Related Research Articles
A guarantee is a private transaction by means of which one person, to obtain some trust, confidence or credit for another, engages to be answerable for them. It may also designate a treaty through which claims, rights or possessions are secured. It is to be differentiated from the colloquial "personal guarantee" in that a guarantee is a legal concept which produces an economic effect. A personal guarantee by contrast is often used to refer to a promise made by an individual which is supported by, or assured through, the word of the individual. In the same way, a guarantee produces a legal effect wherein one party affirms the promise of another by promising to themselves pay if default occurs.
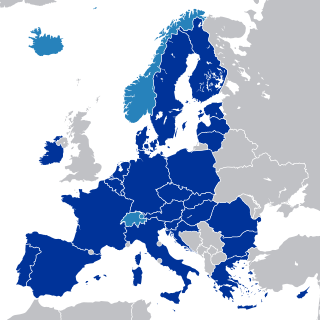
The European single market, internal market or common market is a single market comprising the 27 member states of the European Union (EU) as well as – with certain exceptions – Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway through the Agreement on the European Economic Area, and Switzerland through sectoral treaties. The single market seeks to guarantee the free movement of goods, capital, services, and people, known collectively as the "four freedoms". This is achieved through common rules and standards that all the EU member states are legally committed to following.

Salomon v A Salomon & Co Ltd[1896] UKHL 1, [1897] AC 22 is a landmark UK company law case. The effect of the House of Lords' unanimous ruling was to uphold firmly the doctrine of corporate personality, as set out in the Companies Act 1862, so that creditors of an insolvent company could not sue the company's shareholders for payment of outstanding debts.

A société à responsabilité limitée is a form of private company that exists mainly in French-speaking countries, such as France, Luxembourg, Monaco, Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia, Madagascar, Lebanon, Switzerland, and Belgium. The primary purpose of a SARL is to conduct commercial activity.

The Freedom to Provide Services or sometimes referred to as free movement of services along with the Freedom of Establishment form the core of the European Union's functioning. With the free movement of workers, citizens, goods and capital, they constitute fundamental rights that give companies and citizens the right to provide services without restrictions in any member country of the EU regardless of nationality and jurisdiction.

Norskregistrert utenlandsk foretak or NUF is a Norwegian term meaning Norwegian Registered Foreign Company. NUF are basically Norwegian branches of foreign companies. In this regard, one has to distinguish between companies that are Norwegian in a fiscal sense and Norwegian companies in a company law meaning. The formal legal basis for registration is The Business Enterprise Registration Act of 1985 with later amendments, ss 3–8.

The United Kingdom company law regulates corporations formed under the Companies Act 2006. Also governed by the Insolvency Act 1986, the UK Corporate Governance Code, European Union Directives and court cases, the company is the primary legal vehicle to organise and run business. Tracing their modern history to the late Industrial Revolution, public companies now employ more people and generate more of wealth in the United Kingdom economy than any other form of organisation. The United Kingdom was the first country to draft modern corporation statutes, where through a simple registration procedure any investors could incorporate, limit liability to their commercial creditors in the event of business insolvency, and where management was delegated to a centralised board of directors. An influential model within Europe, the Commonwealth and as an international standard setter, UK law has always given people broad freedom to design the internal company rules, so long as the mandatory minimum rights of investors under its legislation are complied with.
Marleasing SA v La Comercial Internacional de Alimentación SA (1990) C-106/89 was a decision of the European Court of Justice concerning the indirect effect of European Community law, now European Union law. It established that the courts of European Union member states have a duty to interpret national legislation in the light of unimplemented European Union directives.

International Transport Workers Federation v Viking Line ABP (2007) C-438/05 is an EU law case of the European Court of Justice, in which it was held that there is a positive right to strike, but the exercise of that right could infringe a business's freedom of establishment under the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union article 49. Often called The Rosella case or the Viking case, it is relevant to all labour law within the European Union. The decision has been criticised for the Court's inarticulate line of reasoning, and its disregard of fundamental human rights.

Laval un Partneri Ltd v Svenska Byggnadsarbetareförbundet (2007) C-341/05 is an EU law case, relevant to all labour law within the European Union, which held that there is a positive right to strike. However, it also held that the right to strike must be exercised proportionately and in particular this right was subject to justification where it could infringe the right to freedom to provide services under the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union article 56.

European organisational law is a part of European Union law, which concerns the formation, operation and insolvency of public bodies, partnerships, corporations and foundations in the entire European Union. There is no substantive European company law as such, although a host of minimum standards are applicable to companies throughout the European Union. All member states continue to operate separate companies acts, which are amended from time to time to comply with EU Directives and Regulations. There is, however, also the option of businesses to incorporate as a Societas Europaea (SE), which allows a company to operate across all member states.

Überseering BV v Nordic Construction Company Baumanagement GmbH (2002) C-208/00 is a European company law case, concerning the right of freedom of establishment.
Centros Ltd v Erhvervs- og Selskabsstyrelsen (1999) C-212/97 is a European company law case, concerning the right of freedom of establishment.
The Second Company Law Directive2012/30/EU is a European Union Directive concerning the capital requirements of public companies that operating within the European Union. A number of its provisions have become increasingly controversial since its enactment in 1976, as many rules for the maintenance and alteration of capital have been abandoned within EU member states, particularly regarding the use of minimum capital, and the accounting concept of nominal share value. Nevertheless, a large number of its rules are still seen as essential for the protection of creditors, to attempt to forestall insolvency.

The British Virgin Islands company law is the law that governs businesses registered in the British Virgin Islands. It is primarily codified through the BVI Business Companies Act, 2004, and to a lesser extent by the Insolvency Act, 2003 and by the Securities and Investment Business Act, 2010. The British Virgin Islands has approximately 30 registered companies per head of population, which is likely the highest ratio of any country in the world. Annual company registration fees provide a significant part of Government revenue in the British Virgin Islands, which accounts for the comparative lack of other taxation. This might explain why company law forms a much more prominent part of the law of the British Virgin Islands when compared to countries of similar size.

European company law is a part of European Union law, which concerns the formation, operation and insolvency of companies in the European Union. The EU creates minimum standards for companies throughout the EU, and has its own corporate forms. All member states continue to operate separate companies acts, which are amended from time to time to comply with EU Directives and Regulations. There is, however, also the option of businesses to incorporate as a Societas Europaea (SE), which allows a company to operate across all member states.
Gebhard v Consiglio dell'Ordine degli Avvocati e Procuratori di Milano (1995) C-55/94 is an EU law case, concerning the freedom of establishment in the European Union.

Omega Spielhallen und Automatenaufstellungs-GmbH v Oberbürgermeisterin der Bundesstadt Bonn (2004) C-36/02 is an EU law case, concerning the freedom to provide services and the free movement of goods in the European Union.

Netherlands v Essent NV (2013) C‑105/12 is an EU law case relevant for UK enterprise law on electricity generation governance.

Commission v Germany (2007) C-112/05 is an EU law case, relevant for UK enterprise law, concerning European company law. Following a trend in cases such as Commission v United Kingdom, and Commission v Netherlands, it struck down public oversight, through golden shares of Volkswagen by the German state of Lower Saxony. Soon afterwards, the management practices leading to the Volkswagen emissions scandal began.
References
- M Andenas, 'Free Movement of Companies' (2003) 119 LQR 221
- P Dyrberg, 'Full Free Movement of Companies in the European Community at Last' [2003] ELR 528
- WF Ebke, 'Centros – Some Realities and Some Mysteries' (2000) 48 American Journal of Comparative Law 623