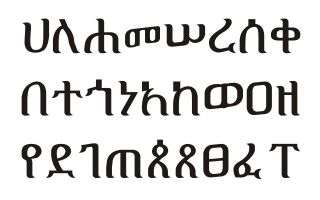Haile Selassie I was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1930 to 1974. He rose to power as Regent Plenipotentiary of Ethiopia (Enderase) for Empress Zewditu from 1916 until 1930. Haile Selassie is widely considered a defining figure in modern Ethiopian history, and the major figure of Rastafari, a religious movement in Jamaica that emerged shortly after he became emperor in the 1930s. Before he rose to power he defeated Ras Gugsa Welle Bitul of Begemder at the Battle of Anchem in 1928. He was a member of the Solomonic dynasty, which claims to trace lineage to Emperor Menelik I, a legendary figure believed by the claimants to be the son of King Solomon and the Queen of Sheba, who they name as Makeda.
Amharic is an Ethiopian Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It is spoken as a first language by the Amharas, and also serves as a lingua franca for all other populations residing in major cities and towns in Ethiopia.

Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the Northeast, East and Southeast, Kenya to the South, South Sudan to the West, and Sudan to the Northwest. Ethiopia covers a land area of 1,112,000 square kilometres. As of 2023, it is home to around 128 million inhabitants, making it the 13th-most populous country in the world, the 2nd-most populous in Africa after Nigeria, and the most populated landlocked country on Earth. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African and Somali tectonic plates.
Operation Moses was the covert evacuation of Ethiopian Jews from Sudan during a civil war that caused a famine in 1984. Originally called Gur Aryeh Yehuda by Israelis, the United Jewish Appeal changed the name to "Operation Moses".

The Beta Israel, or Ethiopian Jews, are an African community of the Jewish diaspora. They coalesced in the Kingdom of Aksum and the Ethiopian Empire, which is currently divided between the Amhara Region and Tigray Region in modern-day Ethiopia. After the founding of the State of Israel in 1948, most of the Beta Israel immigrated to Israel or were evacuated from Africa through several initiatives by the Israeli government.

Berbere is a spice mixture whose constituent elements usually include chili peppers, coriander, garlic, ginger, Ethiopian holy basil (besobela) seeds, korarima, rue, ajwain or radhuni, nigella, and fenugreek. It is a key ingredient in the cuisines of Ethiopia and Eritrea. Berbere also refers to chili pepper itself.

The Hamar people are a community inhabiting southwestern Ethiopia. They live in Hamer woreda, a fertile part of the Omo River valley, in the Debub Omo Zone of the former South Ethiopia Regional State (SERS). They are largely pastoralists, so their culture places a high value on cattle.
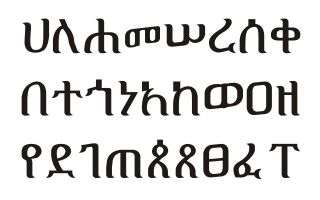
Geʽez is a script used as an abugida (alphasyllabary) for several Afro-Asiatic and Nilo-Saharan languages of Ethiopia and Eritrea. It originated as an abjad and was first used to write the Geʽez language, now the liturgical language of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church, the Eritrean Catholic Church, the Ethiopian Catholic Church, and Haymanot Judaism of the Beta Israel Jewish community in Ethiopia. In the languages Amharic and Tigrinya, the script is often called fidäl (ፊደል), meaning "script" or "letter". Under the Unicode Standard and ISO 15924, it is defined as Ethiopic text.

The Ethiopian dwarf mongoose, also known as the desert dwarf mongoose or Somali dwarf mongoose, is a mongoose native to East Africa, particularly Ethiopia, Kenya, and Somalia.

Jacques Faitlovitch (1881–1955) was an anthropologist.

Tella or talla is a traditional beer from Ethiopia. It is brewed from various grains, which can change depending on location. These typically include barley or teff. Depending on region, wheat, sorghum, or corn may be used; spices can also be added. Dried and ground shiny-leaf buckthorn leaves are used for fermentation. The drink is made in a clay pot. The pot is washed with a plant called grawa. After rinsing it is smoked with weyra or Abyssinian rose. The alcohol content of tella is usually around 2–4 volume percent.

Mitmita is a powdered seasoning mix used in Ethiopia. It is orange-red in color and contains ground African bird's eye chili peppers, Ethiopian cardamom (korerima), cloves, and salt. It occasionally has other spices including cinnamon, cumin, and ginger.

The Ethiopian passport is a travel document issued to citizens of Ethiopia for international travel. The document is a biometric machine-readable passport with a burgundy cover with the text "Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia" above the coat of arms, and the text "passport" below it in Amharic and English. The passport is valid for 5 years and contains 64 pages.

Ethiopian-Greek relations are the international relations between Ethiopia and Greece. In general, bilateral relations between the two countries have been limited, though they have maintained a formal relationship for over a century, including via the signature of several bilateral trade deals.

Ethiopia's participation in the Paralympic Games has been sporadic. The country made its Paralympic début at the 1968 Summer Games in Tel Aviv, sending two competitors who both competed in both athletics and table tennis. Ethiopia was then absent from the Games for almost a decade, returning in 1976 with a one-man delegation Abraham Habte, who entered athletics, lawn bowls and table tennis. In 1980, Habte was again Ethiopia's only representative, this time competing only in lawn bowls. Ethiopia then entered a prolonged period of absence, before sending a single runner to the 2004 Games. In 2008, the country entered a two-man delegation in athletics. In 2012, Wondiye Fikre Indelbu became the first Ethiopian to win a medal in the Paralympic Games, winning a silver in the men's 1500 meters - T46 event in athletics.
La Bohème is a 2009 short film directed by Werner Herzog. The four-minute film features images of life in Ethiopia set to the duet "O soave fanciulla" from Puccini's opera La bohème, sung by Peter Auty and Mary Plazas. It was part of a series of short films commissioned by Sky Arts and English National Opera.
A number of Ethiopian sign languages have been used in various Ethiopian schools for the deaf since 1971, and at the primary level since 1956. Ethiopian Sign Language, presumably a national standard, is used in primary, secondary, and—at Addis Ababa University—tertiary education, and on national television. The Ethiopian Deaf Community uses the language as a marker of identity.

Lamb is a 2015 Ethiopian drama film directed by Yared Zeleke. It was screened in the Un Certain Regard section at the 2015 Cannes Film Festival. It was the first Ethiopian film to be included in the Official Selection. It was screened in the Contemporary World Cinema section of the 2015 Toronto International Film Festival. The film was selected as the Ethiopian entry for the Best Foreign Language Film at the 88th Academy Awards but it was not nominated.
Yared Zeleke is an Ethiopian film director from Addis Ababa. He has an M.F.A. in Writing and Directing from New York University. His first feature film, Lamb, was screened at the 2015 Cannes Film Festival, Un Certain Regard. It is the first film from Ethiopia to have been officially selected in the festival's 68-year history.

The Cinema of Ethiopia and the film industry in general are relatively recent phenomena in Ethiopia. The Ethiopian film industry is growing but faces many problems that have prevented it from fully flourishing. Historically, live stage theater enjoyed more popularity in Ethiopia, creating a handful of relatively successful stage actors. Ethiopian films began modernizing in the 2000s, implementing Amharic, but due to wide home video and DVD distribution, they are often frustrated by copyright infringement in the presence of piracy. This was reduced in the early 2010s with the intervention of the government and the imposition of policy. Despite recent developments, the Ethiopian film industry continues to lack quality compared to modern world cinema and has a low budget amateurish style.