonaventure Plantation was a plantation founded in colonial Savannah, Province of Georgia, on land now occupied by Greenwich and Bonaventure cemeteries. The site was 600 acres (2.4 km2), including a plantation house and private cemetery, located on the Wilmington River, about 3.5 miles east of the Savannah colony.
Josiah Scott may refer to:

Tattnall Street is a prominent street in Savannah, Georgia, United States. Located between Jefferson Street to the west and Barnard Street to the east, it runs for about 0.53 miles (0.85 km) from West Liberty Street in the north to West Gwinnett Street in the south. It passes through the Savannah Historic District, a National Historic Landmark District.
John Mullryne was a British Army colonel who established Bonaventure Plantation in Savannah, Province of Georgia, in 1761. A supporter of the Crown, he later drew the ire of the colonists after aiding the escape of James Wright, the British royal governor of the Province of Georgia, through his property during the American Revolutionary War.

The 1801 Georgia gubernatorial election was held on 6 November 1801 in order to elect the governor of Georgia. Democratic-Republican candidate and former United States senator from Georgia Josiah Tattnall defeated Federalist candidate and former member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Georgia's at-large congressional district Thomas P. Carnes and former Democratic-Republican governor Jared Irwin in a Georgia General Assembly vote.