See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Kaskaskia. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
The Kaskaskia were an indigenous North American tribe of the Northeastern Woodlands.
Kaskaskia may also refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Kaskaskia. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

Randolph County is a county located in the U.S. state of Illinois. According to the 2010 census, it had a population of 33,476. Its county seat is Chester.

Monroe County is a county located in the U.S. state of Illinois. According to the 2010 census, it had a population of 32,957. Its county seat and largest city is Waterloo.

Chester is a city in and the county seat of Randolph County, Illinois, United States, on a bluff above the Mississippi River. The population was 8,586 at the 2010 census. It lies 61 miles (98 km) south of St. Louis, Missouri.

Kaskaskia is a village in Randolph County, Illinois. Having been inhabited by indigenous peoples, it was settled by France as part of the Illinois Country. Its population peaked at about 7,000 in the 18th century, when it was a regional center. During the American Revolutionary War, the town, which by then had become an administrative center for the British Province of Quebec, was taken by the Virginia militia during the Illinois campaign. It was designated as the county seat of Illinois County, Virginia, after which it became part of the Northwest Territory in 1787. Kaskaskia was later named as the capital of the United States' Illinois Territory, created on February 3, 1809. In 1818, when Illinois became the 21st U.S. state, the town briefly served as the state's first capital until 1819, when the capital was moved to more centrally located Vandalia.

The Kaskaskia were one of the indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands. They were one of about a dozen cognate tribes that made up the Illiniwek Confederation, also called the Illinois Confederation. Their longstanding homeland was in the Great Lakes region. Their first contact with Europeans reportedly occurred near present-day Green Bay, Wisconsin, in 1667 at a Jesuit mission station.
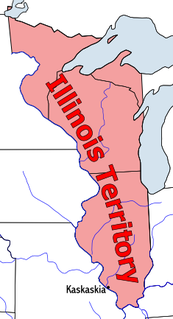
The Territory of Illinois was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 1, 1809, until December 3, 1818, when the southern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Illinois. Its capital was the former French village of Kaskaskia.

Southern Illinois is the southern third of the state of Illinois. The southern part of Illinois has a unique cultural and regional history. Part of downstate Illinois, the Southern Illinois region is bordered by the two most voluminous rivers in the United States: the Mississippi River and its connecting Missouri River to the west, and the Ohio River to the east and south with the Wabash as tributary.

The Kaskaskia River is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately 325 miles (523 km) long, in central and southern Illinois in the United States. The second largest river system within Illinois, it drains a rural area of farms, as well as rolling hills along river bottoms of hardwood forests in its lower reaches. The lower reaches of the river have been canalized to allow barge traffic.

Pierre Menard was a fur trader and U.S. political figure. Pierre Menard was born at St. Antoine-sur-Richelieu, near Montreal, Canada, third in a family of ten children. His father was Jean Baptiste Ménard, a French soldier in the regiment of Guyenne.

