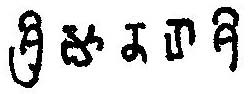Kadamba is a Sanskrit word meaning dove and may refer to:
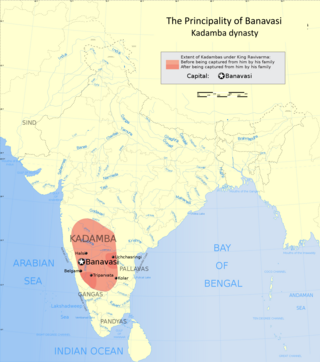
The Kadambas were an ancient royal family from modern Karnataka, India, that ruled northern Karnataka and the Konkan from Banavasi in present-day Uttara Kannada district in India. The kingdom was founded by Mayurasharma in c. 345, and at later times showed the potential of developing into imperial proportions. An indication of their imperial ambitions is provided by the titles and epithets assumed by its rulers, and the marital relations they kept with other kingdoms and empires, such as the Vakatakas and Guptas of northern India. Mayurasharma defeated the armies of the Pallavas of Kanchi possibly with the help of some native tribes and claimed sovereignty. The Kadamba power reached its peak during the rule of Kakusthavarma.
Kirttivarman I was a ruler of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi in India. He ruled parts of present-day Karnataka, Goa, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh.

North Karnataka is a geographical region in Deccan plateau from 300 to 730 metres elevation that constitutes the region of the Karnataka state in India and the region consists of 14 districts. It is drained by the Krishna River and its tributaries the Bhima, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha, and Tungabhadra. North Karnataka lies within the Deccan thorn scrub forests ecoregion, which extends north into eastern Maharashtra.

Hangal, formerly known as 'Viratanagara', is a historic town in Karnataka. It is 80 km (50 mi) away from Hubli through NH 766E.
Ballal is a surname from coastal Karnataka in India. It is found among Shivalli Madhva Brahmins,Hindu Samantha Arasu, Bunt and Jain Royal communities.

Banavasi is an ancient temple town located near Sirsi in Karnataka. Banavasi was the ancient capital of the Kadamba dynasty that ruled all of modern-day Karnataka state. They were the first native empire to bring Kannada and Karnataka to prominence. It is 24 km (15 mi) away from its nearest large city Sirsi through SH 77.

The History of Karnataka goes back several millennia. Several great empires and dynasties have ruled over Karnataka and have contributed greatly to the history, culture and development of Karnataka as well as the entire Indian subcontinent. The Chindaka Nagas of central India Gangas, Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta, Chalukyas of Vengi, Yadava Dynasty of Devagiri were all of Kannada origin who later took to encouraging local languages.

The Pallava script, or Pallava Grantha, is a Brahmic script named after the Pallava dynasty of Southern India (Tamilakam) and is attested to since the 4th century CE. In India, the Pallava script evolved from Tamil-Brahmi. The Grantha script originated from the Pallava script. Pallava also spread to Southeast Asia and evolved into scripts such as Balinese, Baybayin, Javanese, Kawi, Khmer, Lanna, Lao, Mon–Burmese, New Tai Lue, Sundanese, and Thai. This script is the sister of the Vatteluttu script which was used to write Tamil and Malayalam in the past.

The political history of medieval Karnataka spans the 4th to the 16th centuries in Karnataka region of India. The medieval era spans several periods of time from the earliest native kingdoms and imperialism; the successful domination of the Gangetic plains in northern India and rivalry with the empires of Tamilakam over the Vengi region; and the domination of the southern Deccan and consolidation against Muslim invasion. The origins of the rise of the Karnataka region as an independent power date back to the fourth-century birth of the Kadamba Dynasty of Banavasi which was the earliest of the native rulers to conduct administration in the native language of Kannada in addition to the official Sanskrit.
Kakusthavarma or Kakusthavarman was a ruler of the Kadamba dynasty in South India. He succeeded his brother Raghu as king. Under Kakusthavarma's rule the Kadamba kingdom attained the height of its power and influence, and the Kadambas enjoyed close diplomatic relations with the great royal houses of India. The Talagunda and Halmidi inscriptions praise Kakusthavarma as a formidable Kadamba warrior.
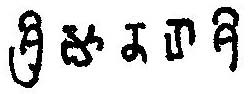
The Kadamba script is the first writing system devised specifically for writing Kannada and it was later adopted to write Telugu language. The Kadamba script is also known as Pre-Old-Kannada script.

Neolamarckia cadamba, with English common names burflower-tree, laran, and Leichhardt pine, and called kadamba or kadam or cadamba locally, is an evergreen, tropical tree native to South and Southeast Asia. The genus name honours French naturalist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck. It has scented orange flowers in dense globe-shaped clusters. The flowers are used in perfumes. The tree is grown as an ornamental plant and for timber and paper-making. Kadamba features in Indian religions.

The Kadambas of Goa were a dynasty during the Late Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, who ruled Goa from the 10th to the 14th century CE. They took over the territories of the Shilaharas and ruled them at first from Chandor, later making Gopakapattana their capital.

Talagunda is a village in the Shikaripura taluk of Shivamogga district in the state of Karnataka, India. Many inscriptions found here have provided insights into the rise of the Kadamba Dynasty.

Kamala Narayana Temple is at Degaon in Belgaum District, Karnataka, India. The temple was built by the Kadamba dynasty. Kamal Narayan Temple was constructed by Tippoja, the chief architect of Kamala Devi, the Queen of the Kadamba king Sivachitta Permadi in the 12th century. This temple built in 1174. A.D. The principal deity is Lord Narayana.

Kadamba architecture was a style of temple architecture founded by Mayurasharma in the 4th century AD in Karnataka, India. Kadambas created new style of architecture which was the basis of the Hoysalas style of architecture, developed original school of sculpture, was the forerunner of series of South Indian sculptors. Many temples at Aihole, Badami and Hampi are built in Kadamba style.

The Kadambas of Hangal was a South Indian dynasty during the Late Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Hangal in Karnataka. Chatta Deva who reigned from 980–1031 CE founded the dynasty. He helped Western Chalukyas in the coup against the Rashtrakutas; re-established the Kadamba Dynasty mostly as a feudatory of Western Chalukyas, but his successors enjoyed considerable independence and were almost sovereign rulers of Goa and Konkan till 14th century CE.

Bonai State was a minor princely state during the British Raj in what is today India. It was one of the Chota Nagpur States and had its capital at Bonaigarh, located in the present-day Sundergarh district of Odisha. It had an area of 8,907 square kilometres (3,439 sq mi), a population of 24,026 in 1892 and an average annual revenue of Rs. 60,000 in 1901.