A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard toothed edge. It is used to cut through material, very often wood though sometimes metal or stone. The cut is made by placing the toothed edge against the material and moving it forcefully forth and less forcefully back or continuously forward. This force may be applied by hand, or powered by steam, water, electricity or other power source. An abrasive saw has a powered circular blade designed to cut through metal or ceramic.
Portable sawmills are sawmills small enough to be moved easily and set up in the field. They have existed for over 100 years but grew in popularity in the United States starting in the 1970s, when the 1973 oil crisis and the back-to-the-land movement had led to renewed interest in small woodlots and in self-sufficiency. Their popularity has grown exponentially since 1982, when the portable bandsaw mill was first commercialized.
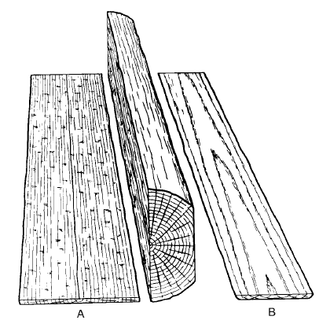
In woodworking, a rip-cut is a type of cut that severs or divides a piece of wood parallel to the grain. The other typical type of cut is a cross-cut, a cut perpendicular to the grain. Unlike cross-cutting, which shears the wood fibers, a rip saw works more like a series of chisels, lifting off small splinters of wood. The nature of the wood grain requires the shape of the saw teeth to be different thus the need for both rip saws and crosscut saws; however some circular saw blades are combination blades and can make both types of cuts. A rip cut is the fundamental type of cut made at a sawmill.

The Japanese saw or nokogiri (鋸) is a type of saw used in woodworking and Japanese carpentry that cuts on the pull stroke, unlike most European saws that cut on the push stroke. Japanese saws are the best known pull saws, but they are also used in Turkey, Iran, Iraq and Nepal. Among European saws, both coping saws for woodworking and jeweler's saws for metal working also cut on the pull stroke like Japanese saws. Cutting on the pull stroke is claimed to cut more efficiently and leave a narrower cut width (kerf). On the other hand, a pull stroke does not easily permit putting one's body weight behind a stroke. This can be readily solved by using a vise or clamping. Another disadvantage, due to the arrangement and form of the teeth, is that Japanese saws do not work as well on hardwoods as European saws do. Japanese saws were originally intended for comparatively soft woods like cypress and pine whereas European saws were intended for hard woods like oak and maple.

A nibbler, or nibblers, is a tool for cutting sheet metal with minimal distortion. One type operates much like a punch and die, with a blade that moves in a linear fashion against a fixed die, removing small bits of metal and leaving a kerf approximately 6 mm wide. Another type operates similar to tin snips, but shears the sheet along two parallel tracks 3–6 mm apart, rolling up the waste in a tight spiral as it cuts. Nibblers may be manual or powered.
A saw filer or saw doctor is a person who maintains and repairs saws in a saw mill. A saw filer's work area in the mill is called the filing room.

A bandsaw is a power saw with a long, sharp blade consisting of a continuous band of toothed metal stretched between two or more wheels to cut material. They are used principally in woodworking, metalworking, and lumbering, but may cut a variety of materials. Advantages include uniform cutting action as a result of an evenly distributed tooth load, and the ability to cut irregular or curved shapes like a jigsaw. The minimum radius of a curve is determined by the width of the band and its kerf. Most bandsaws have two wheels rotating in the same plane, one of which is powered, although some may have three or four to distribute the load. The blade itself can come in a variety of sizes and tooth pitches, which enables the machine to be highly versatile and able to cut a wide variety of materials including wood, metal and plastic.

A hacksaw is a fine-toothed saw, originally and mainly made for cutting metal. The equivalent saw for cutting wood is usually called bow saw.

Metal fabrication is the creation of metal structures by cutting, bending, and assembling processes. It is a value-added process involving the creation of machines, parts, and structures from various raw materials.

A crosscut saw is any saw designed for cutting wood perpendicular to (across) the wood grain. Crosscut saws may be small or large, with small teeth close together for fine work like woodworking or large for coarse work like log bucking, and can be a hand tool or power tool.
A rip saw is a wood saw that is specially designed for making a rip cut, a cut made parallel to the direction of the wood grain.
A miter saw is a saw used to make accurate crosscuts and miters in a workpiece by pulling a large backsaw or a mounted circular saw blade down onto a board in a quick motion. Miter saws are commonly referred to as drop saws and abrasive cut off saws are referred to as a chop saw.

A backsaw is any hand saw which has a stiffening rib on the edge opposite the cutting edge, enabling better control and more precise cutting than with other types of saws. Backsaws are normally used in woodworking for precise work, such as cutting dovetails, mitres, or tenons in cabinetry and joinery. Because of the stiffening rib, backsaws are limited in the depth to which they can cut. Backsaws usually have relatively closely spaced teeth, often with little or no set.

A two-man saw is a saw designed for use by two sawyers. While some modern chainsaws are so large that they require two persons to control, two-man crosscut saws were primarily important when human power was used. Such a saw would typically be 1 to 4 m long, and sometimes up to 5 m, with a handle at each end. In some cases, such as when felling Giant Sequoias, sawblades could be brazed together end-to-end in order to create longer saws.

A hole saw, also known as a hole cutter, is a saw blade of annular (ring) shape, whose annular kerf creates a hole in the workpiece without having to cut up the core material. It is used in a drill. Hole saws typically have a pilot drill bit at their center to keep the saw teeth from walking. The fact that a hole saw creates the hole without needing to cut up the core often makes it preferable to twist drills or spade drills for relatively large holes. The same hole can be made faster and using less power.
A wire saw is a saw that uses a metal wire or cable for cutting. Industrial wire saws are usually powered. There are also hand-powered survivalist wire saws suitable for cutting branches. Wire saws are classified as continuous or oscillating. Sometimes the wire itself is referred to as a "blade".

The fretsaw is a bow saw used for intricate cutting work which often incorporates tight curves. Although the coping saw is often used for similar work, the fretsaw is capable of much tighter radii and more delicate work. It has a distinctive appearance due to the depth of its frame, which together with the relatively short five inch blade makes this tool appear somewhat out of proportion compared with most other saws.

An Alaskan mill or chainsaw mill is a type of sawmill that is used by one or two operators to mill logs into lumber for use in furniture, construction and other uses.

A jigsaw power tool is a jigsaw made up of an electric motor and a reciprocating saw blade.