The American Bottom is the flood plain of the Mississippi River in the Metro-East region of Southern Illinois, extending from Alton, Illinois, south to the Kaskaskia River. It is also sometimes called "American Bottoms". The area is about 175 square miles (450 km2), mostly protected from flooding in the 21st century by a levee and drainage canal system. Immediately across the river from St. Louis, Missouri are industrial and urban areas, but many swamps and the major Horseshoe Lake are reminders of the Bottoms' riparian nature. This plain served as the center for the pre-Columbian Cahokia Mounds civilization, and later the French settlement of Illinois Country. Deforestation of the river banks in the 19th century to fuel steamboats had dramatic environmental effects in this region. The Mississippi River between St. Louis and the confluence with the Ohio River became wider and more shallow, as unstable banks collapsed into the water. This resulted in more severe flooding and lateral changes of the major channel, causing the destruction of several French colonial towns, such as Kaskaskia, which relocated; Cahokia, and St. Philippe, Illinois.
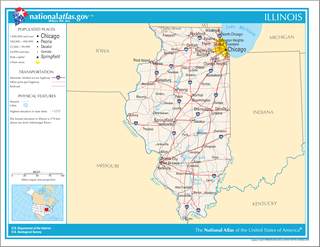
Illinois is in the midwestern United States. Surrounding states are Wisconsin to the north, Iowa and Missouri to the west, Kentucky to the south, and Indiana to the east. Illinois also borders Michigan, but only via a northeastern water boundary in Lake Michigan. Nearly the entire western boundary of Illinois is the Mississippi River, except for a few areas where the river has changed course. Illinois' southeastern and southern boundary is along the Wabash River and the Ohio River. Whereas, its northern boundary and much of its eastern boundary are straight survey lines. Illinois has a maximum north-south distance of 390 miles and 210 miles east-west. Its total area is 57,918 square miles (150,010 km2).
The Grand Illinois Trail is a multipurpose recreational trail in the northern part of the U.S. state of Illinois. At over 575 miles (925 km) in length, it is the longest trail in Illinois. Parts of it are in the coast-to-coast American Discovery Trail.
The Illinois Historic Preservation Division, formerly Illinois Historic Preservation Agency, is a governmental agency of the U.S. state of Illinois, and is a division of the Illinois Department of Natural Resources. It is tasked with the duty of maintaining State-owned historic sites, and maximizing their educational and recreational value to visitors or on-line users. In addition, it manages the process for applications within the state for additions to the National Register of Historic Places.

Central Illinois is a region of the U.S. state of Illinois that consists of the entire central third of the state, divided from north to south. It is mostly an area of flat prairie. The western section was originally part of the Military Tract of 1812 and forms the distinctive western bulge of the state. Also known as the Heart of Illinois, it is characterized by small towns and mid-sized cities. Agriculture, particularly corn and soybeans, as well as educational institutions and manufacturing centers, figure prominently. Major cities include Peoria, Springfield, Decatur, Quincy, Champaign–Urbana, Bloomington-Normal, Galesburg, and Danville.

Kaskaskia River State Fish and Wildlife Area is an Illinois state park on 20,000 acres (8,094 ha) in St. Clair, Monroe, and Randolph Counties, Illinois, United States. A focus of this conservation area is Baldwin Lake, a perched cooling pond managed by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources for fishing.

The Kolmer Site is an archaeological site in the far southwest of the U.S. state of Illinois. Located near Kaskaskia and Prairie du Rocher in western Randolph County, it lies at the site of an early historic Indian village from the French period. Because it occupies a critical chronological and cultural position, it has been given national recognition as a historic site.

The Kaskaskia–Shawneetown and Goshen Trail was developed from an 1816 appropriation of funds from the Congress of the United States. This trail served as an important link between the Ohio River town of Shawneetown across Southern Illinois, through the town of Mulkeytown to the then capital of Illinois in Kaskaskia.
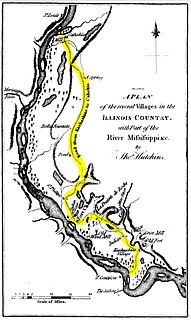
The Kaskaskia–Cahokia Trail was the first road in Illinois, running from Kaskaskia to Cahokia.

The Randolph County Courthouse is a government building in central Chester, the county seat of Randolph County, Illinois, United States. Built in 1972, it is the latest of several buildings to serve as the seat of government in Illinois' oldest county, and the second erected in Chester after the relocation of county government from Kaskaskia in 1847 after a devastating flood.
James Thompson was an American surveyor who created the first plat of Chicago. Born in South Carolina, Thompson moved to Kaskaskia in southern Illinois as a young adult and lived in the area for the rest of his life, working primarily as a surveyor. He was hired to plat settlements at the ends of the proposed Illinois and Michigan Canal in northern Illinois; he completed the plat of Chicago, the settlement at the eastern end, on August 4, 1830. After completing his survey of Chicago he returned to the Kaskaskia area and declined an offer of land in Chicago in favor of a cash payment. In addition to his surveying work, he served in various positions such as Probate Judge, county commissioner, and officer in the Illinois militia during the Black Hawk War.