Jraberd may refer to:
- Jraberd Melikdom , see Melikdoms of Karabakh
- Jraberd, Martakert
- Alternate name for Mülküdərə
- Jraberd FC
Jraberd may refer to:
Khamsa may refer to:

Gardman, also known as Gardmank' or Gardmanadzor, was one of the eight cantons of the ancient province of Utik' in the Kingdom of Armenia and simultaneously, together with the canton of Tuch'katak, an Armenian principality. It roughly corresponded within the Gazakh, Shamkir, Aghstafa, Dashkasan, Goygol, Tovuz, Gadabay districts of modern-day Azerbaijan and the original Tavush Region of Armenia. Gardman was also the name of the central fortress of the canton.
Gulistan, Golestan or Golastan means "flower land" in Persian language.

Yeghishe Arakyal Monastery or Monastery of Yeghishe the Apostle is an Armenian Apostolic Church in Nagorno-Karabakh, located close to the village of Madagiz, on the bank of the Tartar River. The complex comprises the church, seven chapels, a cemetery, and ruins of other buildings.

Мelik was a hereditary Armenian noble title used in Eastern Armenia from the Late Middle Ages until the nineteenth century. The meliks represented some of the last remnants of the old Armenian nobility. The most prominent and powerful meliks were those of Karabagh (Artsakh) and Syunik, which ruled autonomous or semi-autonomous principalities known as melikdoms under Iranian suzerainty. Meliks also existed in Yerevan, Nakhichevan, Sevan, Lori, Northwestern Persia, and other areas, although outside of Karabagh and Syunik most were merely hereditary leaders of local Armenian communities, not rulers of principalities.
Varanda may refer to:

Panah Ali Khan Javanshir was the founder and first ruler of the Karabakh Khanate under Persian suzerainty.

The Hasan-Jalalyans were a medieval Armenian dynasty that ruled over parts of the South Caucasus. From the early thirteenth century, the family held sway in Khachen in what are now the regions of lower Karabakh, Nagorno-Karabakh, and Syunik in modern Armenia. The family was founded by Hasan-Jalal Dawla, an Armenian feudal prince from Khachen. The Hasan-Jalalyans maintained their autonomy over the course of several centuries of nominal foreign domination by the Seljuk Turks, Persians and Mongols. They, along with the other Armenian princes and meliks of Khachen, saw themselves as holding the last bastion of Armenian independence in the region.

Kalbajar is a city and the capital of the Kalbajar District of Azerbaijan. Located on the Tartar river valley, it is 458 kilometres (285 mi) away from the capital Baku.

Martakert or Aghdara is a town de facto in the breakaway Republic of Artsakh as the administrative capital of its Martakert Province, de jure in the Tartar District of Azerbaijan, in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh. The town has an ethnic Armenian-majority population, and also had an Armenian majority in 1989. The town underwent heavy destruction by Azerbaijani forces while under their control during the First Nagorno-Karabakh War.

Zar is a village in the Kalbajar District of Azerbaijan.

Jraberd or Chilabord is a village de facto in the Martakert Province of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh, de jure in the Tartar District of Azerbaijan, in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh. The village has an ethnic Armenian-majority population, and also had an Armenian majority in 1989.
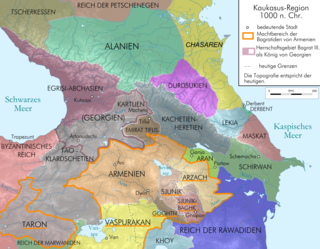
The Kingdom of Artsakh was a medieval dependent Armenian kingdom on the territory of Syunik and Artsakh provinces, Gardman canton of Utik province, Mazaz and Varazhnunik canton of Ayrarat province. Contemporary sources referred to it as the Khachen. However, because the domain of Khachen during the reign of Prince Hasan Jalal included the entire territory of the modern Nagorno Karabakh Republic plus many contiguous lands to its west, south and north, his principality was often called the Kingdom of Artsakh. The royal house of Khachen was a cadet branch of the ancient Syunid dynasty and was named Khachen, after its main stronghold. Hasan-Jalal traced his descent to the Armenian Aranshahik dynasty, a family that predated the establishment of the Parthian Arsacids in the region.

Yerits Mankants Monastery is a 17th-century Armenian monastery de facto in the Martakert Province of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh, de jure in the Tartar District of Azerbaijan. The monastery is located in the mountains to the west of Maghavuz, southwest of Tonashen, and close to the fortress of Jraberd.

The province of Karabakh was a north-western province of the Safavid Iran, centered on the geographic region of Karabakh.

The Five Melikdoms of Karabakh, also known as Khamsa Melikdoms, were Armenian feudal entities on the territory of modern Nagorno-Karabakh and neighboring lands, from the dissolution of the Principality of Khachen in the 15th century to the abolition of ethnic feudal entities by the Russian Empire in 1822.
Shahverdi Khan Ziyadoghlu was the beylerbey of Karabakh from 1740 to 1743 and first khan of Ganja from 1747 to 1760. He was from the Ziyadoglu branch of the Qajar clan who ruled the Beylerbeylik of Karabakh as hereditary governors.

Atabekians — Armenian Princely (Meliqly) house of Lords of the Jraberd principality (Meliqdom) in Artsakh, which ruled in the 19th century. The most renowned representative of this family was Prince Hovhannes (Vani) Atabekian, Prince of Jraberd, who took an active part in the Russo-Persian War (1804–13).
Melik Shahnazar II was the melik of Varanda, one of the five Melikdoms of Karabakh, in the 18th century. He is a controversial figure in Armenian history, whose actions contributed significantly to the demise of Armenian Melikdoms of Karabakh.