
A carbon sink is a natural or artificial reservoir that stores carbon-containing chemical compounds accumulated over an indefinite period of time. The process by which carbon sinks remove carbon dioxide (CO
2) from the atmosphere is known as carbon sequestration. Public awareness of the significance of CO2 sinks has grown since passage of the Kyoto Protocol, which promotes their use as a form of carbon offset. There are also different strategies used to enhance this process.
Gas reinjection is the reinjection of natural gas into an underground reservoir, typically one already containing both natural gas and crude oil, in order to increase the pressure within the reservoir and thus induce the flow of crude oil or else sequester gas that cannot be exported. This is not to be confused with gas lift, where gas is injected into the annulus of the well rather than the reservoir. After the crude has been pumped out, the natural gas is once again recovered. Since many of the wells found around the world contain heavy crude, this process increases their production. The basic difference between light crude and heavy crude is its viscosity and pumpability - the lighter the crude the easier it is to pump. Recovery of hydrocarbons in a well is generally limited to 50% and 75-80%. Recycling of natural gas or other inert gases causes the pressure to rise in the well, thus causing more gas molecules to dissolve in the oil lowering its viscosity and thereby increasing the well's output. Air is not suitable for repressuring wells because it tends to cause deterioration of the oil, thus carbon dioxide or natural gas is used to repressure the well. The term 'gas-reinjection' is also sometimes referred to as repressuring--the term being used only to imply that the pressure inside the well is being increased to aid recovery.
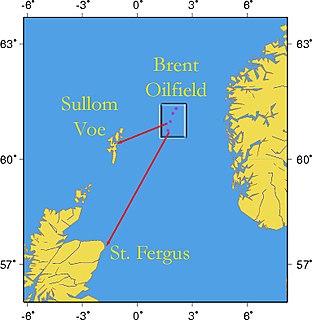
The Brent field is an oil and gas field located in the East Shetland Basin of the North Sea, 186 kilometres (116 mi) north-east of Lerwick, Shetland Islands, Scotland, at the water depth of 140 metres (460 ft). The field operated by Shell UK Limited was once one of the most productive parts of the UK's offshore assets but has reached the stage where production is no longer economically viable. Decommissioning of the Brent field will be conducted over the 2020s decade.

The Statfjord oil field is an enormous oil and gas field covering 580 km2 in the U.K.-Norwegian boundary of the North Sea at a water depth of 145 m, discovered in 1974 by Mobil and since 1987 operated by Statoil.

Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is the process of capturing waste carbon dioxide from large point sources, such as biomass or fossil fuel power plants, transporting it to a storage site, and depositing it where it will not enter the atmosphere, normally an underground geological formation. The aim is to prevent the release of large quantities of CO
2 into the atmosphere. It is a potential means of mitigating the contribution of fossil fuel emissions to global warming and ocean acidification. Although CO
2 has been injected into geological formations for several decades for various purposes, including enhanced oil recovery, the long term storage of CO
2 is a relatively new concept. The first commercial example was the Weyburn-Midale Carbon Dioxide Project in 2000. Another example is SaskPower's Boundary Dam. 'CCS' can also be used to describe the scrubbing of CO
2 from ambient air as a climate engineering technique.
The Dunlin oilfield is situated 195 km northeast of Lerwick, Shetland, Scotland, in block number 211/23a and 211/24a. It was originally operated by Shell but was sold in 2008 and is now operated by Fairfield Energy and partners MCX.

The Cormorant oilfield is located 161 kilometres (100 mi) north east of Lerwick, Shetland, Scotland, in block number 211/26a. It was discovered in September 1972 at a depth of 150 metres (490 ft). Estimated recovery is 90 million barrels of oil. The oil reservoir is located at a depth of 2,895 metres (9,498 ft).
Enhanced oil recovery, also called tertiary recovery, is the extraction of crude oil from an oil field that cannot be extracted otherwise. EOR can extract 30% to 60% or more of a reservoir's oil, compared to 20% to 40% using primary and secondary recovery. According to the US Department of Energy, there are three primary techniques for EOR: thermal, gas injection, and chemical injection. More advanced, speculative EOR techniques are sometimes called quaternary recovery.

