Kayrati (Arabic : كايراتي) is a village in Chad.
In 2004 a water tower with a solar-powered pump was constructed to raise groundwater and distribute it to public taps. It was built as compensation for land lost to oil development.
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It borders Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon and Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west. Due to its distance from the sea and its largely desert climate, the country is sometimes referred to as the "Dead Heart of Africa".

The economy of Chad suffers from the landlocked country's geographic remoteness, drought, lack of infrastructure, and political turmoil. About 85% of the population depends on agriculture, including livestock herding. Of Africa's Francophone countries, Chad benefited least from the 50% devaluation of their currencies in January 1994. Financial aid from the World Bank, the African Development Bank, and other sources is directed mainly at improving agriculture, especially livestock production. Because of a lack of financing, the development of oil fields near Doba, originally due to finish in 2000, was delayed until 2003. It was finally developed and is now operated by ExxonMobil. Regarding gross domestic product, Chad ranks 147th globally with $11.051 billion as of 2018.

Transport infrastructure within Chad is generally poor, especially in the north and east of the country. River transport is limited to the south-west corner. As of 2011 Chad had no railways though two lines are planned - from the capital to the Sudanese and Cameroonian borders during the wet season, especially in the southern half of the country. In the north, roads are merely tracks across the desert and land mines continue to present a danger. Draft animals remain important in much of the country.

Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon to the southwest, Nigeria to the southwest, and Niger to the west. Chad has a population of 16 million, of which 1.6 million live in the capital and largest city of N'Djamena. With a total area of around 1,300,000 km2 (500,000 sq mi), Chad is the fifth-largest country in Africa and the twentieth largest nation by area in the world.

N'Djamena is the capital and largest city of Chad. It is also a special statute region, divided into 10 districts or arrondissements.

Idriss Déby Itno was a Chadian politician and military officer who was the 6th president of Chad from 1991 until his death in 2021 during the Northern Chad offensive. His term of office of more than 30 years makes him Chad's longest-serving president.

The China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) is a major national oil and gas corporation of China and one of the largest integrated energy groups in the world. Its headquarters are in Dongcheng District, Beijing. CNPC was ranked fourth in 2022 Fortune Global 500, a global ranking of the largest corporations by revenue.
The Chad–Cameroon Petroleum Development and Pipeline Project was a controversial project to develop the production capacity of oilfields near Doba in southern Chad, and to create 1,070-kilometre (660 mi) pipeline to transport the oil to a floating storage and offloading vessel, anchored off the coast of Cameroon, near the city of Kribi.

The Ennedi Plateau is located in the northeast of Chad, in the regions of Ennedi-Ouest and Ennedi-Est. It is considered a part of the group of mountains known as the Ennedi Massif found in Chad, which is one of the nine countries that make up the Sahelian belt that spans the Atlantic Ocean to Sudan. The Ennedi is a sandstone bulwark in the middle of the Sahara, which was formed by erosion from wind and temperature. Many people occupied this area, such as hunters-gatherers and pastoralists. The Ennedi area is also known for its large collection of rock art depicting mainly cattle, as these animals had the greatest financial, environmental, and cultural impact. This art dates back nearly 7,000 years ago. Today, two semi-nomadic groups, mainly Muslim, live in the Ennedi during the rainy months and pass through the area during the dry season. They rely on their herds of camels, donkeys, sheep, and goats to survive.
In the late 1980s, the only mineral exploited in Chad was sodium carbonate, or natron. Also called sal soda or washing soda, natron was used as a salt for medicinal purposes, as a preservative for hides, and as an ingredient in the traditional manufacture of soap; herders also fed it to their animals. Natron deposits were located around the shore of Lake Chad and the wadis of Kanem Prefecture, and near the oasis of Faya-Largeau.
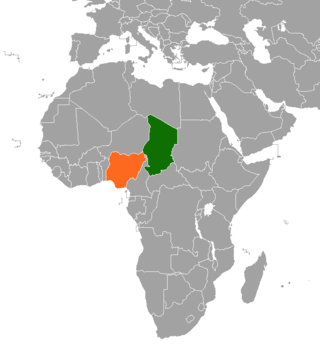
As of the late 1980s, Nigeria considered France its primary rival in its attempt to chart the course of West Africa's political development. Its generally paternalistic relations with Chad intensified after the coup that ousted President François Tombalbaye in 1975. After that, limiting Libyan expansion while avoiding direct clashes with Libyan troops also became important goals. Nigeria sponsored talks among Chad's rival factions in 1979 and promoted a little-known civil servant, Mahmat Shawa Lol, as a compromise head of a coalition government. Lol's perceived status as a Nigerian puppet contributed to mounting opposition during his short term as president in 1979.
The total energy consumption in Chad is of 200.00 million kWh of electric energy per year. Per capita, this is an average of 13 kWh. Chad can provide for itself completely with self-produced energy. The total production of all electric energy producing facilities is 215 m kWh, also 108% of own requirements. The rest of the self-produced energy is either exported into other countries or unused. Along with pure consumptions the production, imports and exports play an important role. Other energy sources such as natural gas or crude oil are also used.
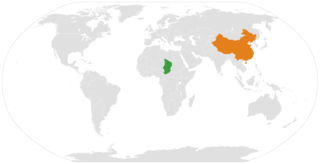
Chad–China relations refers to the current and historical relationship between the Republic of Chad and the People's Republic of China. Bilateral relations were initially established in 1972 but were severed by China in 1997 due to Chad's recognition of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Relations resumed in August 2006 when Chad ended its relationship with Taiwan and pledged adherence to the One China Policy. The ties between the two nations are primarily economic, although there is some cooperation in security. The economic ties are profitable for both countries, with China providing aid and investment in exchange for natural resources to fuel its economic growth.

Chadian cuisine is the cooking traditions, practices, foods and dishes associated with the Republic of Chad. Chadians use a medium variety of grains, vegetables, fruits and meats. Commonly consumed grains include millet, sorghum, and rice as staple foods. Commonly eaten vegetables include okra and cassava. A variety of fruits are also eaten. Meats include mutton, chicken, pork, goat, fish, lamb and beef. The day's main meal is typically consumed in the evening on a large communal plate, with men and women usually eating in separate areas. This meal is typically served on the ground upon a mat, with people sitting and eating around it.

Delphine Djiraibe is a Chadian attorney and co-founder of the Chadian Association for the Promotion and Defense of Human Rights.In 2006 she also founded the Public Interest Law Center (PILC). BBC News has described her as "one of Chad's most prominent human rights lawyers".

Chad–Taiwan relations are relations between Chad and the Republic of China (ROC).

Chad–India relations refers to the bilateral relations between Chad and India. The High Commission of India in Abuja, Nigeria is concurrently accredited to Chad. India also maintains an Honorary Consulate in N'Djamena. In 2019, Chad opened a resident embassy in New Delhi.

Corruption in Chad is characterized by nepotism and cronyism. Chad received a score of 20 in the 2023 Transparency International Corruption Perceptions Index on a scale from 0 to 100. When ranked by score, Chad ranked 162nd among the 180 countries in the Index, where the country ranked first is perceived to have the most honest public sector. For comparison with worldwide scores, the best score was 90, the average score was 43, and the worst score was 11. For comparison with regional scores, the average score among sub-Saharan African countries was 33. The highest score in sub-Saharan Africa was 71 and the lowest score was 11.