The Clair oilfield is an offshore oil field in Scottish territorial waters 75 kilometres (47 mi) west of Shetland in water depths of up to 140 metres (460 ft). It extends over an area of some 220 square kilometres (85 sq mi), covering five licence blocks.

The Harding oilfield is a small oil field operated by TAQA, in the North Sea block 9/23b, approximately 200 miles (320 km) North-East of Aberdeen and in 110 metres (360 ft) of water.
Türkiye Petrolleri Anonim Ortaklığı (TPAO) was founded in 1954 by Law No. 6327 with the responsibility of being involved in hydrocarbon exploration, drilling, production, refinery and marketing activities as Turkey's national company.

The Sleipner gas field is a natural gas field in the block 15/9 of the North Sea, about 250 kilometres (160 mi) west of Stavanger, Norway. Two parts of the field are in production, Sleipner West, and Sleipner East (1981). The field produces natural gas and light oil condensates from sandstone structures about 2,500 metres (8,200 ft) below sea level. It is operated by Statoil. The field is named after the steed Sleipnir in Norse mythology.

Norne is an oil field located around 80 kilometres (50 mi) north of the Heidrun oil field in the Norwegian Sea. The sea depth in the area is 380 metres (1,250 ft). Norne lies in a licence which was awarded in 1986, and embraces blocks 6608/10 and 6608/11. The Alve field nearby started to produce in March 2009 and is commingling into Norne. The Urd field is also comingling with the Norne. 6507/3-1 Alve will be tied to Norne for processing and transport. Natural gas has also been exported from Norne since 2001. It travels through the Norne Gas Export Pipeline and the Åsgard Transport trunkline via Kårstø north of Stavanger to continental Europe.
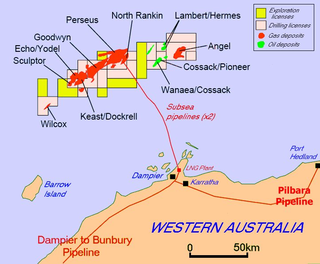
The North West Shelf Venture, situated in the north-west of Western Australia, is Australia's largest resource development project. It involves the extraction of petroleum at offshore production platforms, onshore processing and export of liquefied natural gas, and production of natural gas for industrial, commercial and domestic use within the state.

The Bacton Gas Terminal is a complex of six gas terminals within four sites located on the North Sea coast of North Norfolk in the United Kingdom. The sites are near Paston and between Bacton and Mundesley; the nearest town is North Walsham.

The Abu Dhabi National Energy Company, PJSC (TAQA) is a government controlled energy holding company of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates.

The Hutton oil field, located on the UK continental shelf, was the location for the first ever production Tension Leg Platform (TLP).

The Magnus oilfield is a large oilfield in the United Kingdom's zone of North Sea. It is located 160 kilometres (99 mi) north-east of the Shetland Islands. The field is located mainly in Block 211/12a. Resources are estimated to total 1.54 billion barrels of oil, of which 869 million barrels are recoverable reserves.

The Yuri Korchagin field is an offshore oil field in the Russian sector of the North Caspian Sea. The field is located 180 kilometres (110 mi) from Astrakhan and 240 kilometres (150 mi) from Makhachkala at a sea depth of 11–13 metres (36–43 ft). The field is owned and operated by Lukoil–Nizhnevolzhskneft, a subsidiary of Lukoil. The contractor for drilling operations is a Moscow-based company BKE Shelf. The field is named after the former secretary of the company's board of directors.
The Weyburn-Midale Carbon Dioxide Project is, as of 2008, the world's largest carbon capture and storage project. It is located in Midale, Saskatchewan, Canada.














